Copy data from PostgreSQL V1 using Azure Data Factory or Synapse Analytics
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
This article outlines how to use the Copy Activity in Azure Data Factory and Synapse Analytics pipelines to copy data from a PostgreSQL database. It builds on the copy activity overview article that presents a general overview of copy activity.
Important
The PostgreSQL V2 connector provides improved native PostgreSQL support. If you are using the PostgreSQL V1 connector in your solution, please upgrade your PostgreSQL connector as V1 is at End of Support stage. Refer to this section for details on the difference between V2 and V1.
Supported capabilities
This PostgreSQL connector is supported for the following capabilities:
| Supported capabilities | IR |
|---|---|
| Copy activity (source/-) | ① ② |
| Lookup activity | ① ② |
① Azure integration runtime ② Self-hosted integration runtime
For a list of data stores that are supported as sources/sinks by the copy activity, see the Supported data stores table.
Specifically, this PostgreSQL connector supports PostgreSQL version 7.4 and above.
Prerequisites
If your data store is located inside an on-premises network, an Azure virtual network, or Amazon Virtual Private Cloud, you need to configure a self-hosted integration runtime to connect to it.
If your data store is a managed cloud data service, you can use the Azure Integration Runtime. If the access is restricted to IPs that are approved in the firewall rules, you can add Azure Integration Runtime IPs to the allow list.
You can also use the managed virtual network integration runtime feature in Azure Data Factory to access the on-premises network without installing and configuring a self-hosted integration runtime.
For more information about the network security mechanisms and options supported by Data Factory, see Data access strategies.
The Integration Runtime provides a built-in PostgreSQL driver starting from version 3.7, therefore you don't need to manually install any driver.
Getting started
To perform the Copy activity with a pipeline, you can use one of the following tools or SDKs:
- The Copy Data tool
- The Azure portal
- The .NET SDK
- The Python SDK
- Azure PowerShell
- The REST API
- The Azure Resource Manager template
Create a linked service to PostgreSQL using UI
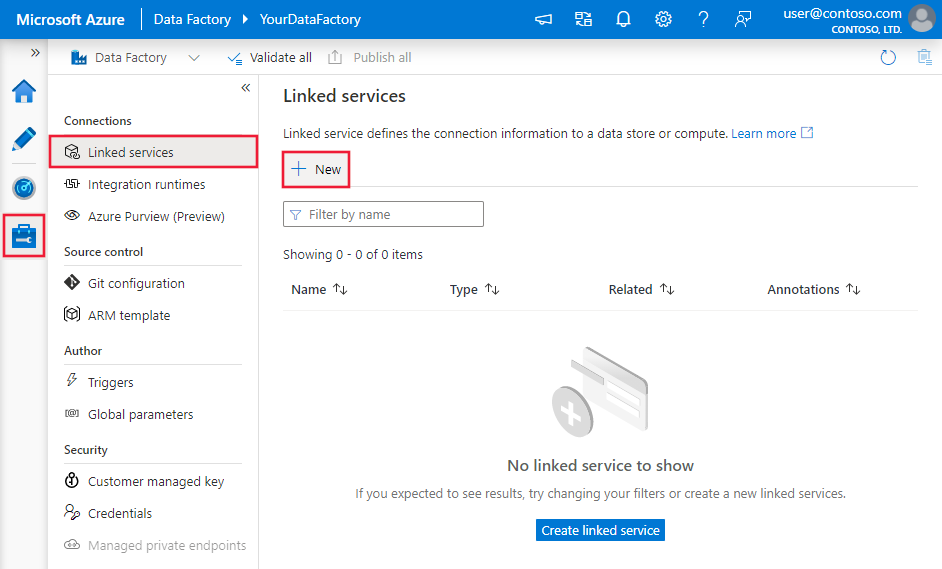
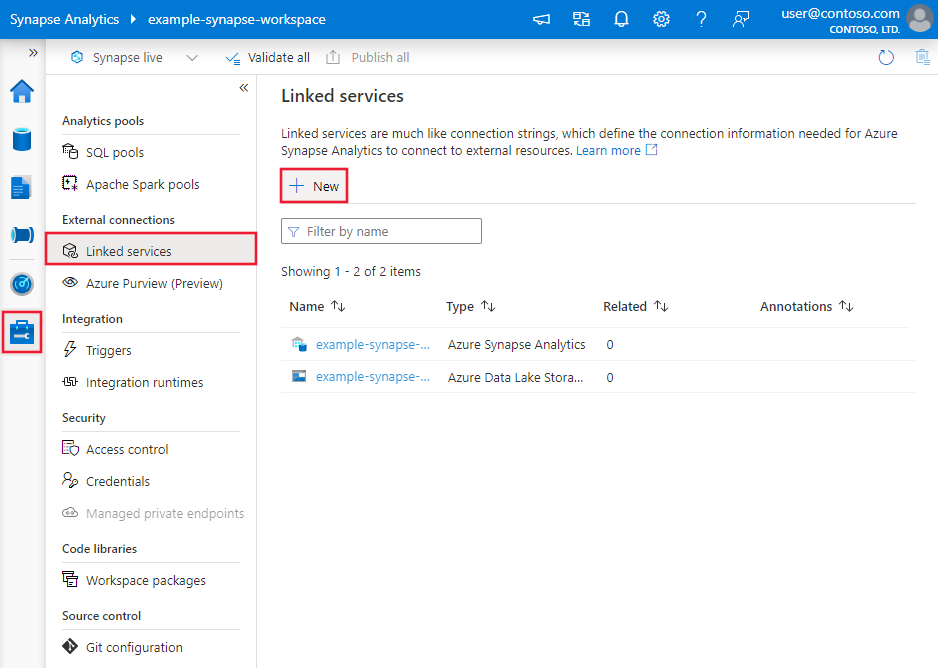
Use the following steps to create a linked service to PostgreSQL in the Azure portal UI.
Browse to the Manage tab in your Azure Data Factory or Synapse workspace and select Linked Services, then click New:
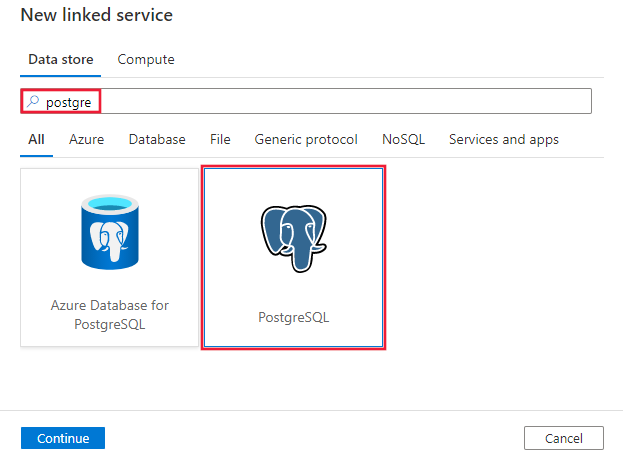
Search for Postgre and select the PostgreSQL connector.
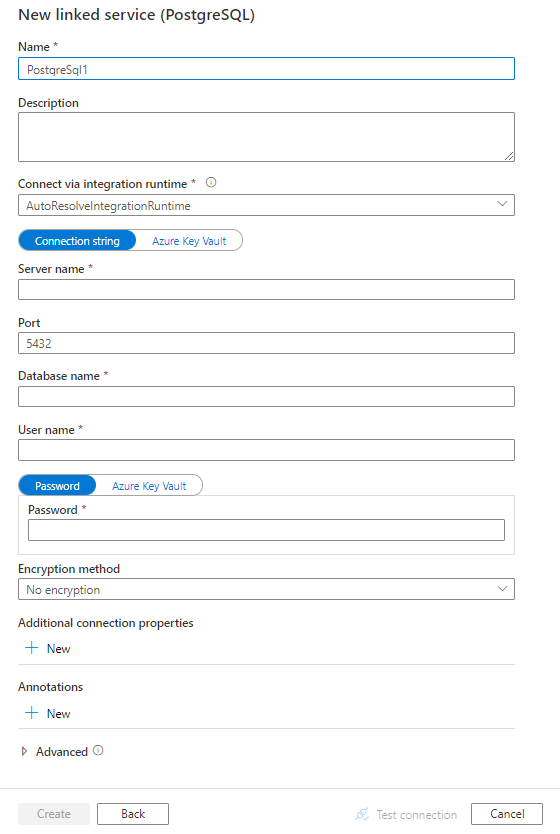
Configure the service details, test the connection, and create the new linked service.
Connector configuration details
The following sections provide details about properties that are used to define Data Factory entities specific to PostgreSQL connector.
Linked service properties
The following properties are supported for PostgreSQL linked service:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to: PostgreSql | Yes |
| connectionString | An ODBC connection string to connect to Azure Database for PostgreSQL. You can also put password in Azure Key Vault and pull the password configuration out of the connection string. Refer to the following samples and Store credentials in Azure Key Vault article with more details. |
Yes |
| connectVia | The Integration Runtime to be used to connect to the data store. Learn more from Prerequisites section. If not specified, it uses the default Azure Integration Runtime. | No |
A typical connection string is Server=<server>;Database=<database>;Port=<port>;UID=<username>;Password=<Password>. More properties you can set per your case:
| Property | Description | Options | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| EncryptionMethod (EM) | The method the driver uses to encrypt data sent between the driver and the database server. E.g., EncryptionMethod=<0/1/6>; |
0 (No Encryption) (Default) / 1 (SSL) / 6 (RequestSSL) | No |
| ValidateServerCertificate (VSC) | Determines whether the driver validates the certificate that is sent by the database server when SSL encryption is enabled (Encryption Method=1). E.g., ValidateServerCertificate=<0/1>; |
0 (Disabled) (Default) / 1 (Enabled) | No |
Note
In order to have full SSL verification via the ODBC connection when using the Self Hosted Integration Runtime you must use an ODBC type connection instead of the PostgreSQL connector explicitly, and complete the following configuration:
- Set up the DSN on any SHIR servers.
- Put the proper certificate for PostgreSQL in C:\Windows\ServiceProfiles\DIAHostService\AppData\Roaming\postgresql\root.crt on the SHIR servers. This is where the ODBC driver looks > for the SSL cert to verify when it connects to the database.
- In your data factory connection, use an ODBC type connection, with your connection string pointing to the DSN you created on your SHIR servers.
Example:
{
"name": "PostgreSqlLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "PostgreSql",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "Server=<server>;Database=<database>;Port=<port>;UID=<username>;Password=<Password>"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Example: store password in Azure Key Vault
{
"name": "PostgreSqlLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "PostgreSql",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "Server=<server>;Database=<database>;Port=<port>;UID=<username>;",
"password": {
"type": "AzureKeyVaultSecret",
"store": {
"referenceName": "<Azure Key Vault linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"secretName": "<secretName>"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
If you were using PostgreSQL linked service with the following payload, it is still supported as-is, while you are suggested to use the new one going forward.
Previous payload:
{
"name": "PostgreSqlLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "PostgreSql",
"typeProperties": {
"server": "<server>",
"database": "<database>",
"username": "<username>",
"password": {
"type": "SecureString",
"value": "<password>"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Dataset properties
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining datasets, see the datasets article. This section provides a list of properties supported by PostgreSQL dataset.
To copy data from PostgreSQL, the following properties are supported:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the dataset must be set to: PostgreSqlTable | Yes |
| schema | Name of the schema. | No (if "query" in activity source is specified) |
| table | Name of the table. | No (if "query" in activity source is specified) |
| tableName | Name of the table with schema. This property is supported for backward compatibility. Use schema and table for new workload. |
No (if "query" in activity source is specified) |
Example
{
"name": "PostgreSQLDataset",
"properties":
{
"type": "PostgreSqlTable",
"typeProperties": {},
"schema": [],
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "<PostgreSQL linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
}
}
}
If you were using RelationalTable typed dataset, it's still supported as-is, while you are suggested to use the new one going forward.
Copy activity properties
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining activities, see the Pipelines article. This section provides a list of properties supported by PostgreSQL source.
PostgreSQL as source
To copy data from PostgreSQL, the following properties are supported in the copy activity source section:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the copy activity source must be set to: PostgreSqlSource | Yes |
| query | Use the custom SQL query to read data. For example: "query": "SELECT * FROM \"MySchema\".\"MyTable\"". |
No (if "tableName" in dataset is specified) |
Note
Schema and table names are case-sensitive. Enclose them in "" (double quotes) in the query.
Example:
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromPostgreSQL",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<PostgreSQL input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "PostgreSqlSource",
"query": "SELECT * FROM \"MySchema\".\"MyTable\""
},
"sink": {
"type": "<sink type>"
}
}
}
]
If you were using RelationalSource typed source, it is still supported as-is, while you are suggested to use the new one going forward.
Lookup activity properties
To learn details about the properties, check Lookup activity.
Related content
For a list of data stores supported as sources and sinks by the copy activity, see supported data stores.