Zero Trust deployment for technology pillars
Because your organization might already have elements of Zero Trust protections already in place, this documentation set provides conceptual information to get you started and deployment plans and implementation recommendations for end-to-end adherence to Zero Trust principles. Each article acts as a checklist of deployment objectives with steps and links to more information.
You deploy Zero Trust principles across your IT infrastructure by implementing Zero Trust controls and technologies across seven technology pillars. Six of these pillars are signal sources, a control plane for enforcement, and a critical resource to be defended. Across these is the pillar that collects those signals and provides visibility for security incidents and automation and orchestration for responding to and mitigating cybersecurity threats.
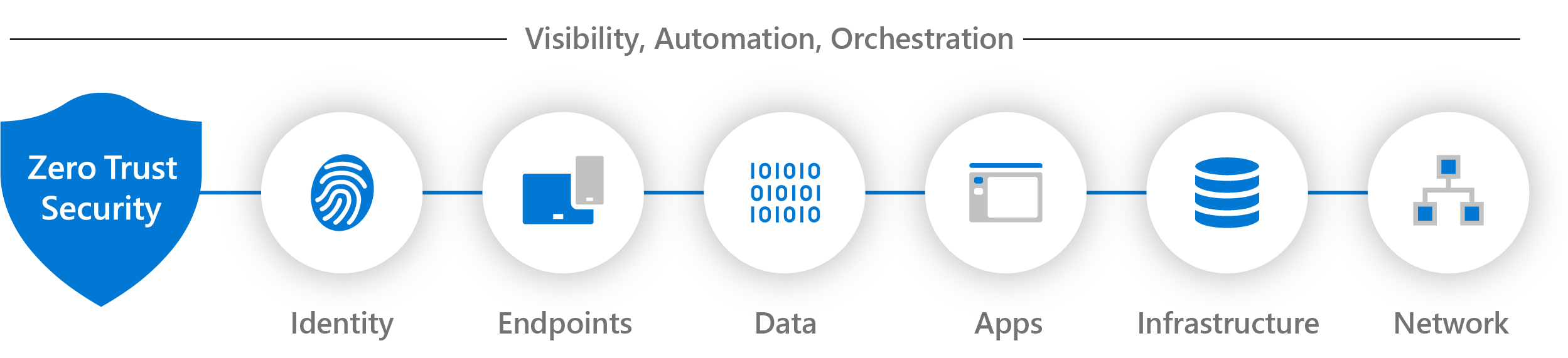
The following articles provide conceptual information and deployment objectives for these seven technology pillars. Use these articles to assess your readiness and build a deployment plan to apply Zero Trust principles.
| Technology pillar | Description |
|---|---|
Identities |
Identities—whether they represent people, services, or IoT devices—define the Zero Trust control plane. When an identity attempts to access a resource, verify that identity with strong authentication, and ensure access is compliant and typical for that identity. Follow least privilege access principles. |
Endpoints |
Once an identity has been granted access to a resource, data can flow to a variety of different endpoints (devices), from IoT devices to smartphones, BYOD to partner-managed devices, and on-premises workloads to cloud-hosted servers. This diversity creates a massive attack surface area. Monitor and enforce device health and compliance for secure access. |
Data |
[Ultimately, security teams are protecting data. Where possible, data should remain safe even if it leaves the devices, apps, infrastructure, and networks the organization controls. Classify, label, and encrypt data, and restrict access based on those attributes. |
Apps |
Applications and APIs provide the interface by which data is consumed. They may be legacy on-premises workloads, lifted-and-shifted to cloud workloads, or modern SaaS applications. Apply controls and technologies to discover shadow IT, ensure appropriate in-app permissions, gate access based on real-time analytics, monitor for abnormal behavior, control user actions, and validate secure configuration options. |
Infrastructure |
Infrastructure—whether on-premises servers, cloud-based VMs, containers, or micro-services—represents a critical threat vector. Assess for version, configuration, and JIT access to harden defense. Use telemetry to detect attacks and anomalies, and automatically block and flag risky behavior and take protective actions. |
Network |
All data is ultimately accessed over network infrastructure. Networking controls can provide critical controls to enhance visibility and help prevent attackers from moving laterally across the network. Segment networks (and do deeper in-network micro-segmentation) and deploy real-time threat protection, end-to-end encryption, monitoring, and analytics. |
Visibility, automation, and orchestration |
In our Zero Trust guides, we define the approach to implement an end-to-end Zero Trust methodology across identities, endpoints (devices), data, apps, infrastructure, and network. These activities increase your visibility, which gives you better data for making trust decisions. With each of these individual areas generating their own relevant alerts, we need an integrated capability to manage the resulting influx of data to better defend against threats and validate trust in a transaction. |
Recommended training
| Training | Establish the guiding principles and core components of Zero Trust |
|---|---|

|
Use this learning path to understand the basics of applying Zero Trust principles to the key technology pillars of identities, endpoints, application access, networks, infrastructure, and data. |
Additional Zero Trust resources
Use these additional Zero Trust resources based on a documentation set or roles in your organization.
Documentation set
Follow this table for the best Zero Trust documentation sets for your needs.
| Documentation set | Helps you... | Roles |
|---|---|---|
| Adoption framework for phase and step guidance for key business solutions and outcomes | Apply Zero Trust protections from the C-suite to the IT implementation. | Security architects, IT teams, and project managers |
| Zero Trust for small businesses | Apply Zero Trust principles to small business customers. | Customers and partners working with Microsoft 365 for business |
| Zero Trust Rapid Modernization Plan (RaMP) for project management guidance and checklists for easy wins | Quickly implement key layers of Zero Trust protection. | Security architects and IT implementers |
| Zero Trust deployment plan with Microsoft 365 for stepped and detailed design and deployment guidance | Apply Zero Trust protections to your Microsoft 365 tenant. | IT teams and security staff |
| Zero Trust for Microsoft Copilots for stepped and detailed design and deployment guidance | Apply Zero Trust protections to Microsoft Copilots. | IT teams and security staff |
| Zero Trust for Azure services for stepped and detailed design and deployment guidance | Apply Zero Trust protections to Azure workloads and services. | IT teams and security staff |
| Partner integration with Zero Trust for design guidance for technology areas and specializations | Apply Zero Trust protections to partner Microsoft cloud solutions. | Partner developers, IT teams, and security staff |
| Develop using Zero Trust principles for application development design guidance and best practices | Apply Zero Trust protections to your application. | Application developers |
Your role
Follow this table for the best documentation sets for the roles in your organization.
| Role | Documentation set | Helps you... |
|---|---|---|
| Security architect IT project manager IT implementer |
Adoption framework for phase and step guidance for key business solutions and outcomes | Apply Zero Trust protections from the C-suite to the IT implementation. |
| Customer or partner for Microsoft 365 for business | Zero Trust for small businesses | Apply Zero Trust principles to small business customers. |
| Security architect IT implementer |
Zero Trust Rapid Modernization Plan (RaMP) for project management guidance and checklists for easy wins | Quickly implement key layers of Zero Trust protection. |
| Member of an IT or security team for Microsoft 365 | Zero Trust deployment plan with Microsoft 365 for stepped and detailed design and deployment guidance for Microsoft 365 | Apply Zero Trust protections to your Microsoft 365 tenant. |
| Member of an IT or security team for Microsoft Copilots | Zero Trust for Microsoft Copilots for stepped and detailed design and deployment guidance | Apply Zero Trust protections to Microsoft Copilots. |
| Member of an IT or security team for Azure services | Zero Trust for Azure services for stepped and detailed design and deployment guidance | Apply Zero Trust protections to Azure workloads and services. |
| Partner developer or member of an IT or security team | Partner integration with Zero Trust for design guidance for technology areas and specializations | Apply Zero Trust protections to partner Microsoft cloud solutions. |
| Application developer | Develop using Zero Trust principles for application development design guidance and best practices | Apply Zero Trust protections to your application. |