Azure NetApp Files regular volume performance benchmarks for Linux
This article describes performance benchmarks Azure NetApp Files delivers for Linux with a regular volume.
Linux scale-out
This section describes performance benchmarks of Linux workload throughput and workload IOPS.
Linux workload throughput
This graph represents a 64 kibibyte (KiB) sequential workload and a 1 TiB working set. It shows that a single Azure NetApp Files volume can handle between ~1,600 MiB/s pure sequential writes and ~4,500 MiB/s pure sequential reads.
The graph illustrates decreases in 10% at a time, from pure read to pure write. It demonstrates what you can expect when using varying read/write ratios (100%:0%, 90%:10%, 80%:20%, and so on).

Linux workload IOPS
The following graph represents a 4-KiB random workload and a 1 TiB working set. The graph shows that an Azure NetApp Files volume can handle between ~130,000 pure random writes and ~460,000 pure random reads.
This graph illustrates decreases in 10% at a time, from pure read to pure write. It demonstrates what you can expect when using varying read/write ratios (100%:0%, 90%:10%, 80%:20%, and so on).

Linux scale-up
The graphs in this section show the validation testing results for the client-side mount option with NFSv3. For more information, see nconnect section of Linux mount options.
The graphs compare the advantages of nconnect to a non-connected mounted volume. In the graphs, FIO generated the workload from a single D32s_v4 instance in the us-west2 Azure region using a 64-KiB sequential workload – the largest I/O size supported by Azure NetApp Files at the time of the testing represented here. Azure NetApp Files now supports larger I/O sizes. For more information, see rsize and wsize section of Linux mount options.
Linux read throughput
The following graphs show 64-KiB sequential reads of ~3,500 MiB/s reads with nconnect, roughly 2.3X non-nconnect.

Linux write throughput
The following graphs show sequential writes. They indicate that nconnect has no noticeable benefit for sequential writes. The sequential write volume upper limit is approximately 1,500 MiB/s; the D32s_v4 instance egress limit is also approximately 1,500 MiB/s.

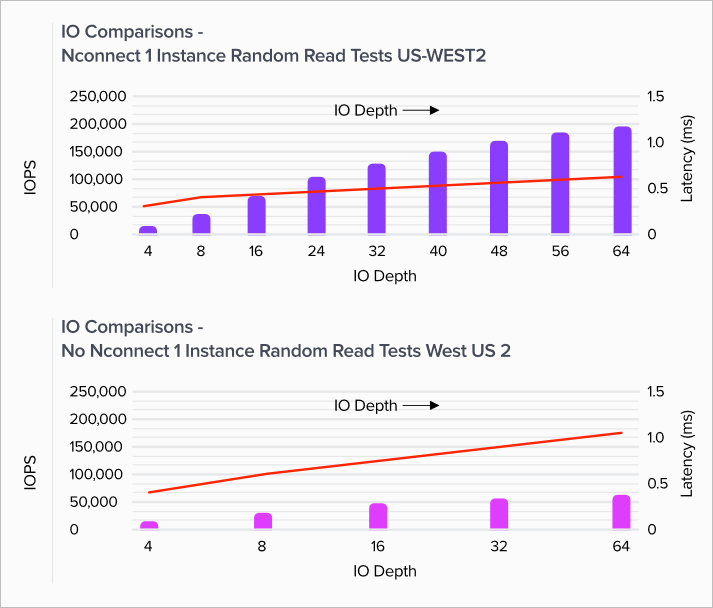
Linux read IOPS
The following graphs show 4-KiB random reads of ~200,000 read IOPS with nconnect, roughly 3X non-nconnect.
Linux write IOPS
The following graphs show 4-KiB random writes of ~135,000 write IOPS with nconnect, roughly 3X non-nconnect.
