Connect hybrid machines to Azure at scale
You can enable Azure Arc-enabled servers for multiple Windows or Linux machines in your environment with several flexible options depending on your requirements. Using the template script we provide, you can automate every step of the installation, including establishing the connection to Azure Arc. However, you are required to execute this script manually with an account that has elevated permissions on the target machine and in Azure.
One method to connect the machines to Azure Arc-enabled servers is to use a Microsoft Entra service principal. This service principal method can be used instead of your privileged identity to interactively connect the machine. This service principal is a special limited management identity that has only the minimum permission necessary to connect machines to Azure using the azcmagent command. This method is safer than using a higher privileged account like a Tenant Administrator and follows our access control security best practices. The service principal is used only during onboarding; it is not used for any other purpose.
Before you start connecting your machines, review the following requirements:
Make sure you have administrator permission on the machines you want to onboard.
Administrator permissions are required to install the Connected Machine agent on the machines; on Linux by using the root account, and on Windows as a member of the Local Administrators group.
Review the prerequisites and verify that your subscription and resources meet the requirements. You will need to have the Azure Connected Machine Onboarding role or the Contributor role for the resource group of the machine. Make sure to register the below Azure resource providers beforehand in your target subscription.
- Microsoft.HybridCompute
- Microsoft.GuestConfiguration
- Microsoft.HybridConnectivity
- Microsoft.AzureArcData (if you plan to Arc-enable SQL Server instances)
See detailed how to here: Azure resource providers prerequisites
For information about supported regions and other related considerations, see supported Azure regions. Also review our at-scale planning guide to understand the design and deployment criteria, as well as our management and monitoring recommendations.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Automatic connection for SQL Server
When you connect a Windows or Linux server to Azure Arc that also has Microsoft SQL Server installed, the SQL Server instances will automatically be connected to Azure Arc as well. SQL Server enabled by Azure Arc provides a detailed inventory and additional management capabilities for your SQL Server instances and databases. As part of the connection process, an extension is deployed to your Azure Arc-enabled server and new roles will be applied to your SQL Server and databases. If you don't want to automatically connect your SQL Servers to Azure Arc, you can opt out by adding a tag to the Windows or Linux server with the name ArcSQLServerExtensionDeployment and value Disabled when it's connected to Azure Arc.
For more information, see Manage automatic connection for SQL Server enabled by Azure Arc.
Create a service principal for onboarding at scale
You can create a service principal in the Azure portal or by using Azure PowerShell.
Note
To create a service principal, your Microsoft Entra tenant needs to allow users to register applications. If it does not, your account must be a member of the Application Administrator or Cloud Application Administrator administrative role. See Delegate app registration permissions in Microsoft Entra ID for more information about tenant-level requirements. To assign Arc-enabled server roles, your account must be a member of the Owner or User Access Administrator role in the subscription that you want to use for onboarding.
Azure portal
The Azure Arc service in the Azure portal provides a streamlined way to create a service principal that can be used to connect your hybrid machines to Azure.
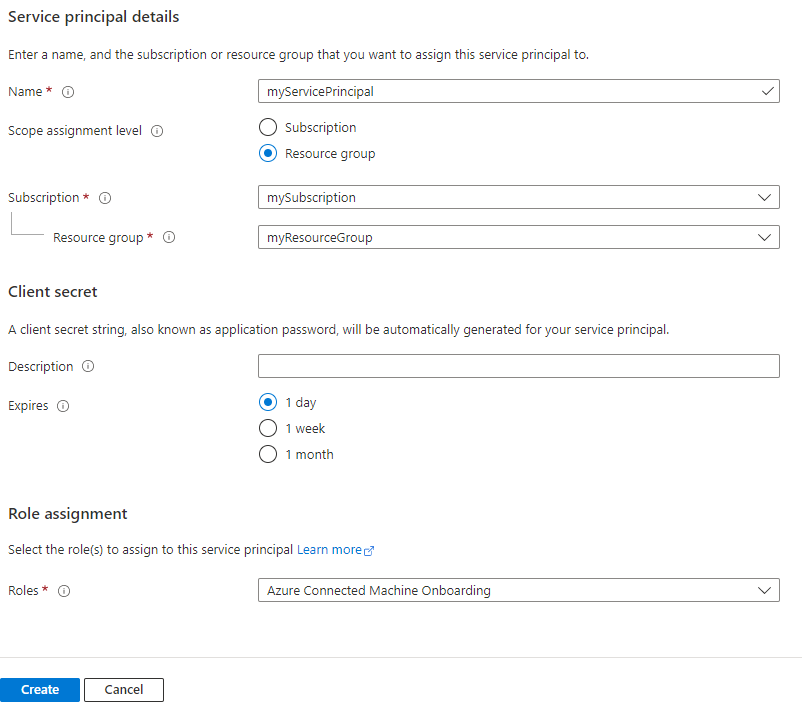
- In the Azure portal, navigate to Azure Arc, then select Service principals in the left menu.
- Select Add.
- Enter a name for your service principal.
- Choose whether the service principal will have access to an entire subscription, or only to a specific resource group.
- Select the subscription (and resource group, if applicable) to which the service principal will have access.
- In the Client secret section, select the duration for which your generated client secret will be in use. You can optionally enter a friendly name of your choice in the Description field.
- In the Role assignment section, select Azure Connected Machine Onboarding.
- Select Create.
Azure PowerShell
You can use Azure PowerShell to create a service principal with the New-AzADServicePrincipal cmdlet.
Check the context of your Azure PowerShell session to ensure you're working in the correct subscription. Use Set-AzContext if you need to change the subscription.
Get-AzContextRun the following command to create a service principal and assign it the Azure Connected Machine Onboarding role for the selected subscription. After the service principal is created, it will print the application ID and secret. The secret is valid for 1 year, after which you'll need to generate a new secret and update any scripts with the new secret.
$sp = New-AzADServicePrincipal -DisplayName "Arc server onboarding account" -Role "Azure Connected Machine Onboarding" $sp | Format-Table AppId, @{ Name = "Secret"; Expression = { $_.PasswordCredentials.SecretText }}AppId Secret ----- ------ aaaaaaaa-bbbb-cccc-dddd-eeeeeeeeeeee PASSWORD_SHOWN_HEREThe values from the following properties are used with parameters passed to the
azcmagent:- The value from the AppId property is used for the
--service-principal-idparameter value - The value from the Secret property is used for the
--service-principal-secretparameter used to connect the agent.
- The value from the AppId property is used for the
Generate the installation script from the Azure portal
Use the Azure portal to create a script that automates the agent download and installation and establishes the connection with Azure Arc. To complete the process, do the following steps:
From your browser, go to the Azure portal.
On the Machines - Azure Arc page, select Add/Create at the upper left, then select Add a machine from the drop-down menu.
On the Add servers with Azure Arc page, select the Add multiple servers tile, and then select Generate script.
On the Basics page, provide the following:
- Select the Subscription and Resource group for the machines.
- In the Region drop-down list, select the Azure region to store the servers' metadata.
- In the Operating system drop-down list, select the operating system that the script is configured to run on.
- For Connectivity method, choose how the Azure Connected Machine agent should connect to the internet:
- Public endpoint
- Proxy server—Enter the proxy server IP address or the name and port number that the machine will use in the format
http://<proxyURL>:<proxyport>. - Private endpoint—Select an existing private link scope and endpoint or create a new one.
- Select Next.
- In the Authentication section, under the Service principal drop-down list, select Arc-for-servers. Then select, Next.
On the Tags page, review the default Physical location tags suggested and enter a value, or specify one or more Custom tags to support your standards.
Select Next.
On the Download and run script page, review the summary information, and then select Download. If you still need to make changes, select Previous.
For Windows, you are prompted to save OnboardingScript.ps1, and for Linux OnboardingScript.sh to your computer.
Install the agent and connect to Azure
Taking the script template created earlier, you can install and configure the Connected Machine agent on multiple hybrid Linux and Windows machines using your organizations preferred automation tool. The script performs similar steps described in the Connect hybrid machines to Azure from the Azure portal article. The difference is in the final step, where you establish the connection to Azure Arc using the azcmagent command using the service principal.
The following are the settings that you configure the azcmagent command to use for the service principal.
service-principal-id: The unique identifier (GUID) that represents the application ID of the service principal.service-principal-secret| The service principal password.tenant-id: The unique identifier (GUID) that represents your dedicated instance of Microsoft Entra ID.subscription-id: The subscription ID (GUID) of your Azure subscription that you want the machines in.resource-group: The resource group name where you want your connected machines to belong to.location: See supported Azure regions. This location can be the same or different, as the resource group's location.resource-name: (Optional) Used for the Azure resource representation of your on-premises machine. If you do not specify this value, the machine hostname is used.
You can learn more about the azcmagent command-line tool by reviewing the Azcmagent Reference.
Note
The Windows PowerShell script only supports running from a 64-bit version of Windows PowerShell.
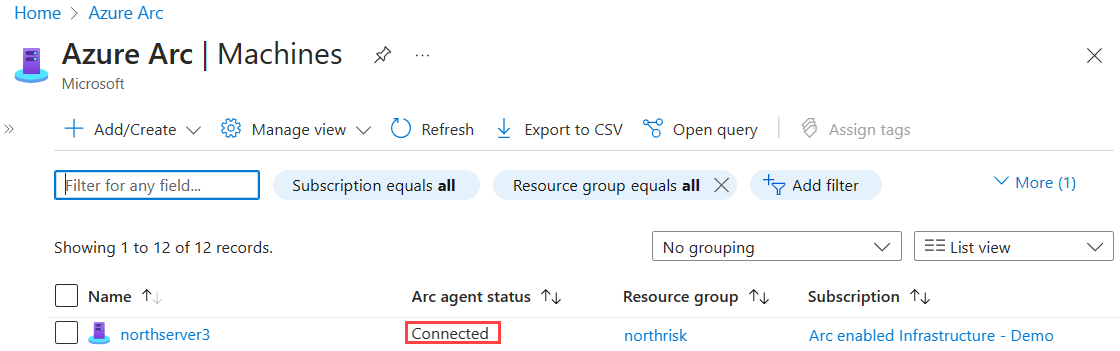
After you install the agent and configure it to connect to Azure Arc-enabled servers, go to the Azure portal to verify that the server has successfully connected. View your machines in the Azure portal.
Next steps
- Review the Planning and deployment guide to plan for deploying Azure Arc-enabled servers at any scale and implement centralized management and monitoring.
- Learn how to troubleshoot agent connection issues.
- Learn how to manage your machines using Azure Policy for such things as VM guest configuration, verifying that machines are reporting to the expected Log Analytics workspace, monitoring with VM insights, and more.