MultiPoint Stations
In a MultiPoint Services system environment, stations are the user endpoints for connecting to the computer running MultiPoint Services. Each station provides the user with an independent Windows 10 experience. The following station types are supported:
Direct-video-connected stations
USB-zero-client-connected stations (including USB-over-Ethernet zero clients)
RDP-over-LAN-connected stations (for rich client or thin client computers)
Full PCs that have the MultiPoint Connector installed can also be monitored and controlled using the MultiPoint Dashboard. On Windows 10 the MultiPoint Connector can be enabled through the control panel for Windows features.
Multipoint Services supports any combination of these station types, but it is recommended that one station be a direct-video-connected station, which can serve as the primary station. The reason for this recommendation is to be able to anticipate support scenarios. For example, to interact with the system's BIOS before MultiPoint Services is running.
Primary stations and standard stations
One direct-video-connected station is defined as the primary station. The remaining stations are referred to as standard stations.
The primary station displays the startup screens when the computer is turned on. It provides access to system configuration and troubleshooting information that is only available during startup. The primary station must be a direct-video-connected station. After startup, you can use the primary station like any other MultiPoint station.
Direct-video-connected stations
The computer running MultiPoint Services can contain multiple video cards, each of which can have one or more video ports. This allows you to plug monitors for multiple stations directly into the computer. Keyboards and mice are connected through USB hubs that are associated with each monitor. These hubs are referred to as station hubs. Other peripheral devices, such as speakers, headphones, or USB storage devices can also be connected to a station hub, and they are available only to the user of that station.
Important
There should be at least one direct-video-connected station per server to act as the primary station to display the startup process when the computer is turned on.
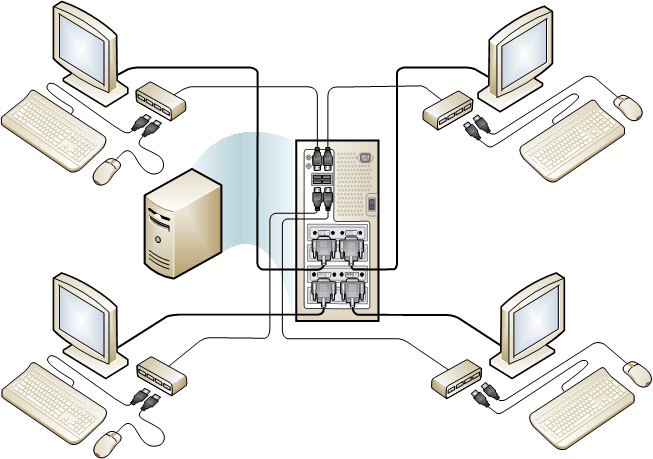
Figure 1 MultiPoint services system with four direct-video-connected stations
PS/2 stations
With MultiPoint Services, you can map the PS/2 keyboard and mouse on the motherboard to a direct video connected monitor to create a PS/2 station. High-definition analog audio on the motherboard is the audio associated with this type of station. This does not apply to computers where there are no PS/2 jacks on the motherboard.
USB-zero-client-connected stations
USB-zero-client-connected stations utilize a USB zero client as a station hub. USB zero clients are sometimes referred to as a multifunction hub with video. They are a hub that connects to the computer through a USB cable, and these hubs typically support a video monitor, a mouse and keyboard (PS/2 or USB), audio, and additional USB devices. This guide refers to these specialized hubs as USB zero clients.
The following diagram shows a MultiPoint server system with a primary station (direct video connected station) and two additional USB zero client connected stations.
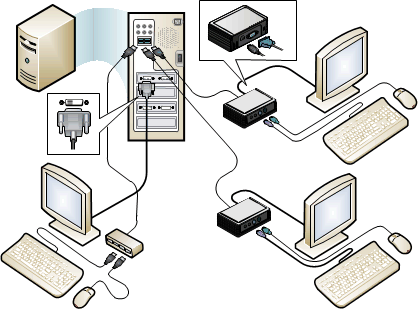
Figure 2 MultiPoint Services system with a primary station and two USB zero-client-connected stations
USB-over-Ethernet zero clients
USB-over-Ethernet zero clients are a variation of USB zero clients that send USB over LAN to the MultiPoint Services system. These types of USB zero clients function similarly to other USB zero clients, but are not limited by USB cable length maximums. USB-over-Ethernet zero clients are not traditional thin clients, and they appear as virtual USB devices on the MultiPoint Services system. When using these devices, refer to the device manufacturer for specific performance and site planning recommendations. Most devices have a third-party plugin for MultiPoint Manager that allows you to associate and connect devices to the MultiPoint Services system.
RDP-over-LAN connected stations
Thin clients and traditional desktop, laptop, or tablet computers, can connect to the computer running MultiPoint Services through the local area network (LAN) by using Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) or a proprietary protocol and the Remote Desktop Protocol Provider. RDP connections provide an end-user experience that is very similar to any other MultiPoint station, but makes use of the local client computer's hardware. Learn more about our remote desktop applications available for Android, iOS, Mac and Windows in Remote Desktop clients.
Clients and devices that are running Microsoft RemoteFX can provide a rich multimedia experience by taking advantage of the processor and video hardware capabilities of the local thin client or computer to provide high-definition video over the network.
If you have existing LAN clients MultiPoint Services can provide a quick and cost effective way to simultaneously upgrade all of your users to a Windows 10 experience.
From a deployment and administration perspective, the following differences exist when you use RDP-over-LAN-connected stations:
Not limited to physical USB connection distances
Potential to reuse older computer hardware as stations
Easier to scale to a higher number of stations. Any client on your network can potentially be used as a remote station
No hardware troubleshooting through the MultiPoint Manager console
No split-screen functionality.
For more information, see Split-screen Stations later in this topic
No station rename or configuring automatic logon through the MultiPoint Manager console
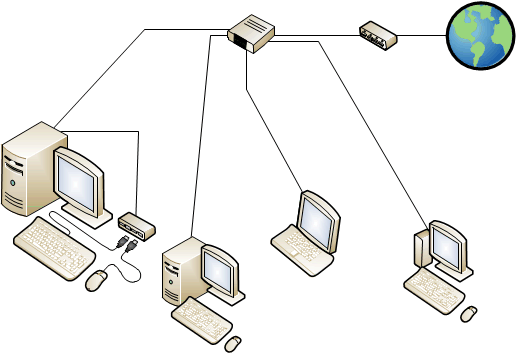
Figure 3 MultiPoint Services system with RDP-over-LAN-connected stations
Additional configuration options
Split-screen stations
MultiPoint Services offers a split screen option on computers with direct-video-connected stations or USB-zero-client-connected stations. A split screen provides the ability to create an additional station per monitor. Instead of requiring two monitors, you can use one monitor with two station hub setups to create two stations with one monitor. You can quickly increase the number of available stations without purchasing additional monitors, USB-zero clients, or video cards.
The benefits of using a split-screen station can include:
Reducing cost and space by accommodating more users on a MultiPoint Services system.
Allowing two users to collaborate side-by-side on a project.
Allowing a teacher to demonstrate a procedure on one station while a student follows along on the other station.
Any MultiPoint Services station monitor that has a 1024x768 resolution or greater can be split into two station screens. For the best split screen user experience, a wide screen with a minimum 1600x900 resolution is recommended. A mini keyboard without a number pad is also recommended to allow the two keyboards to fit in front of the monitor.
To create split-screen stations, you set up one direct-video-connected or USB-zero-client-connected station. Then you add an additional station hub by plugging in a keyboard and mouse to a USB hub that is connected to the server. You can then convert the station into two stations by using MultiPoint Manager to split the screen and map the new hub to half of the monitor. The left half of the screen becomes one station and the right half becomes a second station.
After a station is split, one user can log on to the left station while another user logs on to the right station.
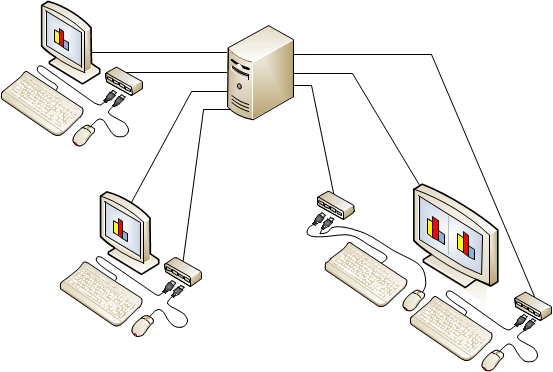
Figure 4 MultiPoint Services system with split screen stations
Station type comparison
| Description | Direct Video Connected | USB Zero Client Connected | RDP-over-LAN Connected |
|---|---|---|---|
| Video performance | Recommended for best video performance | Use thin clients that support RemoteFX for improved video quality at lower network bandwidth | |
| Physical limitations | Limited by video cable length and USB hub and cable length (Recommended 15 meter maximum length) | Limited by USB hub and cable length (Recommended 15 meter maximum length) | Limited by LAN distribution |
| Number of stations allowed | Limited by number of available PCIe slots on the motherboard times the video ports per video card | Total number may be limited by USB zero client manufacturer (For more information, see the Note that follows this table.) | Limited by available ports on network switch |
| Split-screen | Yes | Yes | No |
| MultiPoint Manager station peripheral status, auto-logon configuration, station renaming | Yes | Yes | No |
| Access to server startup menus | Yes | No | No |
Note
The total number of USB zero clients that are connected to the server may be limited by the manufacturer or the hardware capability of the computer running MultiPoint Services.