Use availability zones zonal placement for application high availability with Azure NetApp Files
Azure availability zones are physically separate locations within each supporting Azure region that are tolerant to local failures. Failures can range from software and hardware failures to events such as earthquakes, floods, and fires. Tolerance to failures is achieved because of redundancy and logical isolation of Azure services. To ensure resiliency, a minimum of three separate availability zones are present in all availability zone-enabled regions.
Important
Availability zones are referred to as logical zones. Each data center is assigned to a physical zone. Physical zones are mapped to logical zones in your Azure subscription, and the mapping is different with different subscriptions. Azure subscriptions are automatically assigned this mapping when a subscription is created. Azure NetApp Files aligns with the generic logical-to-physical availability zone mapping for all Azure services for the subscription.
Azure availability zones are highly available, fault tolerant, and more scalable than traditional single or multiple data center infrastructures. Azure availability zones let you design and operate applications and databases that automatically transition between zones without interruption. You can design resilient solutions by using Azure services that use availability zones.
The use of high availability (HA) architectures with availability zones are now a default and best practice recommendation in Azure’s Well-Architected Framework. Enterprise applications and resources are increasingly deployed into multiple availability zones to achieve this level of high availability (HA) or failure domain (zone) isolation.
Many applications are built for HA across multiple availability zones using application-based replication and failover technologies, like SQL Server Always-On Availability Groups (AOAG), SAP HANA with HANA System Replication (HSR), and Oracle with Data Guard.
Before using an availability zone, understand the following concepts:
Zonal placement: Resources are pinned to a specific availability zone. You can combine multiple zonal deployments across different zones to meet high reliability requirements. You're responsible for managing data replication and distributing requests across zones. If an outage occurs in a single availability zone, you're responsible for failover to another availability zone.
Zone redundancy: Resources are spread across multiple availability zones. Microsoft manages spreading requests across zones and the replication of data across zones. If an outage occurs in a single availability zone, Microsoft manages failover automatically.
Important
Although the use of zonal placement with Azure NetApp Files combined with application-based replication and failover technologies can be used to create a highly-available architecture, using Azure NetApp Files zonal placement alone does not provide zonal redundancy. If your workload does not support application-based replication and failover, consider using Azure NetApp Files cross-zone replication for additional redundancy.
Azure NetApp Files' availability zone volume placement feature lets you deploy each volume in the specific availability zone of your choice, in alignment with Azure compute and other services in the same zone.
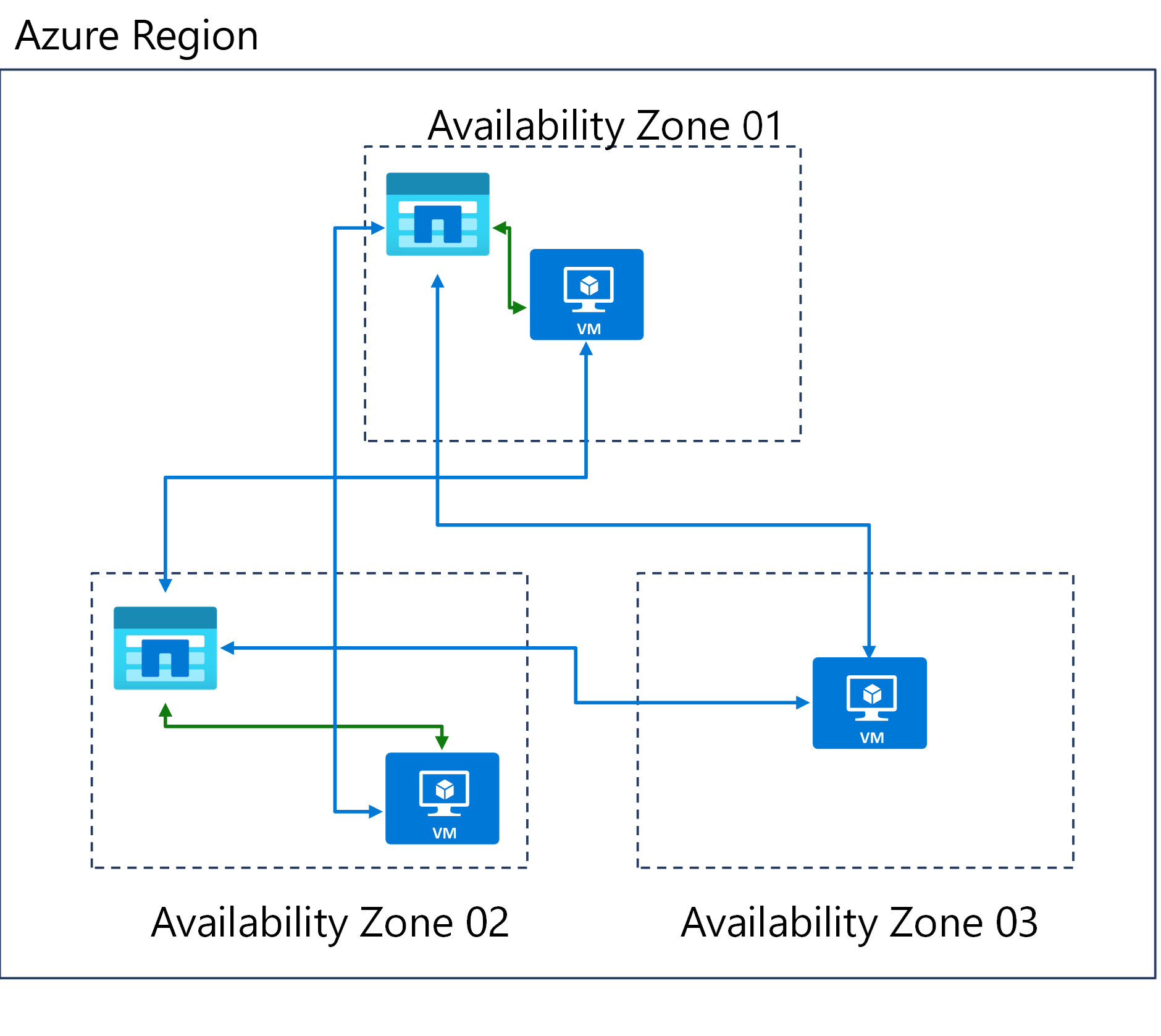
In the diagram, all virtual machines (VMs) within the region in (peered) VNets can access all Azure NetApp Files resources (blue arrows). VMs accessing Azure NetApp Files volumes in the same zone (green arrows) share the availability zone failure domain. Note there's no replication between the different volumes at the platform level.
Azure NetApp Files deployments occur in the availability of zone of choice if Azure NetApp Files is present in that availability zone and has sufficient capacity.
Important
Azure NetApp Files availability zone volume placement provides zonal placement. It does not provide proximity placement towards compute. As such, it does not provide lowest latency guarantee. VM-to-storage latencies are within the availability zone latency envelopes.
You can co-locate your compute, storage, networking, and data resources across an availability zone, and replicate this arrangement in other availability zones.
Latency is subject to availability zone latency for within availability zone access and the regional latency envelope for cross-availability zone access.
Important
It's not recommended that you use availability zones with Terraform-managed volumes. If you do, you must add the zone property to your volume.
Azure regions with availability zones
For a list of regions that currently support availability zones, see Azure regions with availability zone support.
Next steps
Feedback
Kommer snart: I hele 2024 udfaser vi GitHub-problemer som feedbackmekanisme for indhold og erstatter det med et nyt feedbacksystem. Du kan få flere oplysninger under: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Indsend og få vist feedback om