Per-site configuration by policy
This article describes the per-site configurations by policy and how the browser handles page loads from a site.
The browser as a decision maker
As a part of every page load, browsers make many decisions. Some, but not all, of these decisions include: whether a particular API is available, should a resource load be permitted, and should a script be allowed to run.
In most cases, browser decisions are governed by the following inputs:
- A user setting
- The URL of the page for which the decision is made
In the Internet Explorer web platform, each of these decisions was called a URLAction. For more information, see URL Action Flags. The URLAction, Enterprise Group Policy, and user settings in the Internet Control Panel controlled how the browser would handle each decision.
In Microsoft Edge, most per-site permissions are controlled using settngs and policies expressed using a simple syntax with limited wild-card support. Windows Security Zones are still used for a few configuration decisions.
Windows Security Zones
To simplify configuration for the user or admin, the legacy platform classified sites into one of five different Security Zones. These Security Zones are: Local Machine, Local Intranet, Trusted, Internet, and Restricted Sites.
When making a page load decision, the browser maps the website to a Zone, then consults the setting for the URLAction for that Zone to decide what to do. Reasonable defaults like "Automatically satisfy authentication challenges from my Intranet" means that most users never need to change any default settings.
Users can use the Internet Control Panel to assign specific sites to Zones and to configure the permission results for each zone. In managed environments, administrators can use Group Policy to assign specific sites to Zones (via "Site to Zone Assignment List" policy) and specify the settings for URLActions on a per-zone basis. Beyond manual administrative or user assignment of sites to Zones, other heuristics could assign sites to the Local Intranet Zone. In particular, dotless host names (for example, http://payroll) were assigned to the Intranet Zone. If a Proxy Configuration script was used, any sites configured to bypass the proxy would be mapped to the Intranet Zone.
EdgeHTML, used in WebView1 controls and Microsoft Edge Legacy, inherited the Zones architecture from its Internet Explorer predecessor with a few simplifying changes:
- Windows' five built-in Zones were collapsed to three: Internet (Internet), Trusted (Intranet+Trusted), and Local Computer. The Restricted Sites Zone was removed.
- Zone to URLAction mappings were hardcoded into the browser, ignoring Group Policies and settings in the Internet Control Panel.
Per site permissions in Microsoft Edge
Microsoft Edge makes limited use of Windows Security Zones. Instead, most permissions and features that offer administrators per-site configuration via policy rely on lists of rules in the URL Filter Format.
When end users open a settings page like edge://settings/content/siteDetails?site=https://example.com, they find a long list of configuration switches and lists for various permissions. Users rarely use the Settings page directly, instead they make choices while browsing and using various widgets and toggles in the page info dropdown. This list appears when you select the lock icon in the address bar. You can also use the various prompts or buttons at the right-edge of the address bar. The next screenshot shows an example of page information.
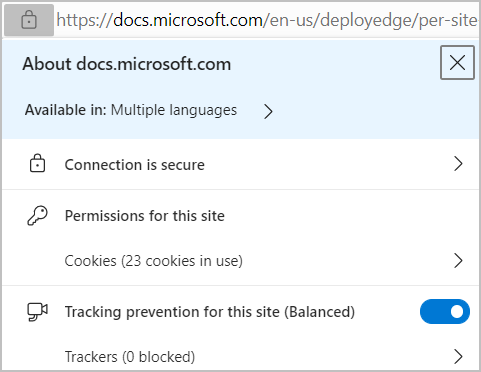
Enterprises can use Group Policy to set up site lists for individual policies that control the browser's behavior. To find these policies, open the Microsoft Edge Group Policy documentation and search for "ForUrls" to find the policies that allow and block behavior based on the loaded site's URL. Most of the relevant settings are listed in the Group Policy for Content Settings section.
There are also many policies (whose names contain "Default") that control the default behavior for a given setting.
Many of the settings are obscure (WebSerial, WebMIDI) and there's often no reason to change a setting from the default.
Security Zones in Microsoft Edge
While Microsoft Edge relies mostly on individual policies using the URL Filter format, it continues to use Windows' Security Zones by default in a few cases. This approach simplifies deployment in Enterprises that have historically relied upon Zones configuration.
Zone policy controls the following behaviors:
- Deciding whether to release Windows Integrated Authentication (Kerberos or NTLM) credentials automatically.
- Deciding how to handle file downloads.
- For Internet Explorer mode.
Credential release
By default, Microsoft Edge evaluates URLACTION_CREDENTIALS_USE to decide whether Windows Integrated Authentication is used automatically, or if the user will see a manual authentication prompt. Configuring the AuthServerAllowlist site list policy prevents Zone Policy from being consulted.
File downloads
Evidence about the origins of a file download (also known as "Mark of the Web" is recorded for files downloaded from the Internet Zone. Other applications, such as the Windows Shell, and Microsoft Office may take this origin evidence into account when deciding how to handle a file.
If the Windows Security Zone policy is configured to disable the setting for launching applications and download unsafe files, Microsoft Edge's download manager blocks file downloads from sites in that Zone. A user will see this note: "Couldn't download – Blocked".
IE mode
IE mode can be configured to open all Intranet sites in IE mode. When using this configuration, Microsoft Edge evaluates the Zone of a URL when deciding whether or not it should open in IE mode. Beyond this initial decision, IE mode tabs are really running Internet Explorer, and as a result they evaluate Zones settings for every policy decision just as Internet Explorer did.
Summary
In most cases, Microsoft Edge settings can be left at their defaults. Administrators who wish to change the defaults for all sites or specific sites can use the appropriate Group Policies to specify Site Lists or default behaviors. In a handful of cases, such as credential release, file download, and IE mode, admins will continue to control behavior by configuring Windows Security Zones settings.
Frequently asked questions
Can the URL filter format match on a site's IP address?
No, the format doesn't support specifying an IP range for allowlists and blocklists. It does support specification of individual IP literals, but such rules are only respected if the user navigates to the site using said literal (for example, http://127.0.0.1/). If a hostname is used (http://localhost), the IP Literal rule will not be respected even though the resolved IP of the host matches the filter-listed IP.
Can URL filters match dotless host names?
No. You must list each hostname, for example https://payroll, https://stock, https://who, and so on.
If you were forward-thinking enough to structure your intranet such that your host names are of the following form, then you've implemented a best practice.
https://payroll.contoso-intranet.comhttps://timecard.contoso-intranet.comhttps://sharepoint.contoso-intranet.com
In the preceding scenario, you can configure each policy with a *.contoso-intranet.com entry and your entire intranet will be opted in.