URL Compression <urlCompression>
Overview
The <urlCompression> element specifies the following settings for static and dynamic content compression in IIS 7 and later:
- The doDynamicCompression attribute of the
<urlCompression>element enables or disables dynamic content compression at the site, application, or folder level. - The doStaticCompression attribute of the
<urlCompression>element enables or disables static content compression at the site, application, or folder level. - The dynamicCompressionBeforeCache attribute specifies whether IIS will dynamically compress content that has not been cached. When the dynamicCompressionBeforeCache attribute is true, IIS dynamically compresses the response the first time a request is made and queues the content for compression. Subsequent requests are served dynamically until the compressed response has been added to the cache directory. Once the compressed response is added to the cache directory, the cached response is sent to clients for subsequent requests. When dynamicCompressionBeforeCache is false, IIS returns the uncompressed response until the compressed response has been added to the cache directory.
Note
If the dynamicCompressionBeforeCache attribute is true when the output cache response has been flushed, dynamic compression will not be performed before the response is put into the output cache. However, if the doDynamicCompression attribute is true, dynamic compression will still occur after the output cache has been filled with the response.
Compatibility
| Version | Notes |
|---|---|
| IIS 10.0 | The <urlCompression> element was not modified in IIS 10.0. |
| IIS 8.5 | The <urlCompression> element was not modified in IIS 8.5. |
| IIS 8.0 | The <urlCompression> element was not modified in IIS 8.0. |
| IIS 7.5 | In IIS 7.5, the default value of the doDynamicCompression attribute changed from false to true. |
| IIS 7.0 | The <urlCompression> element was introduced in IIS 7.0. |
| IIS 6.0 | The <urlCompression> element replaces the following IIS 6.0 metabase properties:
|
Setup
HTTP compression is usually available on the default installation of IIS 7 and later. However, only static compression is installed by default. To install static or dynamic compression, use the following steps.
Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager.
- In Server Manager, click the Manage menu, and then click Add Roles and Features.
- In the Add Roles and Features wizard, click Next. Select the installation type and click Next. Select the destination server and click Next.
- On the Server Roles page, expand Web Server (IIS), expand Web Server, expand Performance, and then select Static Content Compression and/or Dynamic Content Compression. Click Next.
 .
. - On the Select features page, click Next.
- On the Confirm installation selections page, click Install.
- On the Results page, click Close.
Windows 8 or Windows 8.1
- On the Start screen, move the pointer all the way to the lower left corner, right-click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows features on or off.
- Expand Internet Information Services, expand World Wide Web Services, expand Performance Features, and then select Dynamic Content Compression and/or Static Content Compression.

- Click OK.
- Click Close.
Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Server Manager.
- In the Server Manager hierarchy pane, expand Roles, and then click Web Server (IIS).
- In the Web Server (IIS) pane, scroll to the Role Services section, and then click Add Role Services.
- On the Select Role Services page of the Add Role Services Wizard, select Dynamic Content Compression if you want to install dynamic compression and Static Content Compression if you want to install static compression, and then click Next.

- On the Confirm Installation Selections page, click Install.
- On the Results page, click Close.
Windows Vista or Windows 7
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows Features on or off.
- Expand Internet Information Services, then World Wide Web Services, then Performance Features.
- Select Http Compression Dynamic if you want to install dynamic compression and Static Content Compression if you want to install static compression.

- Click OK.
How To
How to enable or disable static and dynamic compression for a site or application
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, go to the connection, site, application, or directory for which you want to enable compression.
In the Home pane, double-click Compression.

In the Compression pane, check the boxes to enable static or dynamic compression, or remove the check marks to disable static or dynamic compression.

Once you have completed the above steps, click Apply in the Actions pane.
How to enable or disable static and dynamic compression for a server
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, highlight the name of your server.
In the server's Home pane, double-click Compression.
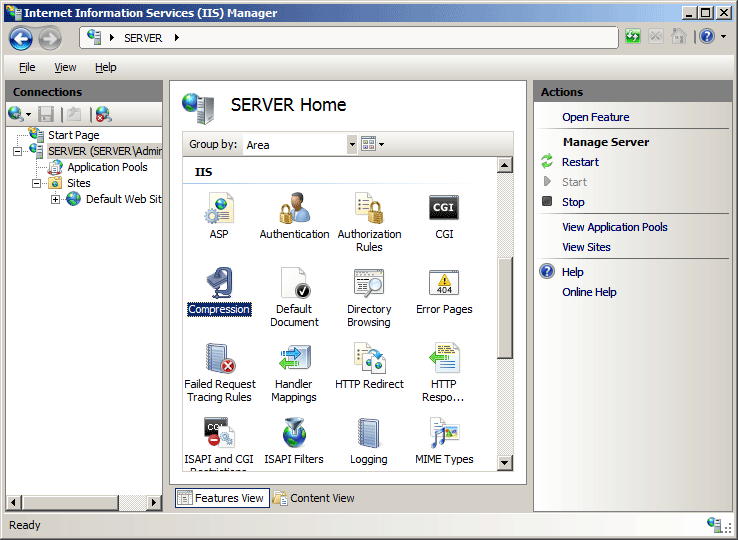
In the Compression pane, check the boxes to enable static or dynamic compression, or remove the check marks to disable static or dynamic compression.
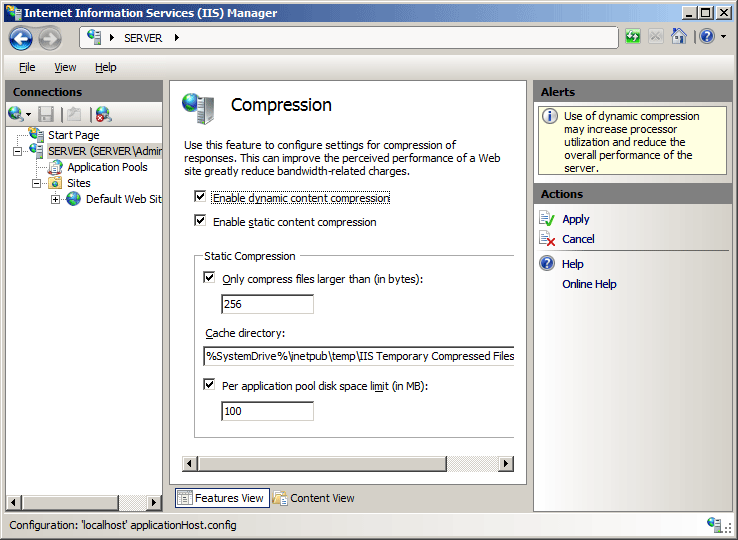
Once you have completed the above steps, click Apply in the Actions pane.
How to configure staticCompressionIgnoreHitFrequency
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, select the server, and then double-click Configuration Editor.
In the Configuration Editor, for the section, select system.webServer, and then select httpCompression.
For staticCompressionIgnoreHitFrequency, enter
Trueto disable the behavior that a static file is compressed only if it is hit a certain number of times within a time period, or enterFalseto enable the behavior.

In the Actions pane, click Apply.
Configuration
Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
doDynamicCompression |
Optional Boolean attribute. Specifies whether dynamic compression is enabled for URLs. Note: In IIS 7.0, the use of dynamic compression was disabled by default because of increased processor utilization that may have reduced the overall performance of the Web server. In IIS 7.5, changes were made to dynamic compression that resulted in better performance, so dynamic compression is enabled by default in IIS 7.5 and later. The default value is true. |
doStaticCompression |
Optional Boolean attribute. Specifies whether static compression is enabled for URLs. The default value is true. |
dynamicCompressionBeforeCache |
Optional Boolean attribute. Specifies whether the currently available response is dynamically compressed before it is put into the output cache. The default value is false. |
Child Elements
None.
Configuration Sample
The following configuration sample enables static compression and disable dynamic compression for the Default Web Site.
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<urlCompression doStaticCompression="true" doDynamicCompression="false" />
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
Sample Code
The following code samples enable static compression and disable dynamic compression for the Default Web Site.
AppCmd.exe
appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" -section:system.webServer/urlCompression /doDynamicCompression:"False"
appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" -section:system.webServer/urlCompression /doStaticCompression:"True"
C#
using System;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.Web.Administration;
internal static class Sample
{
private static void Main()
{
using (ServerManager serverManager = new ServerManager())
{
Configuration config = serverManager.GetWebConfiguration("Default Web Site");
ConfigurationSection urlCompressionSection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/urlCompression");
urlCompressionSection["doStaticCompression"] = true;
urlCompressionSection["doDynamicCompression"] = false;
serverManager.CommitChanges();
}
}
}
VB.NET
Imports System
Imports System.Text
Imports Microsoft.Web.Administration
Module Sample
Sub Main()
Dim serverManager As ServerManager = New ServerManager
Dim config As Configuration = serverManager.GetWebConfiguration("Default Web Site")
Dim urlCompressionSection As ConfigurationSection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/urlCompression")
urlCompressionSection("doStaticCompression") = True
urlCompressionSection("doDynamicCompression") = False
serverManager.CommitChanges()
End Sub
End Module
JavaScript
var adminManager = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager');
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST/Default Web Site";
var urlCompressionSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.webServer/urlCompression", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST/Default Web Site");
urlCompressionSection.Properties.Item("doStaticCompression").Value = true;
urlCompressionSection.Properties.Item("doDynamicCompression").Value = false;
adminManager.CommitChanges();
VBScript
Set adminManager = WScript.CreateObject("Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager")
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST/Default Web Site"
Set urlCompressionSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.webServer/urlCompression", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST/Default Web Site")
urlCompressionSection.Properties.Item("doStaticCompression").Value = True
urlCompressionSection.Properties.Item("doDynamicCompression").Value = False
adminManager.CommitChanges()