Бележка
Достъпът до тази страница изисква удостоверяване. Можете да опитате да влезете или да промените директориите.
Достъпът до тази страница изисква удостоверяване. Можете да опитате да промените директориите.
APPLIES TO: Developer | Premium
This article describes the steps for deploying the self-hosted gateway component of Azure API Management to a Kubernetes cluster.
Note
You can also deploy self-hosted gateway to an Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster as a cluster extension.
Prerequisites
Complete the following quickstart: Create an Azure API Management instance.
Create a Kubernetes cluster, or have access to an existing one.
Tip
Single-node clusters work well for development and evaluation purposes. Use Kubernetes Certified multi-node clusters on-premises or in the cloud for production workloads
Provision a self-hosted gateway resource in your API Management instance.
Deploy to Kubernetes
Tip
The following steps deploy the self-hosted gateway to Kubernetes and enable authentication to the API Management instance by using a gateway access token (authentication key). You can also deploy the self-hosted gateway to Kubernetes and enable authentication to the API Management instance by using Microsoft Entra ID.
- Select Gateways under Deployment and infrastructure.
- Select the self-hosted gateway resource that you want to deploy.
- Select Deployment.
- An access token in the Token text box was autogenerated for you, based on the default Expiry and Secret key values. If needed, choose values in either or both controls to generate a new token.
- Select the Kubernetes tab under Deployment scripts.
- Select the <gateway-name>.yml file link and download the YAML file.
- Select the copy icon at the lower-right corner of the Deploy text box to save the
kubectlcommands to the clipboard. - When using Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), run
az aks get-credentials --resource-group <resource-group-name> --name <resource-name> --adminin a new terminal session. - Run the commands to create the necessary Kubernetes objects in the default namespace and start self-hosted gateway pods from the container image downloaded from the Microsoft Artifact Registry.
- The first step creates a Kubernetes secret that contains the access token generated in step 4. Next, it creates a Kubernetes deployment for the self-hosted gateway, which uses a ConfigMap with the configuration of the gateway.
Confirm that the gateway is running
Run the following command to check if the deployment succeeded. It might take a little time for all the objects to be created and for the pods to initialize.
kubectl get deploymentsIt should return
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE <gateway-name> 1/1 1 1 18sRun the following command to check if the services were successfully created. Your service IPs and ports will be different.
kubectl get servicesIt should return
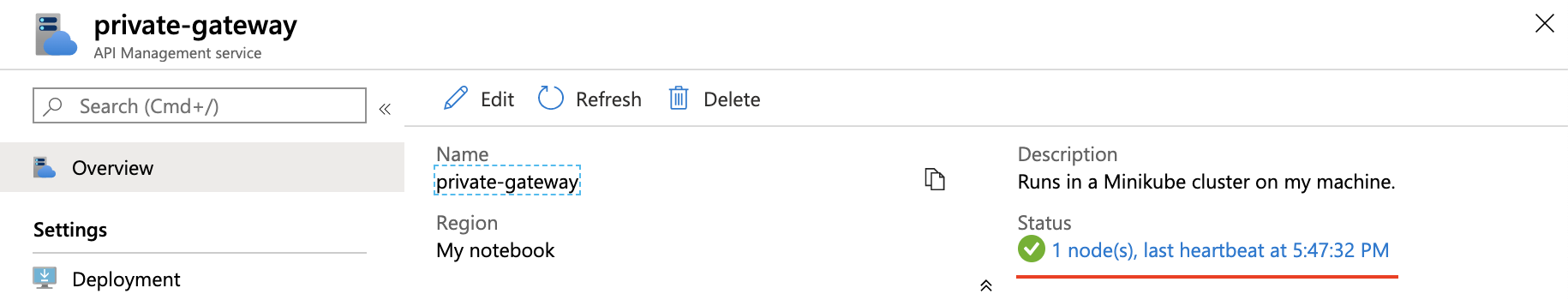
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE <gateway-name>-live-traffic ClusterIP None <none> 4290/UDP,4291/UDP 9m1s <gateway-name>-instance-discovery LoadBalancer 10.99.236.168 <pending> 80:31620/TCP,443:30456/TCP 9m1sGo back to the Azure portal and select Overview.
Confirm that Status shows a green check mark, followed by a node count that matches the number of replicas specified in the YAML file. This status means the deployed self-hosted gateway pods are successfully communicating with the API Management service and have a regular "heartbeat."
Tip
- Run the
kubectl logs deployment/<gateway-name>command to view logs from a randomly selected pod if there's more than one. - Run
kubectl logs -hfor a complete set of command options, such as how to view logs for a specific pod or container.
Related content
- To learn more about the self-hosted gateway, see Self-hosted gateway overview.
- Learn how to deploy API Management self-hosted gateway to Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters.
- Learn more about guidance for running the self-hosted gateway on Kubernetes in production.