在本課程模組中,我們將撰寫最小的 Windows 桌面程式。 它所做的就是建立並顯示空白視窗。 第一個程式包含大約 50 行的程式代碼,不會計算空白行和批注。 這將是我們的起點:稍後我們將新增圖形、文字、使用者輸入和其他功能。
如果您要尋找如何在 Visual Studio 中建立傳統 Windows 傳統型應用程式的詳細資訊,請參閱 逐步解說:建立傳統 Windows 傳統型應用程式 (C++)。
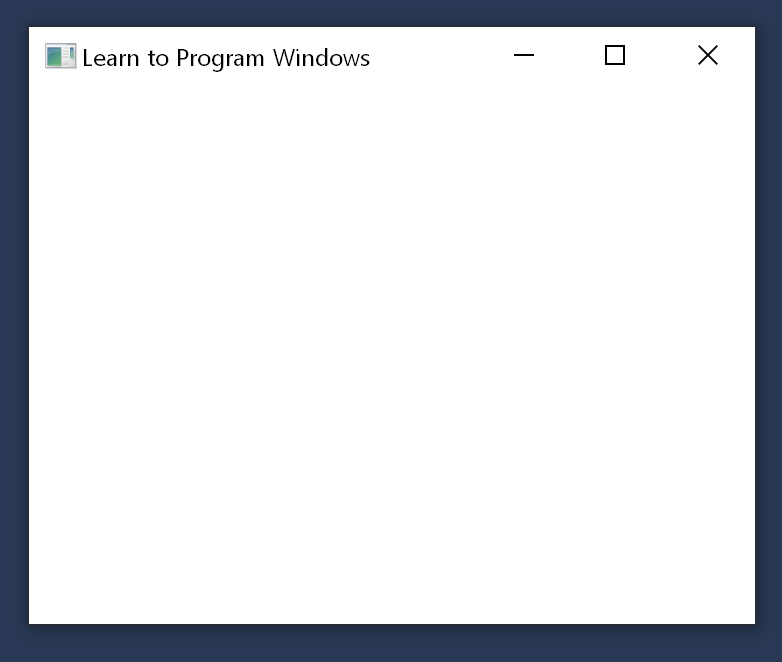
以下是程式的完整程式代碼:
#ifndef UNICODE
#define UNICODE
#endif
#include <windows.h>
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(HWND hwnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam);
int WINAPI wWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, PWSTR pCmdLine, int nCmdShow)
{
// Register the window class.
const wchar_t CLASS_NAME[] = L"Sample Window Class";
WNDCLASS wc = { };
wc.lpfnWndProc = WindowProc;
wc.hInstance = hInstance;
wc.lpszClassName = CLASS_NAME;
RegisterClass(&wc);
// Create the window.
HWND hwnd = CreateWindowEx(
0, // Optional window styles.
CLASS_NAME, // Window class
L"Learn to Program Windows", // Window text
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, // Window style
// Size and position
CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT,
NULL, // Parent window
NULL, // Menu
hInstance, // Instance handle
NULL // Additional application data
);
if (hwnd == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow);
// Run the message loop.
MSG msg = { };
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0) > 0)
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
return 0;
}
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(HWND hwnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
switch (uMsg)
{
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
return 0;
case WM_PAINT:
{
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hdc = BeginPaint(hwnd, &ps);
// All painting occurs here, between BeginPaint and EndPaint.
FillRect(hdc, &ps.rcPaint, (HBRUSH) (COLOR_WINDOW+1));
EndPaint(hwnd, &ps);
}
return 0;
}
return DefWindowProc(hwnd, uMsg, wParam, lParam);
}
您可以從 Windows Hello World 範例下載完整的 Visual Studio 專案。
提供此程式代碼用途的簡短大綱可能很有用。 稍後的主題會詳細檢查程序代碼。
-
wWinMain 是程序進入點。 程序啟動時,它會註冊應用程式窗口行為的一些資訊。 其中一個最重要的專案是函式的位址,在此範例中名為
WindowProc。 此函式會定義窗口的行為—其外觀、與用戶互動的方式等等。 - 接下來,程式會建立視窗,並接收可唯一識別視窗的句柄。
- 如果已成功建立視窗,程式會在 循環時輸入。 程式會維持在此迴圈中,直到使用者關閉視窗並結束應用程式為止。
請注意,程式不會明確呼叫 WindowProc 函式,儘管我們表示這是定義大部分應用程式邏輯的位置。 Windows 會傳遞一系列 訊息,與程序通訊。
循環驅動此程式時, 內的程序代碼。 每次程式呼叫 DispatchMessage 函式時,都會間接導致 Windows 針對每個訊息叫用 WindowProc 函式一次。
在本節中
相關主題
-
學習在 C++ 中為 Windows 進行程式設計