Bemærk
Adgang til denne side kræver godkendelse. Du kan prøve at logge på eller ændre mapper.
Adgang til denne side kræver godkendelse. Du kan prøve at ændre mapper.
In this tutorial, you add an OpenTelemetry collector as a sidecar container to a Linux (bring-your-own-code) app in Azure App Service. For custom containers, see Tutorial: Configure a sidecar container for custom container in Azure App Service.
If you don't have an Azure account, create a free account before you begin.
Sidecar containers in App Service let you deploy extra services and features to your Linux apps without tightly coupling them to the built-in or custom main container. The sidecar containers run alongside the main application container in the same App Service plan.
You can add up to nine sidecar containers for each Linux app in App Service. For example, you can add monitoring, logging, configuration, and networking services as sidecar containers. An OpenTelemetry collector sidecar is one example for monitoring.
1. Set up the needed resources
First you create the resources that the tutorial uses. They're used for this particular scenario and aren't required for sidecar containers in general.
In the Azure Cloud Shell, run the following commands. Be sure to supply the
<environment-name>.git clone https://github.com/Azure-Samples/app-service-sidecar-tutorial-prereqs cd app-service-sidecar-tutorial-prereqs azd env new <environment-name> azd provisionWhen prompted, supply the subscription and region of your choice. For example:
- Subscription: Your subscription.
- Region: (Europe) West Europe.
When deployment completes, you should see the following output:
APPLICATIONINSIGHTS_CONNECTION_STRING = InstrumentationKey=...;IngestionEndpoint=...;LiveEndpoint=... Azure container registry name = <registry-name> Managed identity resource ID = <managed-identity-resource-id> Managed identity client ID = <managed-identity-client-id> Open resource group in the portal: https://portal.azure.com/#@/resource/subscriptions/<subscription-id>/resourceGroups/<group-name>
Copy these output values for later. You can also find them in the portal, in the management pages of the respective resources.
Note
azd provisionuses the included templates to create the following Azure resources:- A resource group based on the environment name.
- A container registry with two images deployed:
- An Nginx image with the OpenTelemetry module.
- An OpenTelemetry collector image, configured to export to Azure Monitor.
- A user-assigned managed identity with the
AcrPullpermission on the resource group (to pull images from the registry). - A log analytics workspace.
- An Application Insights component.
2. Create a web app
In this step, you deploy a template ASP.NET Core application. Back in the Azure Cloud Shell, run the following commands. Replace <app-name> with a unique app name.
cd ~
dotnet new webapp -n MyFirstAzureWebApp --framework net8.0
cd MyFirstAzureWebApp
az webapp up --name <app-name> --os-type linux
After a few minutes, this .NET web application is deployed as MyFirstAzureWebApp.dll to a new App Service app.
3. Add a sidecar container
In this section, you add a sidecar container to your Linux app.
In the Azure portal, navigate to the app's management page
In the app's management page, from the left menu, select Deployment Center.
Select the banner Interested in adding containers to run alongside your app? Click here to give it a try.
When the page reloads, select the Containers (new) tab.
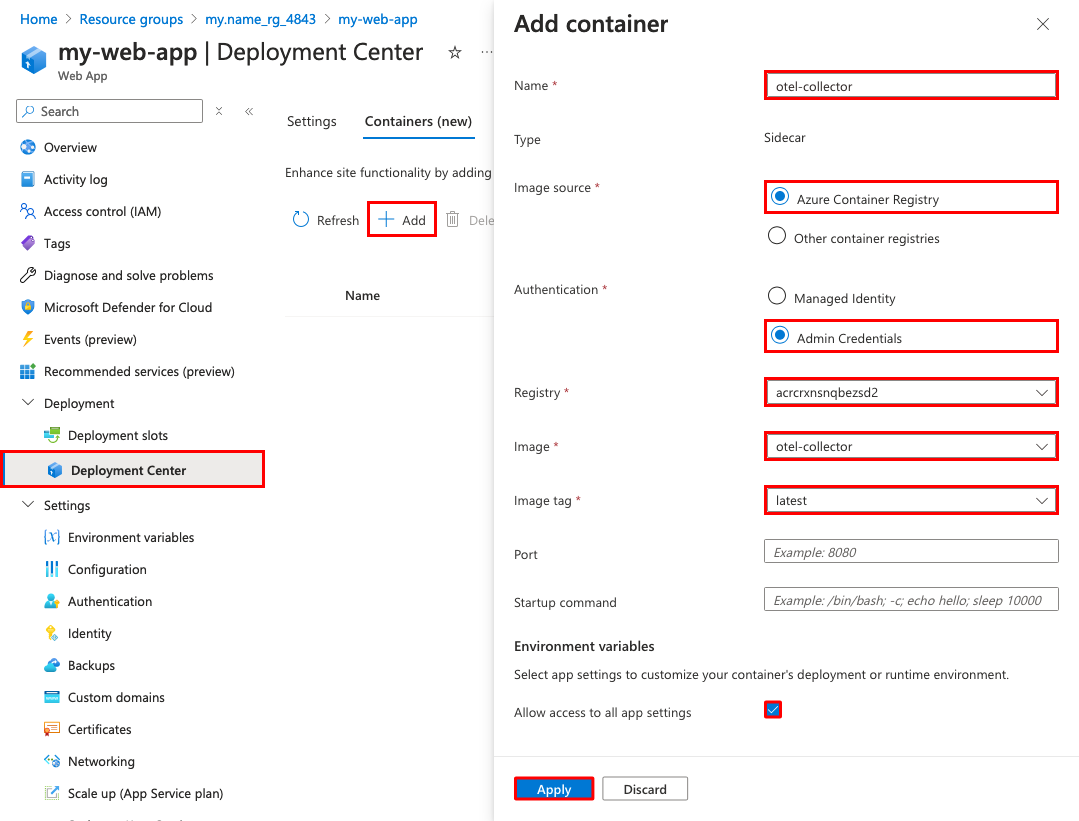
Select Add and configure the new container as follows:
- Name: otel-collector
- Image source: Azure Container Registry
- Authentication: Admin Credentials
- Registry: The registry created by
azd provision - Image: otel-collector
- Tag: latest
Select Apply.
4. Configure environment variables
For the sample scenario, the otel-collector sidecar is configured to export the OpenTelemetry data to Azure Monitor, but it needs the connection string as an environment variable (see the OpenTelemetry configuration file for the otel-collector image).
You configure environment variables for the containers like any App Service app, by configuring app settings. The app settings are accessible to all the containers in the app.
Navigate to the App Service app's management page.
From the left menu, select Environment variables.
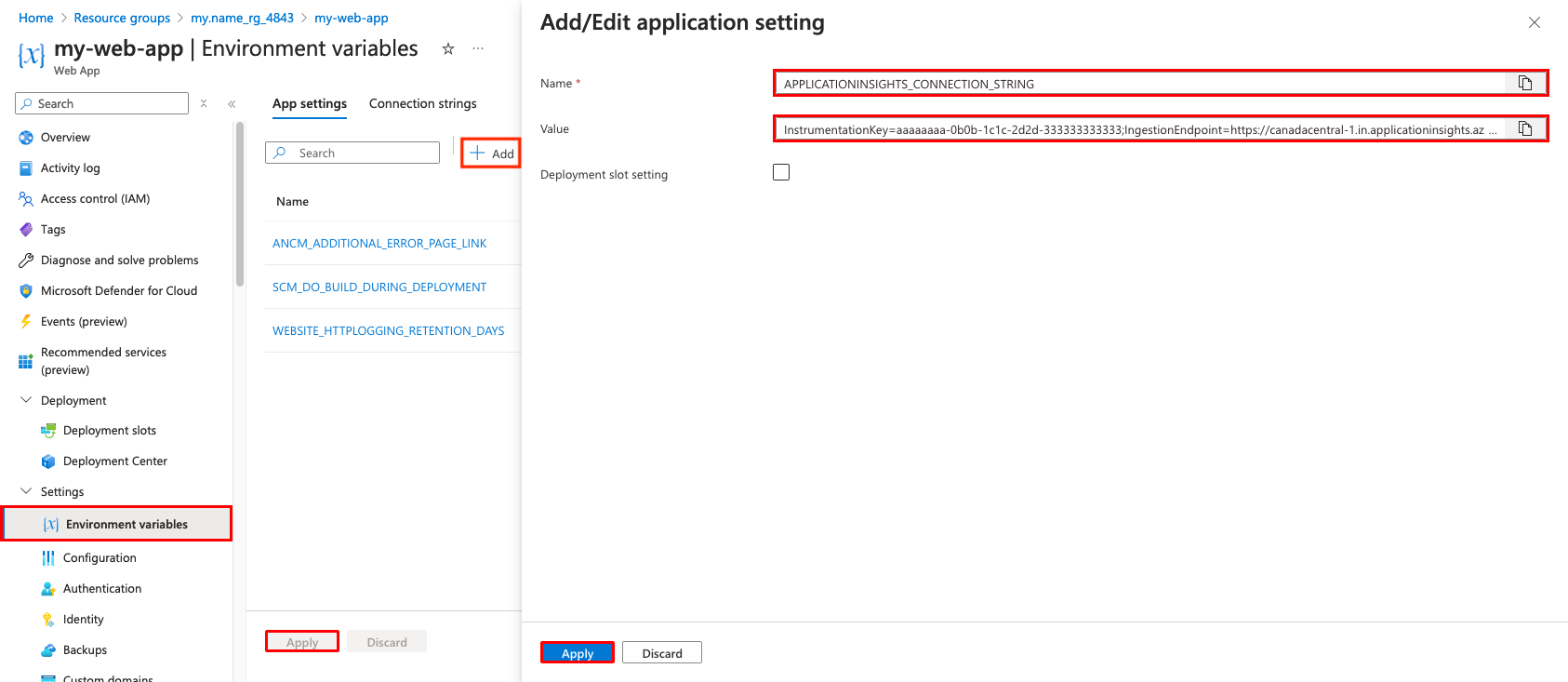
Add an app setting by selecting Add and configure it as follows:
- Name: APPLICATIONINSIGHTS_CONNECTION_STRING
- Value: The connection string in the output of
azd provision. If you lost the Cloud Shell session, you can also find it in the Overview page of the Application Insight resource, under Connection String.
Select Apply, then Apply, then Confirm.
5. Configure instrumentation at startup
In this step, you create the instrumentation for your app according to the steps outlined in the OpenTelemetry .NET zero-code instrumentation.
Back in the Cloud Shell, create startup.sh with the following lines.
cat > startup.sh << 'EOF' #!/bin/bash # Download the bash script curl -sSfL https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-dotnet-instrumentation/releases/latest/download/otel-dotnet-auto-install.sh -O # Install core files sh ./otel-dotnet-auto-install.sh # Enable execution for the instrumentation script chmod +x $HOME/.otel-dotnet-auto/instrument.sh # Setup the instrumentation for the current shell session . $HOME/.otel-dotnet-auto/instrument.sh export OTEL_SERVICE_NAME="MyFirstAzureWebApp-Azure" export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT="http://localhost:4318" export OTEL_TRACES_EXPORTER="otlp" export OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER="otlp" export OTEL_LOGS_EXPORTER="otlp" # Run your application with instrumentation OTEL_SERVICE_NAME=myapp OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES=deployment.environment=staging,service.version=1.0.0 dotnet /home/site/wwwroot/MyFirstAzureWebApp.dll EOFDeploy this file to your app with the following Azure CLI command. If you're still in the ~/MyFirstAzureWebApp directory, then no other parameters are necessary because
az webapp upalready set defaults for the resource group and the app name.az webapp deploy --src-path startup.sh --target-path /home/site/startup.sh --type staticTip
This approach deploys the startup.sh file separately from your application. That way, the instrumentation configuration is separate from your application code. However, you can use other deployment methods to deploy the script together with your application.
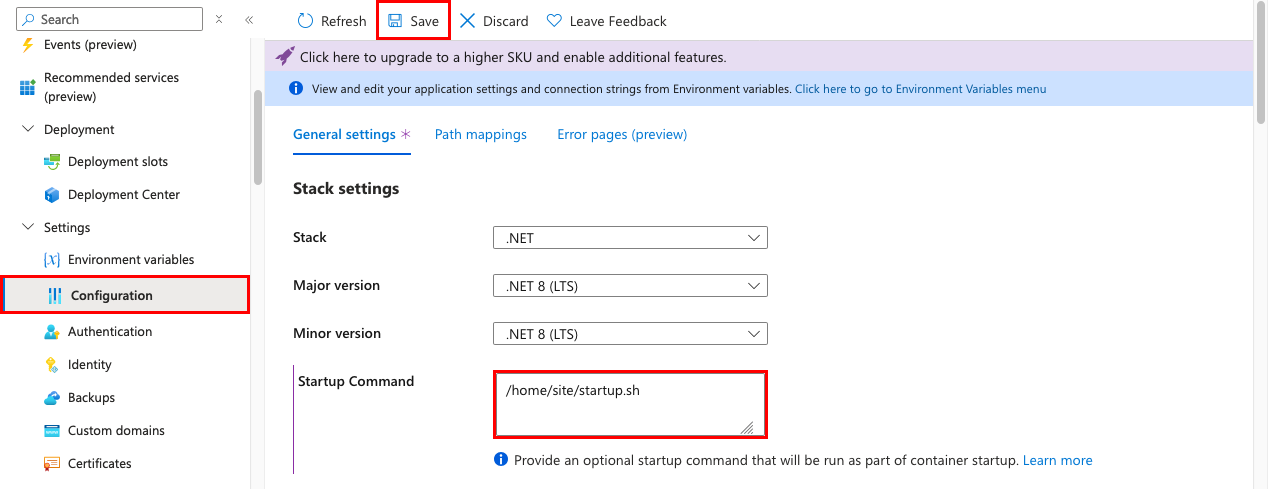
Back in the app's management page, from the left menu, select Configuration.
Set Startup Command to /home/site/startup.sh. It's the same path that you deployed to in the previous step.
Select Save, then Continue.
5. Verify in Application Insights
The otel-collector sidecar should export data to Application Insights now.
Back in the browser tab for
https://<app-name>.azurewebsites.net, refresh the page a few times to generate some web requests.Go back to the resource group overview page, then select the Application Insights resource that
azd upcreated. You should now see some data in the default charts.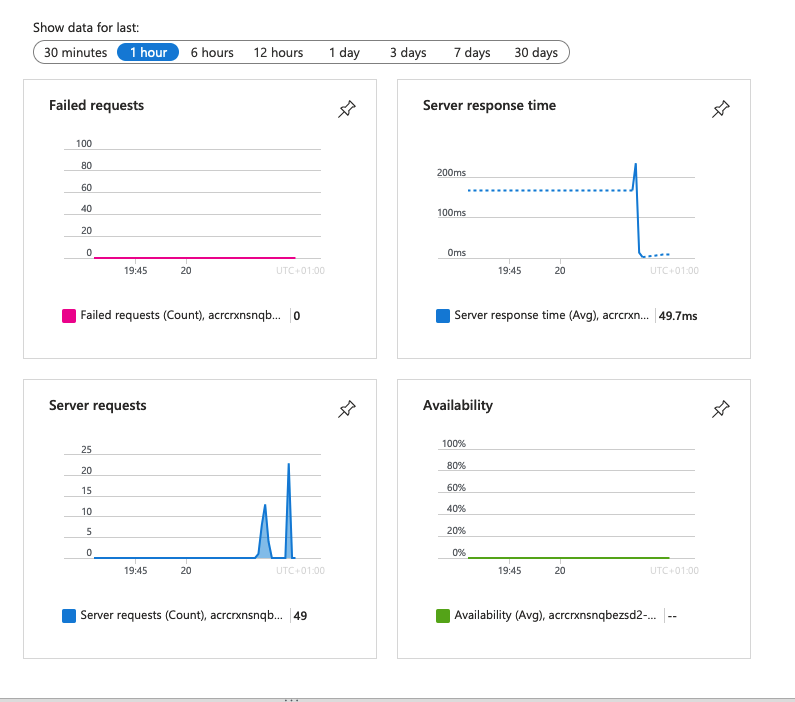
Note
In this very common monitoring scenario, Application Insights is just one of the OpenTelemetry targets you can use, such as Jaeger, Prometheus, and Zipkin.
6. Clean up resources
When you no longer need the environment, you can delete the resource groups and all related resources. Just run these commands in the Cloud Shell:
cd ~/MyFirstAzureWebApp
az group delete --yes
cd ~/app-service-sidecar-tutorial-prereqs
azd down