Building a Secure Login Form (Parameterized Queries Part 2)
In my first post on parameterized queries I built a simple login form that really was a contrived example meant to showcase how to use the TableAdapter Configuration Wizard to configure a parameterized query. However, since I opened myself up here, I felt it socially responsible to show how to make this a bit more secure by showing you how to store passwords in a secure way in a database.
There are actually many many secure ways to store data in your database including using the encryption features of SQL-Server 2005 which allows you to protect columns inside your database at the database level, independent of the application. Additionally, if we're just talking about user's logins and you're building a multi-tier or SO application then using the ASP.NET membership services is probably your best choice. In next version of Visual Studio, Microsoft made these ASP.NET services easily accessible to any client application (Winforms, WPF, Silverlight) not just WebForms. But what if you're building a single-user application or a client-server app with only a handful of users and you don't have (or want) a web server or maybe you're not using SQL-Server as your database?
The first recommendation for this scenario is don't store passwords at all. If you don't have passwords in your application then you don't have to worry about someone stealing them. Instead, consider using the Windows Identity as the user of your application. This means that your application will not need to store passwords, only user names, because it would be using the logged in Windows user which has already been authenticated through the Windows OS. To access the user name of the currently logged in user from your client code:
Imports System.Security.Principal
...
Dim user As WindowsIdentity = WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent()
Dim userName As String = user.Name
The only thing you would need to do in your database Login table is make the UserName field unique. Then you could write a very simple parameterized query.
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Login WHERE UserName = @UserName
So your login code would be very simple. If you name the above parameterized query on your TableAdapter "GetLoginByUserName" then it would be something like:
Imports System.Security.Principal
...
Dim user As WindowsIdentity = WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent()
Dim userName As String = user.Name
If CType(Me.LoginTableAdapter1.GetLoginByUserName(userName), Integer) = 1 Then
MsgBox("Welcome to my application!")
Else
MsgBox("Invalid username or password.")
End If
(NOTE: This code assumes that the application is connecting to the database directly and not through a service layer. If you are connecting to a service layer then you need to configure your web server to authenticate Windows users by not allowing anonymous access and only allowing Windows Authentication. For more information, read this.)
However, what if you cannot use this method of authentication? For instance, your application runs on a shared computer that remains logged in under one Windows login, but you require users to login separately to your application. In that case you're going to need to store passwords. However, if we store passwords as clear text in our database, anybody that can get a glimpse of the Login table will have a bunch of user credentials to access the application! The safest thing to do is to use a one-way hashing algorithm and store the hashes in your database table instead. The .NET Framework gives you a lot of help here by providing a handful of proven hashing algorithms in the System.Security.Cryptography namespace. The most common are SHA-1 and MD5. To hash a string using the SHA-1 becomes very simple in .NET:
Imports System.Security.Cryptography
Imports System.Text
...
Function HashEncryptString(ByVal s As String) As String
Dim hasher As New SHA1CryptoServiceProvider()
Dim clearBytes As Byte() = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(s)
Dim hashedBytes As Byte() = hasher.ComputeHash(clearBytes)
Return Convert.ToBase64String(hashedBytes)
End Function
Hash algorithms are one-way so it's very very difficult to tell what the original password is from a computed hash. (So if a user forgets their password, you won't be able to tell them what it was.) So when we store user names and passwords in our Login table we can easily hash the value of the submitted password and store that instead. So we're secure now, right? Well almost! Let's take a look at my Login table in this example:
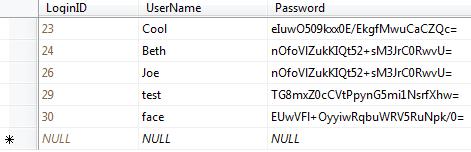
Notice that Beth and Joe both have the same hashed password. This means that both these passwords are the same as clear text as well. An attacker could probably figure out the password by using a dictionary attack on our table. So what can we do?
There's a technique called salting where you take the password and "salt" it with a random value and then hash that. This random value is different for each login. This will create different hashed passwords for the same clear text password, making it extremely difficult to break. To be even more secure, you should store this salt value in a separate table from the passwords. To obtain an appropriate salt (random) value in .NET you can use the RNGCryptoServiceProvider class.
Imports System.Security.Cryptography
...
Function GetSalt(ByVal saltSize As Integer) As String
Dim buffer() As Byte = New Byte(saltSize) {}
Dim rng As New RNGCryptoServiceProvider()
rng.GetBytes(buffer)
Return Convert.ToBase64String(buffer)
End Function
So now we can take the salt value and store that in a table called Salt which has a foreign key to our Login table. Then I can create a couple parameterized queries on my TableAdapters for Login and Salt.
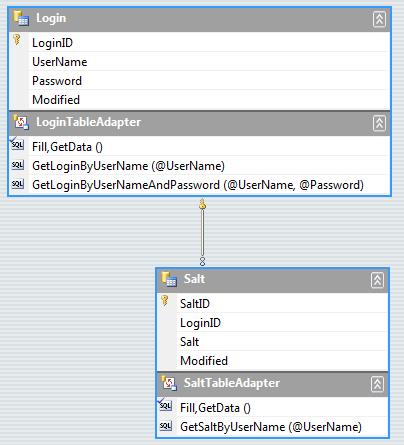
On the LoginTableAdapter we can add a parameterized query called GetLoginByUserNameAndPassword where we pass the UserName and the salted hashed password. The select statement returns a scalar value and we add it through the TableAdapter Query Configuration Wizard just like I showed in my previous post.
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Login WHERE UserName = @UserName AND Password = @Password
In order to pass the correct value for the @Password parameter, we need the salt value first. On the SaltTableAdapter we can add a parameterized query that returns the salt value for a given UserName called GetSaltByUserName.
SELECT TOP (1) Salt.Salt FROM Salt INNER JOIN Login ON Salt.LoginID = Login.LoginID WHERE (Login.UserName = @UserName)
To make it easier to access the hashing functions we can create a module called PasswordCrypto:
Imports System.Security.Cryptography
Imports System.Text
Module PasswordCrypto
Private Hasher As New SHA1CryptoServiceProvider()
Friend Function GetSalt(ByVal saltSize As Integer) As String
Dim buffer() As Byte = New Byte(saltSize) {}
Dim rng As New RNGCryptoServiceProvider()
rng.GetBytes(buffer)
Return Convert.ToBase64String(buffer)
End Function
Friend Function HashEncryptString(ByVal s As String) As String
Dim clearBytes As Byte() = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(s)
Dim hashedBytes As Byte() = Hasher.ComputeHash(clearBytes)
Return Convert.ToBase64String(hashedBytes)
End Function
Friend Function HashEncryptStringWithSalt(ByVal s As String, _
ByVal salt As String) As String
Return HashEncryptString(salt + s)
End Function
End Module
Now that we have our hashing code and our TableAdapters configured, taking our Login form we can add code like this to verify whether a user's entered password matches the hashed password in the Login table:
Try
Dim isOK As Boolean = False
'Get the salt value for this username
Dim saltValue As Object = _
Me.SaltTableAdapter1.GetSaltByUserName(Me.txtUserName.Text)
If Not IsDBNull(saltValue) Then
'Hash the user entered password with the salt value stored in the Salt table
Dim password As String = _
PasswordCrypto.HashEncryptStringWithSalt(Me.txtPassword.Text, saltValue.ToString)
'Now check the Login table to see if this hashed password matches
isOK = CType(Me.LoginTableAdapter1.GetLoginByUserNameAndPassword( _
Me.txtUserName.Text, password), Integer) = 1
End If
If isOK Then
MsgBox("Welcome to my Application!")
Else
MsgBox("Invalid user name or password.")
End If
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox(ex.ToString)
End Try
So this is how we can store passwords in a secure way in our database, even if our database does not support encrypted columns. With .NET, accessing hashing algorithms is a snap. I've attached a complete sample that demonstrates these techniques (as well as saving users passwords and salts) so that you can learn from them. You'll need Visual Studio or Visual Basic Express and SQL-Server Express installed to compile and run the sample.
Enjoy! And be secure!
Comments
Anonymous
June 06, 2007
Beth, fantastic post!! Speaking of Security Engineering, I think worth to mention MS patterns & practices Security Engineering Index http://msdn.com/SecurityEngineering Thanks aliklAnonymous
June 07, 2007
The comment has been removedAnonymous
June 07, 2007
The comment has been removedAnonymous
June 07, 2007
The comment has been removedAnonymous
June 07, 2007
Hi Dave, Re 2) All the more reason to have a strong password from the begining. You can have Windows enforce this and it would be a good idea to have your application do this as well if you took on storing passwords yourself. Regarding SHA-1, there are other providers in the namespace you could use as well. How about a sample? :-) Take Care! -BAnonymous
June 25, 2007
thanks beth!!Anonymous
June 27, 2007
The comment has been removedAnonymous
June 27, 2007
The comment has been removedAnonymous
July 20, 2007
I am trying to figure out how to write the SQL statement without using @. In VS.Net 2005 the@ is not accept. Is there another way to write the statements.Anonymous
July 24, 2007
Hi Kay, What kind of database are you using? If it's Access then you'll need to use just a question mark in place of the variable name: SELECT Fields FROM MyTable WHERE Field1 = ? HTH, -BAnonymous
November 23, 2007
Hi Beth, This tutorial is great! The only thing I am having trouble with is updating the table adapters. Salt and Login. I have replicated the examples from the downloaded source and find my self at a loss. I get an exception: Column 'UserName' does not allow nulls. when ever I try to load the form. I would appreciate a little guidence. kind regards SimonAnonymous
November 28, 2007
Hi Beth, Fantastic post! Thanks a ton! The only question I have is how did you insert the hashed passwords into the table? The hashing is done using a VB.NET procedure, so I'm guessing you have to have a VB.NET procedure for inserting passwords into the table - Is there a way to pre-populate the table without using the application? Thanks a ton! PaulAnonymous
November 29, 2007
Hi Paul, Take a look at the attached sample, I believe it does this by simply updating through the dataset. HTH, -BAnonymous
December 10, 2007
Hi Simon, Does the sample run for you? Sounds like your database allows nulls for the username but your typed DataTable does not. -BAnonymous
December 10, 2007
Ok finally got back to this. I was going to include a sample but all you would have to change would be: Private Hasher As New SHA1CryptoServiceProvider() to Private Hasher As New SHA512Managed()Anonymous
February 03, 2008
Hello Beth, Enjoying your blog. I'm using Access and I'm not getting a salt back from the query when I test it. I had to remove the SELECT TOP (1). It didn't seem to like it. What do I do next?Anonymous
February 03, 2008
You have the GetSalt function but it isn't being called from anywhere that I can see. Where did I go wrong? ThanksAnonymous
February 18, 2008
Hello Beth Thanks very much for this. Great stuff!Anonymous
February 25, 2008
Thanks Beth, Very nicely done and explained.Anonymous
April 17, 2008
very confusing, only a beginner looking for an easier wayAnonymous
July 03, 2008
Hi, If I want to create the login form as the startup form, how to i create an account in my Login database?Anonymous
July 21, 2008
Hi Jason, Take a look at the attached sample at the end of this post. It shows a technique on how to add users and secure passwords to the database. HTH, -BAnonymous
September 24, 2008
The comment has been removedAnonymous
September 24, 2008
The comment has been removedAnonymous
December 21, 2008
I get the following error: Null Reference Exception Occured. Object reference not set to an instance of an object. Which relates to: Dim password As String = _ PasswordCrypto.HashEncryptStringWithSalt(Me.PasswordTextBox.Text, saltValue.ToString) Any thoughts?Anonymous
April 16, 2009
Hi Beth! SELECT TOP(1) Salt.Salt FROM Salt INNER JOIN Login ON Salt.LoginID = Login.LoginID WHERE (Login.UserName = @UserName) is not working, I'm getting this Wizard error result: The wizard detected the following problems when configuring TableAdapter query "SALT": Details: Generated SELECT statement: Error in list of function arguments: '.' not recognized Error in list of function arguments: ')' not recognized Unable to parse query text
What should I do? Thanks much!
Anonymous
June 13, 2009
how to create a secure login form in visual studio for the window application. i have used login form but in dont know how to make the login form to be secure with appropiate username and password.Anonymous
November 21, 2010
Well thanks a lot for the method shown in here. I have only used the HashEncryptString(s) method and it is successfully implemented. But what if we want to retrieve the password? Thank you IndyaKingAnonymous
March 07, 2016
Awesome issues here. I am very happy to see your post.Thanks a lot and I'm looking forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a mail?Anonymous
June 01, 2016
Have you ever considered writing an ebook or guest authoring on other websites?I have a blog based on the same subjects you discuss and would really like to have you share some stories/information. I know mmy audience would enjoy your work. If you're even remotely interested, feel free to send me an e-mail.