在系列的前一個教學中,你會建立一個網頁,裡面有一個 Babylon.js 場景,配有攝影機和燈光。 在這個教學中,你會建立並新增一個鋼琴模型到場景中。

在這個教學中,你會學到如何:
- 建立、定位與合併網格
- 用盒子網格製作鋼琴鍵盤
- 匯入鋼琴框架的 3D 模型
開始之前
請確保你已經完成 系列中之前的教學 ,並準備好繼續添加程式碼。
index.html
<html>
<head>
<title>Piano in BabylonJS</title>
<script src="https://cdn.babylonjs.com/babylon.js"></script>
<script src="scene.js"></script>
<style>
body,#renderCanvas { width: 100%; height: 100%;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="renderCanvas"></canvas>
<script type="text/javascript">
const canvas = document.getElementById("renderCanvas");
const engine = new BABYLON.Engine(canvas, true);
createScene(engine).then(sceneToRender => {
engine.runRenderLoop(() => sceneToRender.render());
});
// Watch for browser/canvas resize events
window.addEventListener("resize", function () {
engine.resize();
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
scene.js
const createScene = async function(engine) {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const alpha = 3*Math.PI/2;
const beta = Math.PI/50;
const radius = 220;
const target = new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("Camera", alpha, beta, radius, target, scene);
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0), scene);
light.intensity = 0.6;
const xrHelper = await scene.createDefaultXRExperienceAsync();
return scene;
}
快速入門
讓我們先從製作一個結構簡單的鋼琴鍵盤開始:
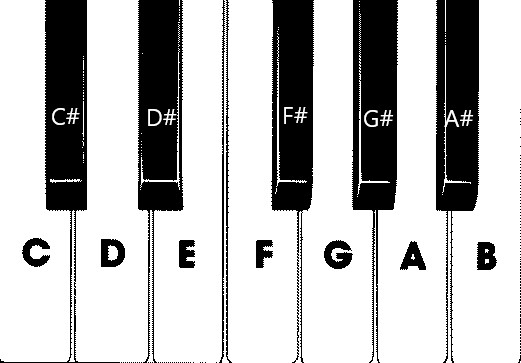
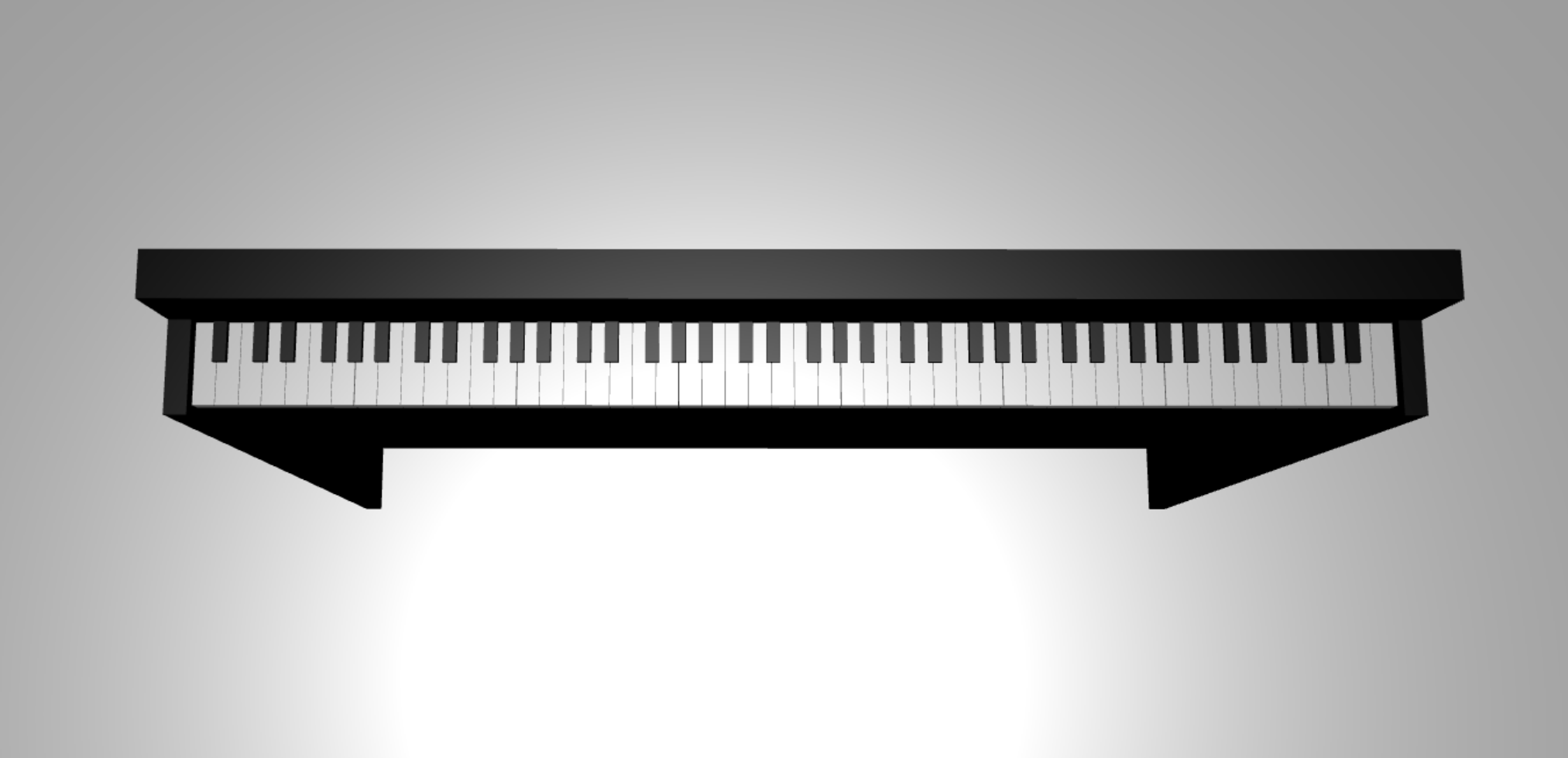
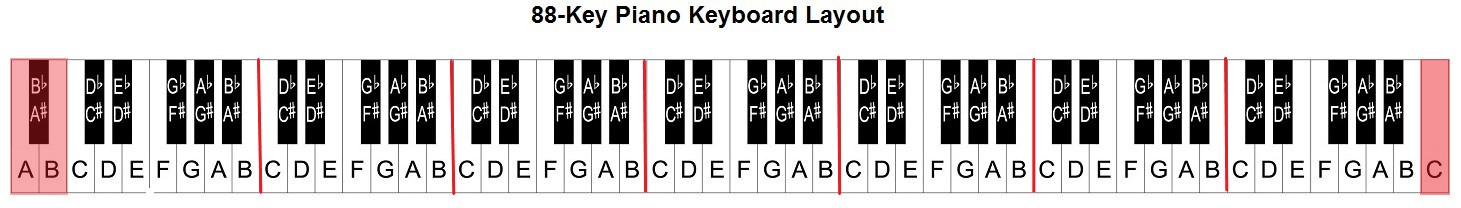
在這張圖片中,有七個白鍵和五個黑鍵,每個鍵上都標有音符名稱。 一台完整的88鍵鋼琴鍵盤包含七個完整的鍵選重複 (也稱為暫存) 及四個額外鍵。 每個暫存器的頻率是前一個暫存器的兩倍。 例如,C5的音高頻率 (,代表第五音區) 的C音是C4的兩倍,D5的音高頻率是D4的兩倍,依此類推。
視覺上,每個音區看起來都完全相同,因此我們可以從如何用這些鍵組成簡單的鋼琴鍵盤開始。 之後,我們可以找到方法將範圍擴展到88鍵全鋼琴鍵盤。
打造一個簡單的鋼琴鍵盤
注意事項
雖然你可以從線上找到預製的鋼琴鍵盤 3D 模型並匯入我們的網頁,但在這個教學中,我們將從零開始打造鍵盤,讓玩家能最大化自訂性,並展示如何透過 Babylon.js 製作 3D 模型。
在開始建立任何用於製作鍵盤的網格之前,請注意每個黑鍵並非完全對齊在周圍兩個白鍵的中間,且每個鍵寬度也不相同。 這表示我們必須為每個金鑰分別建立並定位網格。
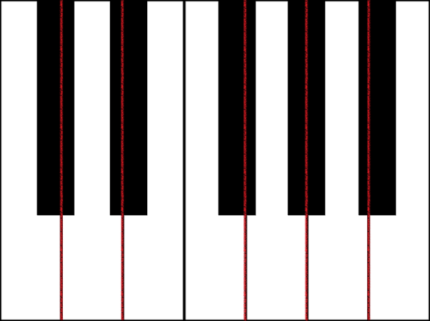
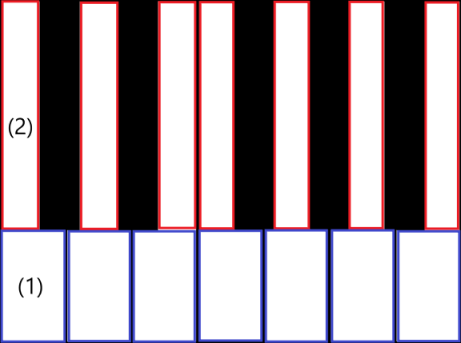
對於白鍵,我們可以觀察到每個白鍵由兩部分組成: (1) 黑鍵下方的底部部分 (s) , (2) 上半部,靠近黑鍵 (s) 。 這兩個部分尺寸不同,但堆疊在一起形成完整的白鍵。
這是為音符 C 建立單一白鍵的程式碼 (暫時不用擔心要加進 scene.js) :
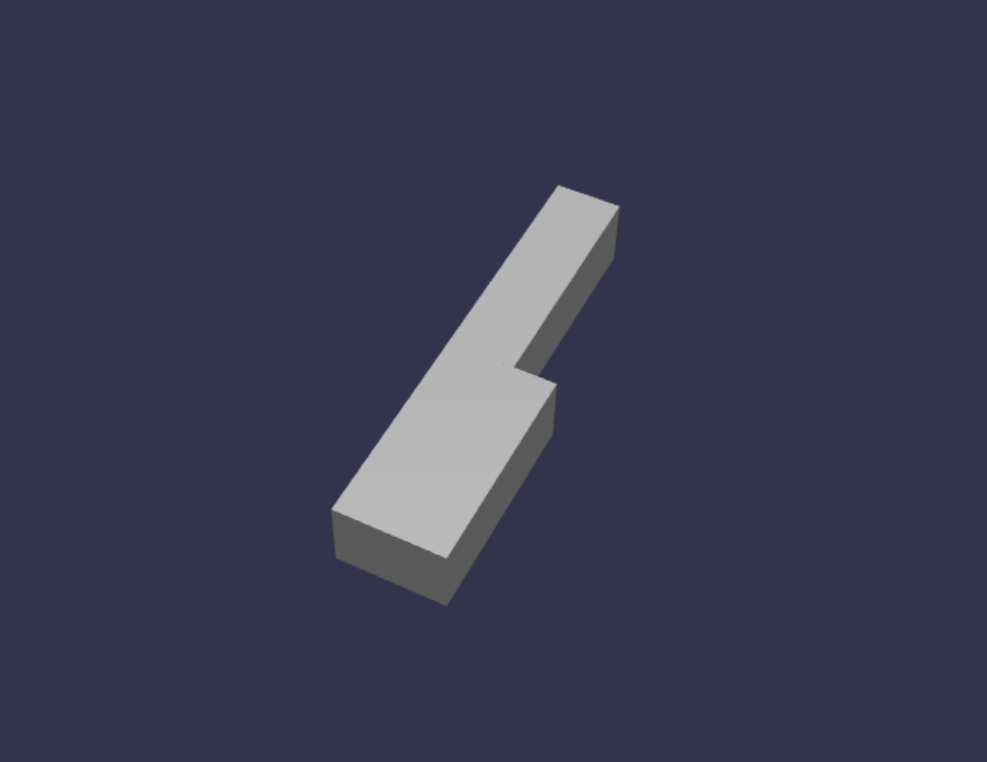
const whiteKeyBottom = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyBottom", {width: 2.3, height: 1.5, depth: 4.5}, scene); const whiteKeyTop = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyTop", {width: 1.4, height: 1.5, depth: 5}, scene); whiteKeyTop.position.z += 4.75; whiteKeyTop.position.x -= 0.45; // Parameters of BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes: // (arrayOfMeshes, disposeSource, allow32BitsIndices, meshSubclass, subdivideWithSubMeshes, multiMultiMaterials) const whiteKeyV1 = BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes([whiteKeyBottom, whiteKeyTop], true, false, null, false, false); whiteKeyV1.material = whiteMat; whiteKeyV1.name = "C4";這裡我們建立了兩個 Box 網格,一個用於白鍵的底部,一個用於上方。 接著我們調整上方部分的位置,將其堆疊在下方部分上方,並往左移動,為鄰近的黑鍵 C# (留出空間 ) 。
最後,這兩個部分透過 MergeMeshes 功能合併成一個完整的白鍵。 這就是這段程式碼所產生的網格:
建立黑鍵比較簡單。 由於所有黑色鍵都是盒子形狀,我們只需用黑色 StandardMaterial 建立盒子網格即可建立黑鍵。
注意事項
由於預設的網格顏色是類似白色的淺灰色,這個教學沒有包含如何為白色按鍵添加白色材質的步驟。 不過,如果你想要在白鍵上呈現真正明亮的白色,也可以自己加上材質。
這是建立黑鍵 C# 的程式碼 (不用擔心要把這個加進 scene.js) :
const blackMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("black"); blackMat.diffuseColor = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 0, 0); const blackKey = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("C#4", {width: 1.4, height: 2, depth: 5}, scene); blackKey.position.z += 4.75; blackKey.position.y += 0.25; blackKey.position.x += 0.95; blackKey.material = blackMat;這組程式碼 (產生的黑鍵與前一個白鍵) 會長如下:
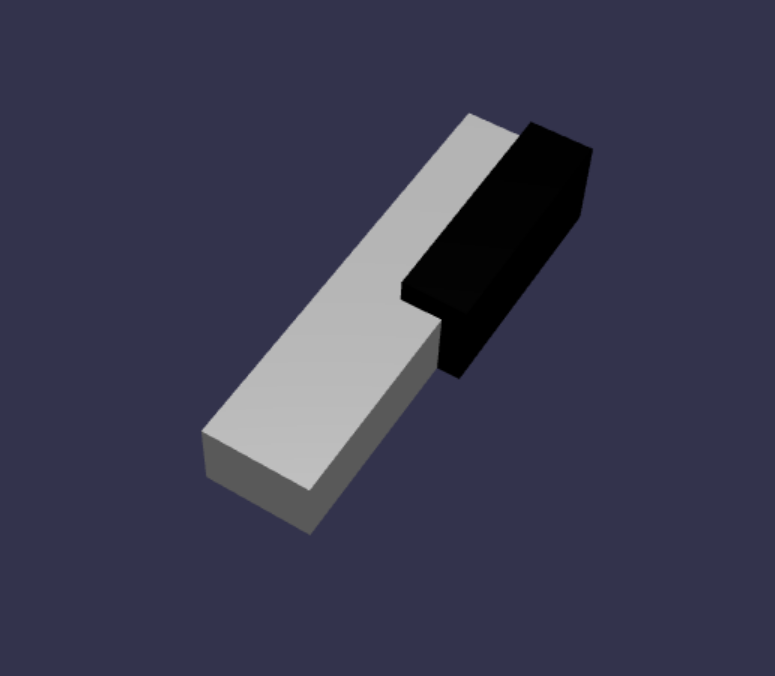
如你所見,建立每個鍵時,會產生許多相似的代碼,因為我們必須指定它們的尺寸和位置。 讓我們在下一節試著讓創作過程更有效率。
有效率地打造一台簡單的鋼琴鍵盤
雖然每個白色鍵的形狀略有不同,但都可以透過結合上下兩部分來製作。 我們來實作一個通用函式來建立並定位任何白鍵。
在函數之外,將下方函數加到 scene.js,函數之外
createScene():const buildKey = function (scene, parent, props) { if (props.type === "white") { /* Props for building a white key should contain: note, topWidth, bottomWidth, topPositionX, wholePositionX, register, referencePositionX As an example, the props for building the middle C white key would be {type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.45, wholePositionX: -14.4, register: 4, referencePositionX: 0} */ // Create bottom part const bottom = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyBottom", {width: props.bottomWidth, height: 1.5, depth: 4.5}, scene); // Create top part const top = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyTop", {width: props.topWidth, height: 1.5, depth: 5}, scene); top.position.z = 4.75; top.position.x += props.topPositionX; // Merge bottom and top parts // Parameters of BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes: (arrayOfMeshes, disposeSource, allow32BitsIndices, meshSubclass, subdivideWithSubMeshes, multiMultiMaterials) const key = BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes([bottom, top], true, false, null, false, false); key.position.x = props.referencePositionX + props.wholePositionX; key.name = props.note + props.register; key.parent = parent; return key; } }在這段程式碼中,我們建立了一個名為
buildKey()的函式,當 為 時"white",它會建立並回傳白鍵。props.type透過在參數props中識別鍵的類型,我們可以在同一函式中同時建立黑鍵和白鍵,方法是透過 if 陳述式分支。的
buildKey()參數如下:- 場景:鑰匙所在的場景
- 父鍵:網格的父鍵 (這讓我們可以將所有鍵鍵群組到單一的父鍵)
- 道具:將要建立的密鑰屬性
白鍵的物品
props將包含以下物品:- 類型:「白色」
- 名稱:該鍵所代表的音符名稱
- topWidth:頂部部分的寬度
- bottomWidth:底部部分的寬度
- topPositionX:上半部相對於下半部的 x-位置
- wholePositionX:整個鍵相對於暫存器末點 (鍵 B) 右邊的 x-位置。
- 登錄器:註冊該金鑰屬於 (介於 0 到 8 之間的數字)
- referencePositionX:暫存器端點的 x 座標 (用作參考點) 。
透過分離
wholePositionX和 ,我們能初始化props建立特定類型的金鑰 (所需的參數,例如 C) 在任何暫存器中,然後在特定暫存器中建立該金鑰時, (C4、C5) 時,再加register和referencePositionXprops。referencePositionX同樣地,我們也可以寫一個通用函式來建立黑鍵。 讓我們將函數擴展
buildKey()到包含這個邏輯:const buildKey = function (scene, parent, props) { if (props.type === "white") { /* Props for building a white key should contain: note, topWidth, bottomWidth, topPositionX, wholePositionX, register, referencePositionX As an example, the props for building the middle C white key would be {type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.45, wholePositionX: -14.4, register: 4, referencePositionX: 0} */ // Create bottom part const bottom = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyBottom", {width: props.bottomWidth, height: 1.5, depth: 4.5}, scene); // Create top part const top = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyTop", {width: props.topWidth, height: 1.5, depth: 5}, scene); top.position.z = 4.75; top.position.x += props.topPositionX; // Merge bottom and top parts // Parameters of BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes: (arrayOfMeshes, disposeSource, allow32BitsIndices, meshSubclass, subdivideWithSubMeshes, multiMultiMaterials) const key = BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes([bottom, top], true, false, null, false, false); key.position.x = props.referencePositionX + props.wholePositionX; key.name = props.note + props.register; key.parent = parent; return key; } else if (props.type === "black") { /* Props for building a black key should contain: note, wholePositionX, register, referencePositionX As an example, the props for building the C#4 black key would be {type: "black", note: "C#", wholePositionX: -13.45, register: 4, referencePositionX: 0} */ // Create black color material const blackMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("black"); blackMat.diffuseColor = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 0, 0); // Create black key const key = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox(props.note + props.register, {width: 1.4, height: 2, depth: 5}, scene); key.position.z += 4.75; key.position.y += 0.25; key.position.x = props.referencePositionX + props.wholePositionX; key.material = blackMat; key.parent = parent; return key; } }對於黑鍵來說,包含
props以下項目:- 類型:「黑色」
- 名稱:該鍵所代表的音符名稱
- wholePositionX:整個鍵相對於暫存器末點 (鍵 B 右邊的 x-位置)
- 登錄器:註冊該金鑰屬於 (介於 0 到 8 之間的數字)
- referencePositionX:暫存器端點的 x 座標 (用作參考點) 。
製作黑鍵的做法
props簡單多了,因為製作黑鍵只需要建立一個框,且每個黑鍵的寬度和 z 位置都相同。現在我們有了更有效率的鍵創建方法,先初始化一個陣列,儲存
props每個鍵對應暫存器中音符的 ,然後呼叫buildKey()每個鍵的函式,在第四暫存器中建立一個簡單的鍵盤。我們也會建立一個 TransformNode
keyboard,作為所有鋼琴鍵的父節點。 由於任何對父鍵的定位或縮放變更也會套用到子鍵,因此將鍵以這種方式分組,可以讓我們能夠整體調整或移動鍵。在函
createScene()式中附加以下程式碼行:const keyParams = [ {type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.45, wholePositionX: -14.4}, {type: "black", note: "C#", wholePositionX: -13.45}, {type: "white", note: "D", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: 0, wholePositionX: -12}, {type: "black", note: "D#", wholePositionX: -10.6}, {type: "white", note: "E", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0.45, wholePositionX: -9.6}, {type: "white", note: "F", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: -0.55, wholePositionX: -7.2}, {type: "black", note: "F#", wholePositionX: -6.35}, {type: "white", note: "G", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.2, wholePositionX: -4.8}, {type: "black", note: "G#", wholePositionX: -3.6}, {type: "white", note: "A", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0.2, wholePositionX: -2.4}, {type: "black", note: "A#", wholePositionX: -0.85}, {type: "white", note: "B", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: 0.55, wholePositionX: 0}, ] // Transform Node that acts as the parent of all piano keys const keyboard = new BABYLON.TransformNode("keyboard"); keyParams.forEach(key => { buildKey(scene, keyboard, Object.assign({register: 4, referencePositionX: 0}, key)); })你可能已經注意到,在這個程式碼區塊中,我們是相對於空間原點放置所有鍵。
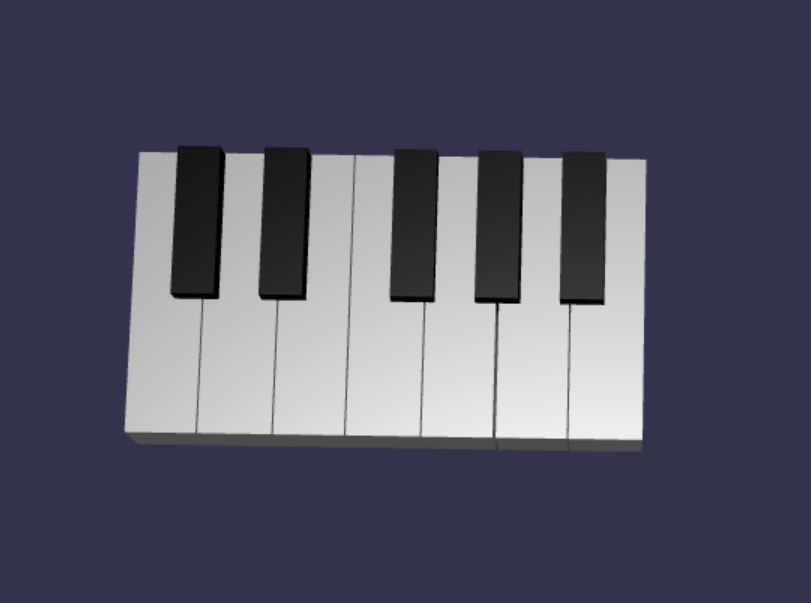
以下是目前 scene.js 包含的程式碼:
const buildKey = function (scene, parent, props) { if (props.type === "white") { /* Props for building a white key should contain: note, topWidth, bottomWidth, topPositionX, wholePositionX, register, referencePositionX As an example, the props for building the middle C white key would be {type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.45, wholePositionX: -14.4, register: 4, referencePositionX: 0} */ // Create bottom part const bottom = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyBottom", {width: props.bottomWidth, height: 1.5, depth: 4.5}, scene); // Create top part const top = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyTop", {width: props.topWidth, height: 1.5, depth: 5}, scene); top.position.z = 4.75; top.position.x += props.topPositionX; // Merge bottom and top parts // Parameters of BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes: (arrayOfMeshes, disposeSource, allow32BitsIndices, meshSubclass, subdivideWithSubMeshes, multiMultiMaterials) const key = BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes([bottom, top], true, false, null, false, false); key.position.x = props.referencePositionX + props.wholePositionX; key.name = props.note + props.register; key.parent = parent; return key; } else if (props.type === "black") { /* Props for building a black key should contain: note, wholePositionX, register, referencePositionX As an example, the props for building the C#4 black key would be {type: "black", note: "C#", wholePositionX: -13.45, register: 4, referencePositionX: 0} */ // Create black color material const blackMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("black"); blackMat.diffuseColor = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 0, 0); // Create black key const key = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox(props.note + props.register, {width: 1.4, height: 2, depth: 5}, scene); key.position.z += 4.75; key.position.y += 0.25; key.position.x = props.referencePositionX + props.wholePositionX; key.material = blackMat; key.parent = parent; return key; } } const createScene = async function(engine) { const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine); const alpha = 3*Math.PI/2; const beta = Math.PI/50; const radius = 220; const target = new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0); const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("Camera", alpha, beta, radius, target, scene); camera.attachControl(canvas, true); const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0), scene); light.intensity = 0.6; const keyParams = [ {type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.45, wholePositionX: -14.4}, {type: "black", note: "C#", wholePositionX: -13.45}, {type: "white", note: "D", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: 0, wholePositionX: -12}, {type: "black", note: "D#", wholePositionX: -10.6}, {type: "white", note: "E", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0.45, wholePositionX: -9.6}, {type: "white", note: "F", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: -0.55, wholePositionX: -7.2}, {type: "black", note: "F#", wholePositionX: -6.35}, {type: "white", note: "G", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.2, wholePositionX: -4.8}, {type: "black", note: "G#", wholePositionX: -3.6}, {type: "white", note: "A", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0.2, wholePositionX: -2.4}, {type: "black", note: "A#", wholePositionX: -0.85}, {type: "white", note: "B", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: 0.55, wholePositionX: 0}, ] // Transform Node that acts as the parent of all piano keys const keyboard = new BABYLON.TransformNode("keyboard"); keyParams.forEach(key => { buildKey(scene, keyboard, Object.assign({register: 4, referencePositionX: 0}, key)); }) const xrHelper = await scene.createDefaultXRExperienceAsync(); return scene; }這就是最終鍵盤的樣子:

擴展至88鍵鋼琴
在本節中,我們將擴展按鍵創建功能的使用,來生成一台完整的 88 鍵鋼琴鍵盤。
如前所述,一台完整的88鍵鋼琴鍵盤包含七個重複音區及四個其他音符。 其中三個額外音符位於鍵盤) 左端 (0號,1號在鍵盤) 右端 (8號。
我們會先在之前寫的環周圍加一個額外的迴圈,來建立七個完整重複。 將先前的迴圈
buildKey()替換為以下程式碼:// Register 1 through 7 var referencePositionX = -2.4*14; for (let register = 1; register <= 7; register++) { keyParams.forEach(key => { buildKey(scene, keyboard, Object.assign({register: register, referencePositionX: referencePositionX}, key)); }) referencePositionX += 2.4*7; }在這個迴圈中,我們建立了暫存器 1 到 7 的鍵,並在每次進入下一個暫存器時遞增參考位置。
接著,讓我們製作剩下的鑰匙。 在函
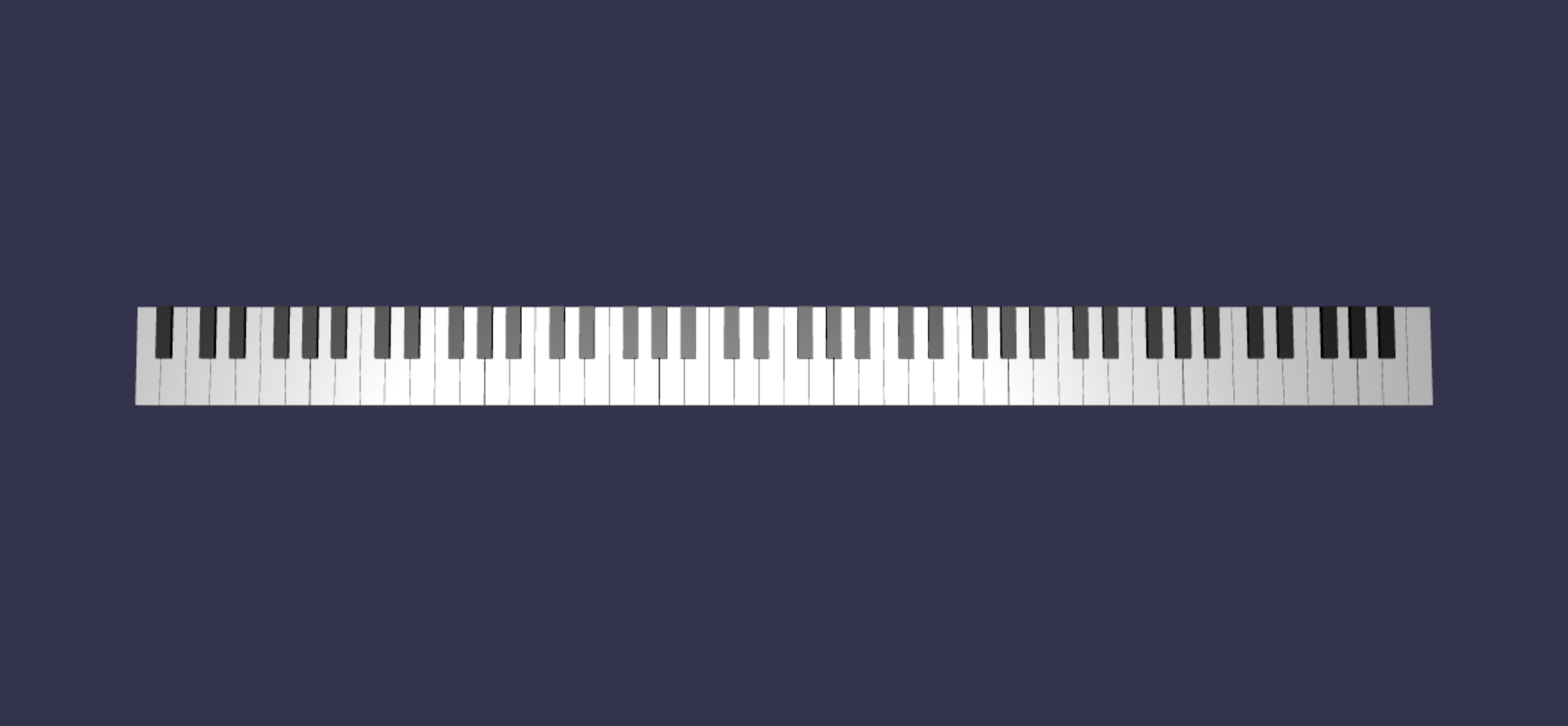
createScene()式中加入以下片段:// Register 0 buildKey(scene, keyboard, {type: "white", note: "A", topWidth: 1.9, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.20, wholePositionX: -2.4, register: 0, referencePositionX: -2.4*21}); keyParams.slice(10, 12).forEach(key => { buildKey(scene, keyboard, Object.assign({register: 0, referencePositionX: -2.4*21}, key)); }) // Register 8 buildKey(scene, keyboard, {type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 2.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0, wholePositionX: -2.4*6, register: 8, referencePositionX: 84});請注意,鋼琴鍵盤最左邊的琴鍵和最右邊的琴鍵不符合 (中道具的
keyParams尺寸,因為它們不在邊緣) 的黑鍵旁邊,因此我們需要為每個道具定義一個新的props物件來指定它們的特殊形狀。修改後產生的鍵盤應該是這樣的樣子:

加裝鋼琴框架
畫面看起來有點奇怪,只有一個鍵盤漂浮在空間裡。 讓我們在鍵盤周圍加一個鋼琴框架,營造出立式鋼琴的外觀。
就像我們創建鍵一樣,我們也可以透過定位並組合一組方塊網格來建立框架。
不過,我們會把這個挑戰留給你自己嘗試,並使用 BABYLON。SceneLoader.ImportMesh 來匯入一個立式鋼琴框架的預設網格。 將此程式碼附加於
createScene():// Transform node that acts as the parent of all piano components const piano = new BABYLON.TransformNode("piano"); keyboard.parent = piano; // Import and scale piano frame BABYLON.SceneLoader.ImportMesh("frame", "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MicrosoftDocs/mixed-reality/docs/mixed-reality-docs/mr-dev-docs/develop/javascript/tutorials/babylonjs-webxr-piano/files/", "pianoFrame.babylon", scene, function(meshes) { const frame = meshes[0]; frame.parent = piano; });請注意,我們再次建立
TransformNode一個父節點piano,將鍵盤與框架整體分組在一起。 如果需要,移動或調整整架鋼琴會變得容易許多。當畫面匯入後,會注意到鍵盤位於畫面 (底部,因為按鍵的 y 座標預設) 為 0。 讓我們把鍵盤抬起來,讓它能放進站立鋼琴的框架裡:
// Lift piano keys keyboard.position.y += 80;由於
keyboard是所有鋼琴鍵的父鍵,我們只要改變 的keyboardy 位置,就能提升所有鋼琴鍵。最終的 scene.js 代碼應該是這樣:
const buildKey = function (scene, parent, props) { if (props.type === "white") { /* Props for building a white key should contain: note, topWidth, bottomWidth, topPositionX, wholePositionX, register, referencePositionX As an example, the props for building the middle C white key would be {type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.45, wholePositionX: -14.4, register: 4, referencePositionX: 0} */ // Create bottom part const bottom = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyBottom", {width: props.bottomWidth, height: 1.5, depth: 4.5}, scene); // Create top part const top = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyTop", {width: props.topWidth, height: 1.5, depth: 5}, scene); top.position.z = 4.75; top.position.x += props.topPositionX; // Merge bottom and top parts // Parameters of BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes: (arrayOfMeshes, disposeSource, allow32BitsIndices, meshSubclass, subdivideWithSubMeshes, multiMultiMaterials) const key = BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes([bottom, top], true, false, null, false, false); key.position.x = props.referencePositionX + props.wholePositionX; key.name = props.note + props.register; key.parent = parent; return key; } else if (props.type === "black") { /* Props for building a black key should contain: note, wholePositionX, register, referencePositionX As an example, the props for building the C#4 black key would be {type: "black", note: "C#", wholePositionX: -13.45, register: 4, referencePositionX: 0} */ // Create black color material const blackMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("black"); blackMat.diffuseColor = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 0, 0); // Create black key const key = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox(props.note + props.register, {width: 1.4, height: 2, depth: 5}, scene); key.position.z += 4.75; key.position.y += 0.25; key.position.x = props.referencePositionX + props.wholePositionX; key.material = blackMat; key.parent = parent; return key; } } const createScene = async function(engine) { const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine); const alpha = 3*Math.PI/2; const beta = Math.PI/50; const radius = 220; const target = new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0); const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("Camera", alpha, beta, radius, target, scene); camera.attachControl(canvas, true); const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0), scene); light.intensity = 0.6; const keyParams = [ {type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.45, wholePositionX: -14.4}, {type: "black", note: "C#", wholePositionX: -13.45}, {type: "white", note: "D", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: 0, wholePositionX: -12}, {type: "black", note: "D#", wholePositionX: -10.6}, {type: "white", note: "E", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0.45, wholePositionX: -9.6}, {type: "white", note: "F", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: -0.55, wholePositionX: -7.2}, {type: "black", note: "F#", wholePositionX: -6.35}, {type: "white", note: "G", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.2, wholePositionX: -4.8}, {type: "black", note: "G#", wholePositionX: -3.6}, {type: "white", note: "A", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0.2, wholePositionX: -2.4}, {type: "black", note: "A#", wholePositionX: -0.85}, {type: "white", note: "B", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: 0.55, wholePositionX: 0}, ] // Transform Node that acts as the parent of all piano keys const keyboard = new BABYLON.TransformNode("keyboard"); // Register 1 through 7 var referencePositionX = -2.4*14; for (let register = 1; register <= 7; register++) { keyParams.forEach(key => { buildKey(scene, keyboard, Object.assign({register: register, referencePositionX: referencePositionX}, key)); }) referencePositionX += 2.4*7; } // Register 0 buildKey(scene, keyboard, {type: "white", note: "A", topWidth: 1.9, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.20, wholePositionX: -2.4, register: 0, referencePositionX: -2.4*21}); keyParams.slice(10, 12).forEach(key => { buildKey(scene, keyboard, Object.assign({register: 0, referencePositionX: -2.4*21}, key)); }) // Register 8 buildKey(scene, keyboard, {type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 2.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0, wholePositionX: -2.4*6, register: 8, referencePositionX: 84}); // Transform node that acts as the parent of all piano components const piano = new BABYLON.TransformNode("piano"); keyboard.parent = piano; // Import and scale piano frame BABYLON.SceneLoader.ImportMesh("frame", "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MicrosoftDocs/mixed-reality/docs/mixed-reality-docs/mr-dev-docs/develop/javascript/tutorials/babylonjs-webxr-piano/files/", "pianoFrame.babylon", scene, function(meshes) { const frame = meshes[0]; frame.parent = piano; }); // Lift the piano keyboard keyboard.position.y += 80; const xrHelper = await scene.createDefaultXRExperienceAsync(); return scene; }現在我們應該有一台長這樣樣的立式鋼琴:
