What is Azure Quantum?
Azure Quantum is the cloud quantum computing service of Azure, with a diverse set of quantum solutions and technologies. Azure Quantum ensures an open, flexible, and future-proofed path to quantum computing that adapts to your way of working, accelerates your progress, and protects your technology investments.
Azure Quantum provides the best development environment to create quantum algorithms for multiple platforms at once while preserving flexibility to tune the same algorithms for specific systems. You can write your code once and run it with little to no change against multiple targets of the same family which allows you to focus your programming at the algorithm level.
To learn more about how you can use quantum computing and quantum algorithms, see Understanding Quantum Computing.
How to get started with Azure Quantum?
There are different ways to get started with Azure Quantum. You can start by exploring the Azure Quantum website, or you can create your first Azure Quantum workspace.
The Azure Quantum website
Azure Quantum (quantum.microsoft.com) is a central resource for exploring quantum computing. You can engage with the Copilot in Azure Quantum, a quantum-focused chatbot that helps you write code and better understand quantum concepts. You can also learn from experts and enthusiasts through blogs, articles and videos.
Try out Q# code samples in the online code editor, Code with Azure Quantum, submit your job the to the cloud-based Quantinuum H-Series Emulator, or with one click in the online code editor, open your code in VS Code for the Web and continue working in a pre-configure quantum environment.
The Azure Quantum website is free of charge and doesn't require an Azure account. To get started, all you need is a Microsoft (MSA) email account. For more information, see Explore Azure Quantum.
The Azure portal
Tip
First-time users automatically get USD500 free Azure Quantum Credits for use with each participating quantum hardware provider. If you have consumed all the credits and you need more, you can apply to the Azure Quantum Credits program.
Start using Azure Quantum is very easy and free of cost for new users. To submit your quantum programs to Azure Quantum you only need two things:
An Azure account: If you don’t have an Azure account, register for free and sign up for a pay-as-you-go subscription. If you are a student, you can take advantage of a free Azure account for students.
An Azure Quantum workspace: An Azure Quantum workspace is a collection of assets associated with running quantum. To create an Azure Quantum workspace, go to the Azure portal, select Quick create and it automatically creates the workspace and adds the default providers. Or select Advance create, and enter the details of your workspace and choose the providers.
For more information, see Create an Azure Quantum workspace.
What is Q#?
Q# is an open-source quantum programming language for developing and running quantum programs.
A quantum program can be seen as a particular set of classical subroutines which, when called, perform a computation by interacting with a quantum system; a program written in Q# does not directly model the quantum state, but rather describes how a classical control computer interacts with qubits. This allows you to be entirely agnostic about what a quantum state even is on each target machine, which might have different interpretations depending on the machine.
Q# is a standalone language offering a high level of abstraction. There is no notion of a quantum state or a circuit; instead, Q# implements programs in terms of statements and expressions, much like classical programming languages. Thus, the Q# language supports the integration of rich classical and quantum computing.
For more information, see The quantum programming language Q#.
How can I write Q# quantum programs?
Azure Quantum offers the Azure Quantum Development Kit (QDK). With the QDK, you can write Q# quantum programs, debug your code, get real-time code feedback, and choose your target machine. The QDK is the only development kit ready for Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computing (FTQC).
The QDK offers two ways to run your quantum programs on Azure Quantum:
- Online development: Write your quantum code in the online code editor, and in Visual Studio Code for the Web.
- Local development: Install the QDK extension for Visual Studio Code and write your quantum code locally. For more information, see Installing the QDK on VS Code.
Besides supporting for Q#, the QDK offers support for Qiskit and Cirq for quantum computing, so if you are already working in other development languages, you can also run your circuits on Azure Quantum.
Note
An Azure Quantum workspace is required to run your local quantum programs on Azure Quantum providers. For more information, see Create an Azure Quantum workspace.
What is hybrid quantum computing?
Hybrid quantum computing refers to the processes and architecture of a classical computer and a quantum computer working together to solve a problem. With the latest generation of hybrid quantum computing architecture available in Azure Quantum you can start programming quantum computers by mixing classical and quantum instructions together.
- Batch quantum computing: Batching multiple circuits into one job eliminates the wait between job submissions, allowing you to run multiple jobs faster. Examples of problems that can take advantage of batch quantum computing include Shor's algorithm and simple quantum phase estimation.
- Interactive quantum computing (Sessions): Jobs can be grouped logically into one session and prioritized over non-session jobs. Examples of problems that can use this approach are Variational Quantum Eigensolvers (VQE) and Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithms (QAOA).
- Integrated quantum computing: By integrating quantum and classical computing, quantum programs can move away from just circuits. Programs can now use common programming constructs to perform mid-circuit measurements, optimize and reuse qubits, and adapt in real-time to the QPU. Examples of scenarios that can take advantage of this model are adaptive phase estimation and machine learning.
- Distributed quantum computing: The distributed quantum computing model enables real-time computations across quantum and distributed resources. Examples of scenarios that can take advantage of this model are complex materials modeling or the evaluation of full catalytic reactions.
For more information, see Hybrid quantum computing.
Resource estimation in quantum computing
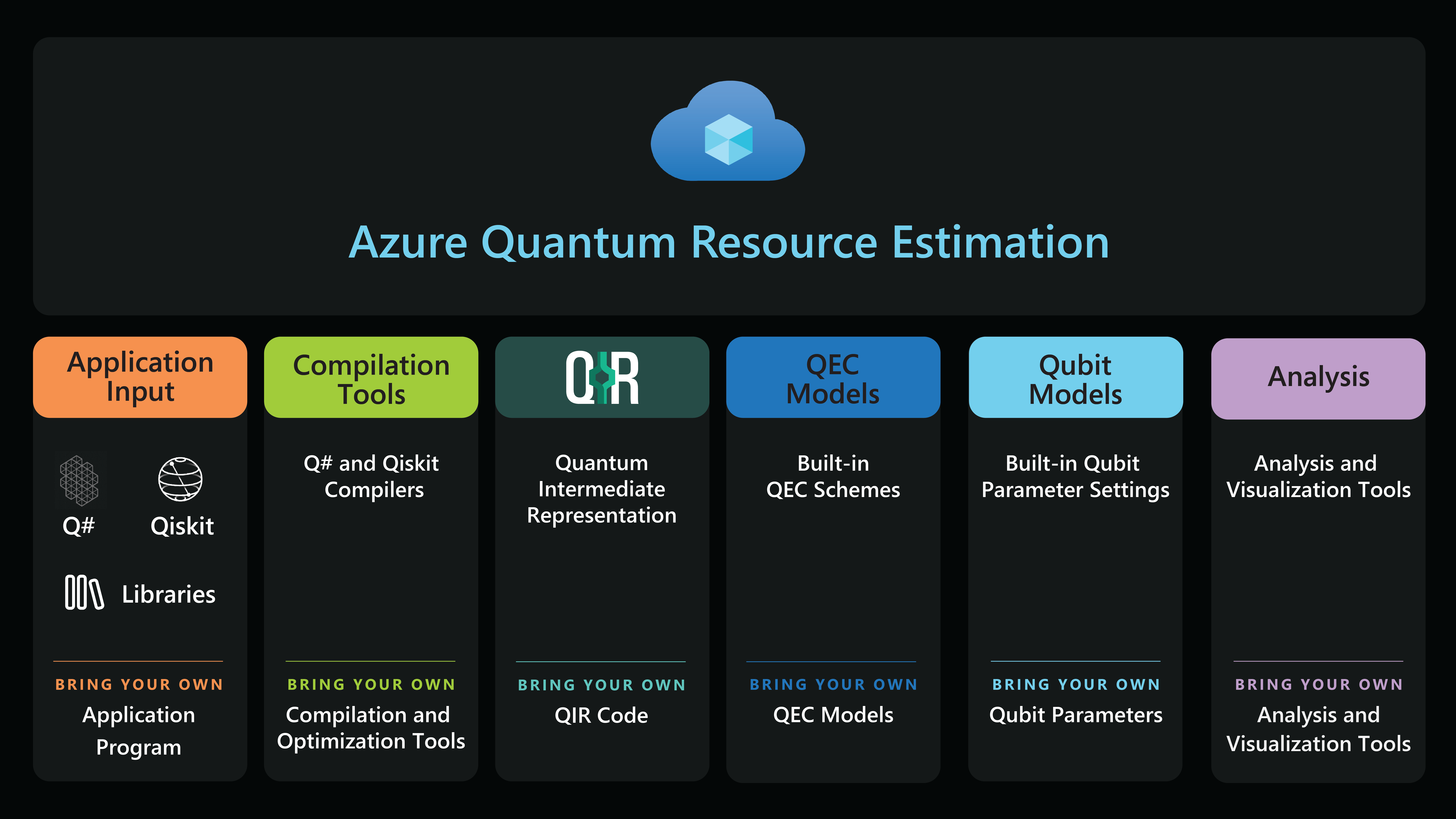
In quantum computing, resource estimation is the ability to understand the resources, that is the number of qubits, number of quantum gates, processing time, etc., that will be required for a given algorithm, assuming (or taking as parameters) certain hardware characteristics. Understanding the number of qubits required for a quantum solution and the differences between qubit technologies allows innovators to prepare and refine their quantum solutions to run on future scaled quantum machines and ultimately accelerate their quantum impact.
Designed specifically for scaled quantum fault-tolerant error-corrected systems, the Azure Quantum Resource Estimator allows you to assess architectural decisions, compare qubit technologies, and determine the resources needed to execute a given quantum algorithm. You can choose from pre-defined fault-tolerant protocols and specify assumptions of the underlying physical qubit model.
The Azure Quantum Resource Estimator computes post-layout physical resource estimation by taking a set of inputs such as qubit parameters, the quantum error correction (QEC) code, the error budget, and other parameters into account. It takes a Quantum Intermediate Representation (QIR) program as input and, therefore, supports any language that translates to QIR, for example, you can use the Azure Quantum Resource Estimator with Q# and Qiskit.
Providers available on Azure Quantum
Azure Quantum offers some of the most compelling and diverse quantum resources available today from industry leaders. Azure Quantum currently partners with the following providers to enable you to run your Q# quantum programs on real hardware, and the option to test your code on simulated quantum computers.
Choose the provider that best suits the characteristics of your problem and your needs.
- IONQ: Dynamically reconfigurable trapped-ion quantum computers for up to 11 fully connected qubits, that lets you run a two-qubit gate between any pair.
- PASQAL (Private Preview): Neutral atom-based quantum processors operating at room temperature, with long coherence times and impressive qubit connectivity.
- Quantinuum: Trapped-ion systems with high-fidelity, fully connected qubits, low error rates, qubit reuse, and the ability to perform mid-circuit measurements.
- Rigetti: Rigetti's systems are powered by superconducting qubit-based quantum processors. They offer fast gate times, low-latency conditional logic, and fast program execution times.
For more information on the specifications of each provider, see the full Quantum computing target list.
Providers coming soon
- Quantum Circuits, Inc: Full-stack superconducting circuits, with real-time feedback that enables error correction, encoding-agnostic entangling gates.
Related content
Start using Azure Quantum:
Feedback
Kommer snart: I hele 2024 udfaser vi GitHub-problemer som feedbackmekanisme for indhold og erstatter det med et nyt feedbacksystem. Du kan få flere oplysninger under: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Indsend og få vist feedback om