投影是指將對象轉換成新的形式,其通常僅包括後續需要使用的屬性。 藉由使用投影,您可以建構從每個物件建置的新類型。 您可以投影屬性,並在其上執行數學函式。 您也可以投影原始物件,而不需變更它。
執行投影的標準查詢運算符方法會列在下一節中。
方法
| 方法名稱 | 說明 | Visual Basic 查詢表達式語法 | 詳細資訊 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 選擇 | 投影以轉換函式為基礎的值。 | Select |
Enumerable.Select Queryable.Select |
| SelectMany | 投影以轉換函式為基礎的值序列,然後將它們扁平化成一個序列。 | 可以使用多個 From 子句 |
Enumerable.SelectMany Queryable.SelectMany |
| 壓縮檔 | 產出一個由 2-3 個指定序列中的元素組成的元組序列。 | 不適用。 | Enumerable.Zip Queryable.Zip |
查詢表達式語法範例
選擇
下列範例使用 Select 子句來投射字串清單中每個字串的第一個字母。
Dim words = New List(Of String) From {"an", "apple", "a", "day"}
Dim query = From word In words
Select word.Substring(0, 1)
Dim sb As New System.Text.StringBuilder()
For Each letter As String In query
sb.AppendLine(letter)
Next
' Display the output.
MsgBox(sb.ToString())
' This code produces the following output:
' a
' a
' a
' d
SelectMany
下列範例會使用多個 From 子句,從字串清單中每個字串投影每個單字。
Dim phrases = New List(Of String) From {"an apple a day", "the quick brown fox"}
Dim query = From phrase In phrases
From word In phrase.Split(" "c)
Select word
Dim sb As New System.Text.StringBuilder()
For Each str As String In query
sb.AppendLine(str)
Next
' Display the output.
MsgBox(sb.ToString())
' This code produces the following output:
' an
' apple
' a
' day
' the
' quick
' brown
' fox
Select 與 SelectMany
Select() 和 SelectMany() 的工作是從來源值產生一個或多個結果值。
Select() 會為每個來源值產生一個結果值。 因此,整體結果是集合,其項目數目與來源集合相同。 相反地, SelectMany() 會產生單一整體結果,其中包含來自每個來源值的串連子集合。 傳遞為 自變數的 SelectMany() 轉換函式必須針對每個來源值傳回可列舉的值序列。 接著會串連 SelectMany() 這些可列舉的序列,以建立一個大型序列。
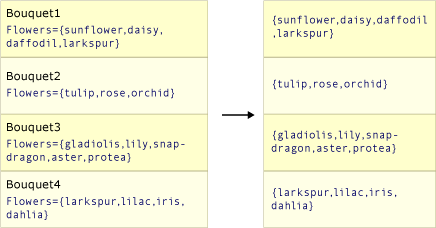
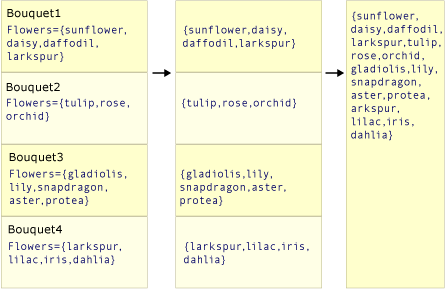
下列兩個圖例顯示這兩種方法動作之間的概念差異。 在每個案例中,假設選取器 (transform) 函式會從每個來源值選取花朵陣列。
此圖描述如何 Select() 傳回與來源集合具有相同項目數目的集合。
此圖說明如何將 SelectMany() 陣列的中繼序列串連成一個最終結果值,其中包含每個中繼數位中的每個值。
程式代碼範例
下列範例會比較 Select() 和 SelectMany() 的行為。 程式碼透過從來源集合中的每個花名清單提取元素,以建立花朵的「花束」。 在此範例中,轉換函 Select<TSource,TResult>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource,TResult>) 式使用的「單一值」本身就是值的集合。 這需要額外的 For Each 迴圈,才能列舉每個子序列中的每個字串。
Class Bouquet
Public Flowers As List(Of String)
End Class
Sub SelectVsSelectMany()
Dim bouquets = New List(Of Bouquet) From {
New Bouquet With {.Flowers = New List(Of String)(New String() {"sunflower", "daisy", "daffodil", "larkspur"})},
New Bouquet With {.Flowers = New List(Of String)(New String() {"tulip", "rose", "orchid"})},
New Bouquet With {.Flowers = New List(Of String)(New String() {"gladiolis", "lily", "snapdragon", "aster", "protea"})},
New Bouquet With {.Flowers = New List(Of String)(New String() {"larkspur", "lilac", "iris", "dahlia"})}}
Dim output As New System.Text.StringBuilder
' Select()
Dim query1 = bouquets.Select(Function(b) b.Flowers)
output.AppendLine("Using Select():")
For Each flowerList In query1
For Each str As String In flowerList
output.AppendLine(str)
Next
Next
' SelectMany()
Dim query2 = bouquets.SelectMany(Function(b) b.Flowers)
output.AppendLine(vbCrLf & "Using SelectMany():")
For Each str As String In query2
output.AppendLine(str)
Next
' Display the output
MsgBox(output.ToString())
' This code produces the following output:
'
' Using Select():
' sunflower
' daisy
' daffodil
' larkspur
' tulip
' rose
' orchid
' gladiolis
' lily
' snapdragon
' aster
' protea
' larkspur
' lilac
' iris
' dahlia
' Using SelectMany()
' sunflower
' daisy
' daffodil
' larkspur
' tulip
' rose
' orchid
' gladiolis
' lily
' snapdragon
' aster
' protea
' larkspur
' lilac
' iris
' dahlia
End Sub
