記憶體映射檔案包含虛擬記憶體中檔案的內容。 檔案與記憶體空間之間的此對應可讓應用程式,包括多個進程,藉由直接讀取和寫入記憶體來修改檔案。 您可以使用管理的程式碼,以像原生 Windows 函式存取記憶體對應檔案的方式來存取這些檔案,如管理 Memory-Mapped 檔案中所述。
記憶體對應檔案有兩種類型:
持久化記憶體對應檔案
持久化檔案是與磁碟上來源檔案相關聯的記憶體映射檔案。 當最後一個程式完成檔案處理時,數據會儲存至磁碟上的來源檔案。 這些記憶體對映檔案適用於處理極大型的原始檔案。
非持久化的記憶體映射檔案
未持久化的檔案是指那些未與磁碟上的檔案相關聯的記憶體對應檔案。 當最後一個程式完成處理檔案時,數據會遺失,而檔案會由垃圾收集回收。 這些檔案適用於建立進程間通訊的共用記憶體(IPC)。
進程、檢視和管理記憶體
記憶體對應檔案可以跨多個程序共用。 程式可以使用創建檔案的程式指定的共同名稱,映射到相同的記憶體對映檔案。
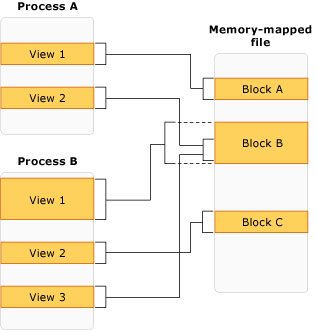
若要使用記憶體對應檔案,您必須建立整個記憶體對應檔案或者其部分的檢視。 您也可以對記憶體對應檔案的相同部分建立多個檢視,藉此建立並行記憶體。 若要讓兩個檢視保持並行,則必須從相同的記憶體對應檔案建立它們。
如果檔案大於應用程式可用於記憶體映射的邏輯記憶體空間大小(在 32 位元電腦上為 2 GB),則可能需要多個檢視。
有兩種類型的檢視:數據流存取檢視和隨機存取檢視。 使用數據流訪問檢視來循序存取檔案;建議用於非持久性檔案和進程間通信 (IPC)。 使用保存的檔案時,偏好使用隨機存取檢視。
記憶體對應檔案是透過作業系統的記憶體管理程式存取,因此檔案會自動分割成多個頁,並視需要存取。 您不需要自行處理記憶體管理。
下圖顯示多個進程如何同時對相同的記憶體對應檔案擁有多個和重疊的檢視。
下圖顯示對記憶體對映檔案的多個重疊檢視:
使用 Memory-Mapped 檔案進行程序設計
下表提供使用記憶體對應檔案物件及其成員的指南。
| 任務 | 要使用的方法或屬性 |
|---|---|
| 若要從磁碟上的檔案獲得 MemoryMappedFile 物件以代表持久化的記憶體對應檔案。 | MemoryMappedFile.CreateFromFile 方法。 |
| 若要取得 MemoryMappedFile 物件,用於表示不持久化的記憶體對映檔案(未與磁碟上的檔案相關聯)。 |
MemoryMappedFile.CreateNew 方法。 (或) MemoryMappedFile.CreateOrOpen 方法。 |
| 若要獲取 MemoryMappedFile 現有記憶體映射檔案的物件(已保留或未保留)。 | MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting 方法。 |
| 若要取得 UnmanagedMemoryStream 記憶體對應檔案之循序存取檢視的物件。 | MemoryMappedFile.CreateViewStream 方法。 |
| 取得用於隨機存取檢視記憶體對應檔案的 UnmanagedMemoryAccessor 物件。 | MemoryMappedFile.CreateViewAccessor 方法。 |
| 取得 SafeMemoryMappedViewHandle 物件以搭配非受控程式碼使用。 |
MemoryMappedFile.SafeMemoryMappedFileHandle 屬性。 (或) MemoryMappedViewAccessor.SafeMemoryMappedViewHandle 屬性。 (或) MemoryMappedViewStream.SafeMemoryMappedViewHandle 屬性。 |
| 若要延遲配置記憶體,直到建立檢視為止(僅限非保存的檔案)。 (若要判斷目前的系統頁面大小,請使用 Environment.SystemPageSize 屬性。 |
CreateNew 方法的 MemoryMappedFileOptions.DelayAllocatePages 值。 (或) CreateOrOpen 以 MemoryMappedFileOptions 列舉作為參數的方法。 |
安全
當您建立記憶體對應檔案時,可以使用以下以列舉作為參數的方法來套用存取權限:
您可以使用接受 OpenExisting 做為參數的方法,指定開啟現有記憶體對應檔案MemoryMappedFileRights的訪問許可權。
此外,您可以包含 MemoryMappedFileSecurity 包含預先定義存取規則的物件。
若要將新的或已變更的存取規則套用至記憶體對應檔案,請使用 SetAccessControl 方法。 若要從現有的檔案擷取存取或稽核規則,請使用 GetAccessControl 方法。
範例
保存 Memory-Mapped 檔案
方法 CreateFromFile 會從磁碟上的現有檔案建立記憶體對應檔案。
下列範例將建立極大型檔案部分的記憶體對應檢視,並操作其中的一部分。
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
long offset = 0x10000000; // 256 megabytes
long length = 0x20000000; // 512 megabytes
// Create the memory-mapped file.
using (var mmf = MemoryMappedFile.CreateFromFile(@"c:\ExtremelyLargeImage.data", FileMode.Open,"ImgA"))
{
// Create a random access view, from the 256th megabyte (the offset)
// to the 768th megabyte (the offset plus length).
using (var accessor = mmf.CreateViewAccessor(offset, length))
{
int colorSize = Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(MyColor));
MyColor color;
// Make changes to the view.
for (long i = 0; i < length; i += colorSize)
{
accessor.Read(i, out color);
color.Brighten(10);
accessor.Write(i, ref color);
}
}
}
}
}
public struct MyColor
{
public short Red;
public short Green;
public short Blue;
public short Alpha;
// Make the view brighter.
public void Brighten(short value)
{
Red = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Red + value);
Green = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Green + value);
Blue = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Blue + value);
Alpha = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Alpha + value);
}
}
Imports System.IO
Imports System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles
Imports System.Runtime.InteropServices
Class Program
Sub Main()
Dim offset As Long = &H10000000 ' 256 megabytes
Dim length As Long = &H20000000 ' 512 megabytes
' Create the memory-mapped file.
Using mmf = MemoryMappedFile.CreateFromFile("c:\ExtremelyLargeImage.data", FileMode.Open, "ImgA")
' Create a random access view, from the 256th megabyte (the offset)
' to the 768th megabyte (the offset plus length).
Using accessor = mmf.CreateViewAccessor(offset, length)
Dim colorSize As Integer = Marshal.SizeOf(GetType(MyColor))
Dim color As MyColor
Dim i As Long = 0
' Make changes to the view.
Do While (i < length)
accessor.Read(i, color)
color.Brighten(10)
accessor.Write(i, color)
i += colorSize
Loop
End Using
End Using
End Sub
End Class
Public Structure MyColor
Public Red As Short
Public Green As Short
Public Blue As Short
Public Alpha As Short
' Make the view brighter.
Public Sub Brighten(ByVal value As Short)
Red = CType(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, (CType(Red, Integer) + value)), Short)
Green = CType(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, (CType(Green, Integer) + value)), Short)
Blue = CType(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, (CType(Blue, Integer) + value)), Short)
Alpha = CType(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, (CType(Alpha, Integer) + value)), Short)
End Sub
End Structure
下列範例會針對另一個進程開啟相同的記憶體對應檔案。
using System;
using System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Assumes another process has created the memory-mapped file.
using (var mmf = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("ImgA"))
{
using (var accessor = mmf.CreateViewAccessor(4000000, 2000000))
{
int colorSize = Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(MyColor));
MyColor color;
// Make changes to the view.
for (long i = 0; i < 1500000; i += colorSize)
{
accessor.Read(i, out color);
color.Brighten(20);
accessor.Write(i, ref color);
}
}
}
}
}
public struct MyColor
{
public short Red;
public short Green;
public short Blue;
public short Alpha;
// Make the view brigher.
public void Brighten(short value)
{
Red = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Red + value);
Green = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Green + value);
Blue = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Blue + value);
Alpha = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Alpha + value);
}
}
Imports System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles
Imports System.Runtime.InteropServices
Class Program
Public Shared Sub Main(ByVal args As String())
' Assumes another process has created the memory-mapped file.
Using mmf = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("ImgA")
Using accessor = mmf.CreateViewAccessor(4000000, 2000000)
Dim colorSize As Integer = Marshal.SizeOf(GetType(MyColor))
Dim color As MyColor
' Make changes to the view.
Dim i As Long = 0
While i < 1500000
accessor.Read(i, color)
color.Brighten(30)
accessor.Write(i, color)
i += colorSize
End While
End Using
End Using
End Sub
End Class
Public Structure MyColor
Public Red As Short
Public Green As Short
Public Blue As Short
Public Alpha As Short
' Make the view brigher.
Public Sub Brighten(ByVal value As Short)
Red = CShort(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, CInt(Red) + value))
Green = CShort(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, CInt(Green) + value))
Blue = CShort(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, CInt(Blue) + value))
Alpha = CShort(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, CInt(Alpha) + value))
End Sub
End Structure
非持久化 Memory-Mapped 檔案
CreateNew 和 CreateOrOpen 方法會建立一個記憶體對應檔案,該檔案不會對應至磁碟上的現有檔案。
下列範例包含三個不同的進程(控制台應用程式),將布爾值寫入記憶體對應檔案。 會發生下列一連串的動作:
Process A會建立記憶體對應檔案,並將值寫入其中。Process B會開啟記憶體對應檔案,並將值寫入其中。Process C會開啟記憶體對應檔案,並將值寫入其中。Process A會讀取並顯示記憶體對應檔案中的值。在
Process A完成記憶體對應檔案之後,垃圾回收機制會立即回收該檔案。
若要執行此範例,請執行下列動作:
編譯應用程式並開啟三個命令提示字元視窗。
在第一個指令提示字元視窗中, 執行
Process A。在第二個指令提示字元視窗中,執行
Process B。返回
Process A,然後按 ENTER 鍵。在第三個指令提示字元視窗中,執行
Process C。返回
Process A,然後按 ENTER 鍵。
Process A輸出如下所示:
Start Process B and press ENTER to continue.
Start Process C and press ENTER to continue.
Process A says: True
Process B says: False
Process C says: True
程序 A
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles;
using System.Threading;
class Program
{
// Process A:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using (MemoryMappedFile mmf = MemoryMappedFile.CreateNew("testmap", 10000))
{
bool mutexCreated;
Mutex mutex = new Mutex(true, "testmapmutex", out mutexCreated);
using (MemoryMappedViewStream stream = mmf.CreateViewStream())
{
BinaryWriter writer = new BinaryWriter(stream);
writer.Write(1);
}
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
Console.WriteLine("Start Process B and press ENTER to continue.");
Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("Start Process C and press ENTER to continue.");
Console.ReadLine();
mutex.WaitOne();
using (MemoryMappedViewStream stream = mmf.CreateViewStream())
{
BinaryReader reader = new BinaryReader(stream);
Console.WriteLine($"Process A says: {reader.ReadBoolean()}");
Console.WriteLine($"Process B says: {reader.ReadBoolean()}");
Console.WriteLine($"Process C says: {reader.ReadBoolean()}");
}
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
Imports System.IO
Imports System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles
Imports System.Threading
Module Module1
' Process A:
Sub Main()
Using mmf As MemoryMappedFile = MemoryMappedFile.CreateNew("testmap", 10000)
Dim mutexCreated As Boolean
Dim mTex As Mutex = New Mutex(True, "testmapmutex", mutexCreated)
Using Stream As MemoryMappedViewStream = mmf.CreateViewStream()
Dim writer As BinaryWriter = New BinaryWriter(Stream)
writer.Write(1)
End Using
mTex.ReleaseMutex()
Console.WriteLine("Start Process B and press ENTER to continue.")
Console.ReadLine()
Console.WriteLine("Start Process C and press ENTER to continue.")
Console.ReadLine()
mTex.WaitOne()
Using Stream As MemoryMappedViewStream = mmf.CreateViewStream()
Dim reader As BinaryReader = New BinaryReader(Stream)
Console.WriteLine("Process A says: {0}", reader.ReadBoolean())
Console.WriteLine("Process B says: {0}", reader.ReadBoolean())
Console.WriteLine("Process C says: {0}", reader.ReadBoolean())
End Using
mTex.ReleaseMutex()
End Using
End Sub
End Module
進程 B
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles;
using System.Threading;
class Program
{
// Process B:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
using (MemoryMappedFile mmf = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("testmap"))
{
Mutex mutex = Mutex.OpenExisting("testmapmutex");
mutex.WaitOne();
using (MemoryMappedViewStream stream = mmf.CreateViewStream(1, 0))
{
BinaryWriter writer = new BinaryWriter(stream);
writer.Write(0);
}
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
catch (FileNotFoundException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Memory-mapped file does not exist. Run Process A first.");
}
}
}
Imports System.IO
Imports System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles
Imports System.Threading
Module Module1
' Process B:
Sub Main()
Try
Using mmf As MemoryMappedFile = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("testmap")
Dim mTex As Mutex = Mutex.OpenExisting("testmapmutex")
mTex.WaitOne()
Using Stream As MemoryMappedViewStream = mmf.CreateViewStream(1, 0)
Dim writer As BinaryWriter = New BinaryWriter(Stream)
writer.Write(0)
End Using
mTex.ReleaseMutex()
End Using
Catch noFile As FileNotFoundException
Console.WriteLine("Memory-mapped file does not exist. Run Process A first." & vbCrLf & noFile.Message)
End Try
End Sub
End Module
處理 C
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles;
using System.Threading;
class Program
{
// Process C:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
using (MemoryMappedFile mmf = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("testmap"))
{
Mutex mutex = Mutex.OpenExisting("testmapmutex");
mutex.WaitOne();
using (MemoryMappedViewStream stream = mmf.CreateViewStream(2, 0))
{
BinaryWriter writer = new BinaryWriter(stream);
writer.Write(1);
}
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
catch (FileNotFoundException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Memory-mapped file does not exist. Run Process A first, then B.");
}
}
}
Imports System.IO
Imports System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles
Imports System.Threading
Module Module1
' Process C:
Sub Main()
Try
Using mmf As MemoryMappedFile = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("testmap")
Dim mTex As Mutex = Mutex.OpenExisting("testmapmutex")
mTex.WaitOne()
Using Stream As MemoryMappedViewStream = mmf.CreateViewStream(2, 0)
Dim writer As BinaryWriter = New BinaryWriter(Stream)
writer.Write(1)
End Using
mTex.ReleaseMutex()
End Using
Catch noFile As FileNotFoundException
Console.WriteLine("Memory-mapped file does not exist. Run Process A first, then B." & vbCrLf & noFile.Message)
End Try
End Sub
End Module
