Getting Started with SSMA for MySQL (MySQLToSQL)
SQL Server Migration Assistant (SSMA) for MySQL lets you quickly convert MySQL database schemas to SQL Server or Azure SQL Database schemas, upload the resulting schemas into SQL Server or Azure SQL Database, and migrate data from MySQL to SQL Server or Azure SQL Database.
This topic introduces the installation process, and then helps familiarize you with the SSMA user interface.
Installing SSMA
To use SSMA, you first must install the SSMA client program on a computer that can access both the source MySQL database and the target instance of SQL Server or Azure SQL Database. Then, install the MySQL providers (MySQL ODBC 5.1 Driver (trusted)) on the computer that is running SSMA Client Program. For installation instructions, see Installing SSMA for MySQL (MySQLToSQL)
To start SSMA, click Start, point to All Programs, point to SQL Server Migration Assistant for MySQL, and then click SQL Server Migration Assistant for MySQL.
SSMA for MySQL User Interface
After SSMA is installed and licensed, you can use SSMA to migrate MySQL databases to SQL Server or Azure SQL Database. It helps to become familiar with the SSMA user interface before you start. The following diagram shows the user interface for SSMA, including the metadata explorers, metadata, toolbars, output pane, and error list pane:
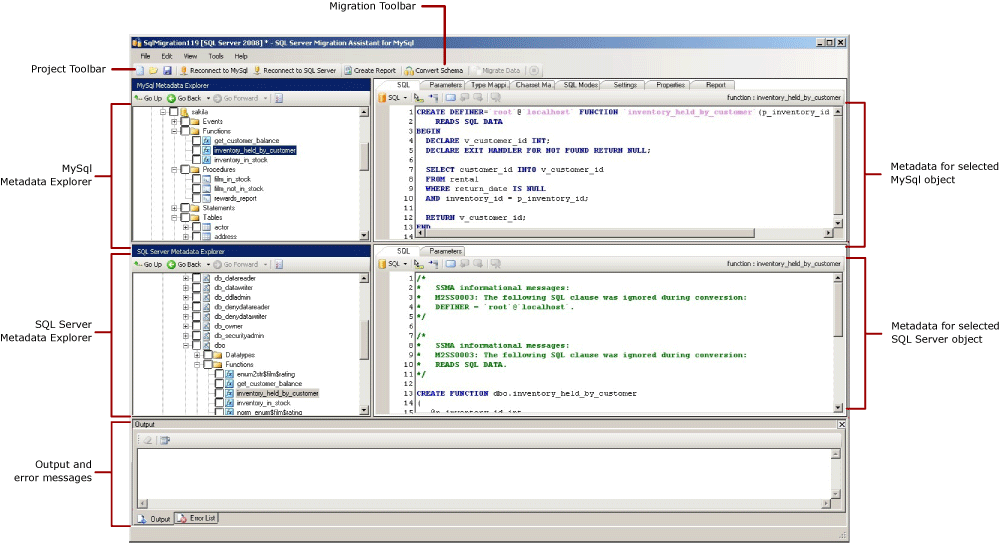
To start a migration, you must:
Create a new project.
Connect to a MySQL database.
After a successful connection, MySQL schemas will appear in MySQL Metadata Explorer. Right-click objects in MySQL Metadata Explorer to perform tasks such as create reports that assess conversions to SQL Server/Azure SQL Database.
You can also perform these tasks by using the toolbars and menus.
You must also connect to an instance of SQL Server. After a successful connection, a hierarchy of SQL Server databases will appear in SQL Server Metadata Explorer. After you convert MySQL schemas to SQL Server schemas, select those converted schemas in SQL Server Metadata Explorer, and then synchronize the schemas with SQL Server.
You must connect to Azure SQL Database if you have selected Azure SQL Database from the Migrate to dropdown in new project dialog box. After a successful connection, a hierarchy of Azure SQL Database databases will appear in Azure SQL Database Metadata Explorer. After you convert MySQL schemas to Azure SQL Database schemas, select those converted schemas in Azure SQL Database Metadata Explorer, and then synchronize the schemas with Azure SQL Database.
After you synchronize converted schemas with SQL Server or Azure SQL Database, you can return to MySQL Metadata Explorer and migrate data from MySQL schemas into SQL Server or Azure SQL Database databases.
For more information about these tasks and how to perform them, see Migrating MySQL Databases to SQL Server - Azure SQL Database (MySQLToSQL).
The following sections describe the features of the SSMA user interface.
Metadata Explorers
SSMA contains two metadata explorers to browse and perform actions on MySQL and SQL Server databases.
MySQL Metadata Explorer
MySQL Metadata Explorer shows information about MySQL schemas. By using MySQL Metadata Explorer, you can perform the following tasks:
Browse the objects in each schema.
Select objects for conversion, and then convert the objects to SQL Server syntax. For more information, see Converting MySQL Databases (MySQLToSQL)
Select tables for data migration, and then migrate the data from those tables to SQL Server. For more information, see Migrating MySQL Data into SQL Server - Azure SQL Database (MySQLToSQL)
SQL Server or Azure SQL Database Metadata Explorer
SQL Server or Azure SQL Database Metadata Explorer shows information about an instance of SQL Server or Azure SQL Database. When you connect to an instance of SQL Server or Azure SQL Database, SSMA retrieves metadata about that instance and stores it in the project file.
You can use this Metadata Explorer to select converted MySQL database objects, and then synchronize those objects with the instance of SQL Server or Azure SQL Database.
For more information, see Synchronization (MySQL to SQL Server / Azure SQL Database)
Metadata
To the right of each metadata explorer are tabs that describe the selected object. For example, if you select a table in MySQL Metadata Explorer, nine tabs will appear: Table, SQL, Type Mapping, Data, Settings, Charset Mapping, SQL Modes, Properties, and Report. The Report tab contains information only after you create a report that contains the selected object. If you select a table in SQL Server Metadata Explorer, three tabs will appear: Table, SQL and Data.
Most metadata settings are read-only. However, you can alter the following metadata:
In MySQL Metadata Explorer, you can alter type mappings, Charset Mapping, SQL Modes. To convert the altered type mappings or Charset Mapping or SQL Modes, make changes before you convert schemas.
In SQL Server Metadata Explorer, you can alter the table and index properties on the Table tab. To see these changes in SQL Server, make these changes before you load the schemas into SQL Server.
Changes made in a metadata explorer are reflected in the project metadata, not in the source or target databases.
Toolbars
SSMA has two toolbars: a project toolbar and a migration toolbar.
The Project Toolbar
The project toolbar contains buttons for working with projects, connecting to MySQL, and connecting to SQL Server or Azure SQL Database. These buttons resemble the commands on the File menu.
Migration Toolbar
The following table shows the migration toolbar commands:
| Button | Function |
|---|---|
| Create Report | Converts the selected MySQL objects to SQL Server or Azure SQL Database objects, and then creates a report that shows how successful the conversion was. This command is disabled unless objects are selected in MySQL Metadata Explorer. |
| Convert Schema | Converts the selected MySQL objects to SQL Server or Azure SQL Database objects. This command is disabled unless objects are selected in MySQL Metadata Explorer. |
| Migrate Data | Migrates data from the MySQL database to SQL Server or Azure SQL Database. Before you run this command, you must convert the MySQL schemas to SQL Server or Azure SQL Database schemas, and then load the objects into SQL Server or Azure SQL Database. This command is disabled unless objects are selected in MySQL Metadata Explorer. |
| Stop | Stops the current process. |
Menus
The following table shows the SSMA menus.
| Menu | Description |
|---|---|
| File | Contains commands for working with projects, connecting to MySQL, and connecting to SQL Server or Azure SQL Database. |
| Edit | Contains commands for finding and working with text in the details pages. To open Manage Bookmarks dialog, on the Edit menu click Manage Bookmarks. In the dialog you will see a list of existing bookmarks. You can use the buttons on the right side of the dialog to manage the bookmarks. |
| View | Contains the Synchronize Metadata Explorers command. That synchronizes the objects between MySQL Metadata Explorer and SQL Server or Azure SQL Database Metadata Explorer. Also contains commands to show and hide the Output and Error List panes and an option Layouts to manage with the Layouts. |
| Tools | Contains commands to create reports, convert schema, refresh from database, migrate objects and data, and Save as Script. Also provides access to the Global Settings, Default Project Settings and Project Settings dialog boxes. |
| Help | Provides access to SSMA Help and to the About dialog box. |
Output Pane and Error List Pane
The View menu provides commands to toggle the visibility of the Output pane and the Error List pane:
The Output pane shows status messages from SSMA during object conversion, object synchronization, and data migration.
The Error List pane shows error, warning, and informational messages in a sortable list.
See Also
User Interface Reference (MySQLToSQL)
Migrating MySQL Data into SQL Server - Azure SQL Database (MySQLToSQL)