Anzeigen von Featureinformationen
Hinweis
Auslauf des Azure Maps Android SDK
Das Azure Maps Native SDK für Android ist jetzt veraltet und wird am 31.03.2025 eingestellt. Um Dienstunterbrechungen zu vermeiden, migrieren Sie bis zum 31.03.2025 zum Azure Maps Web SDK. Weitere Informationen finden Sie im Migrationshandbuch zum Azure Maps iOS SDK.
Räumliche Daten werden häufig mithilfe von Punkten, Linien und Polygonen dargestellt. Diesen Daten sind häufig Metadateninformationen zugeordnet. Ein Punkt kann beispielsweise den Standort eines Restaurants darstellen, und die Metadaten zu diesem Restaurant können den Namen, die Adresse und die Art des Speisenangebots umfassen. Diese Metadaten können als Eigenschaften eines GeoJSON-Features (Feature) hinzugefügt werden. Der folgende Code erstellt ein einfaches Punktmerkmal mit einer Eigenschaft vom Typ title und dem Wert „Hello World!“:
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
DataSource source = new DataSource();
map.sources.add(source);
//Create a point feature.
Feature feature = Feature.fromGeometry(Point.fromLngLat(-122.33, 47.64));
//Add a property to the feature.
feature.addStringProperty("title", "Hello World!");
//Create a point feature, pass in the metadata properties, and add it to the data source.
source.add(feature);
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
val source = DataSource()
map.sources.add(source)
//Create a point feature.
val feature = Feature.fromGeometry(Point.fromLngLat(-122.33, 47.64))
//Add a property to the feature.
feature.addStringProperty("title", "Hello World!")
//Create a point feature, pass in the metadata properties, and add it to the data source.
source.add(feature)
Weitere Informationen zum Erstellen der Karte und zum Hinzufügen von Daten zur Karte finden Sie unter Erstellen einer Datenquelle.
Wenn ein Benutzer mit einem Merkmal auf der Karte interagiert, kann mithilfe von Ereignissen auf diese Aktionen reagiert werden. Ein gängiges Szenario ist das Anzeigen einer Nachricht, die sich aus den Metadateneigenschaften eines Merkmals zusammensetzt, mit dem der Benutzer interagiert hat. Das Ereignis OnFeatureClick ist das Hauptereignis, das verwendet wird, um zu erkennen, wann der Benutzer auf ein Merkmal auf der Karte getippt hat. Es gibt auch ein Ereignis vom Typ OnLongFeatureClick. Wenn der Karte das Ereignis OnFeatureClick hinzugefügt wird, kann dieses auf eine einzelne Ebene begrenzt werden, indem die ID einer Ebene übergeben wird, auf die es begrenzt werden soll. Wird keine Ebenen-ID übergeben, wird das Ereignis ausgelöst, wenn auf ein beliebiges Merkmal auf der Karte getippt wird (unabhängig von der Ebene, auf der sich das Merkmal befindet). Der folgende Code erstellt eine Symbolebene zum Rendern von Punktdaten auf der Karte. Anschließend wird ein Ereignis vom Typ OnFeatureClick hinzugefügt und auf diese Symbolebene beschränkt.
//Create a symbol and add it to the map.
SymbolLayer layer = new SymbolLayer(source);
map.layers.add(layer);
//Add a feature click event to the map.
map.events.add((OnFeatureClick) (features) -> {
//Retrieve the title property of the feature as a string.
String msg = features.get(0).getStringProperty("title");
//Do something with the message.
//Return a boolean indicating if event should be consumed or continue bubble up.
return false;
}, layer.getId()); //Limit this event to the symbol layer.
//Create a symbol and add it to the map.
val layer = SymbolLayer(source)
map.layers.add(layer)
//Add a feature click event to the map.
map.events.add(OnFeatureClick { features: List<Feature> ->
//Retrieve the title property of the feature as a string.
val msg = features[0].getStringProperty("title")
//Do something with the message.
//Return a boolean indicating if event should be consumed or continue bubble up.
return false
}, layer.getId()) //Limit this event to the symbol layer.
Anzeigen einer Popupmeldung
Eine Popupmeldung ist eine der einfachsten Methoden, um dem Benutzer Informationen anzuzeigen, und steht in allen Versionen von Android zur Verfügung. Sie unterstützt keinerlei Benutzereingaben und wird nur kurz angezeigt. Wenn Sie den Benutzer schnell über etwas informieren möchten, worauf er getippt hat, ist eine Popupmeldung ggf. eine gute Option. Der folgende Code zeigt, wie eine Popupmeldung mit dem Ereignis OnFeatureClick verwendet werden kann:
//Add a feature click event to the map.
map.events.add((OnFeatureClick) (features) -> {
//Retrieve the title property of the feature as a string.
String msg = features.get(0).getStringProperty("title");
//Display a toast message with the title information.
Toast.makeText(this, msg, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
//Return a boolean indicating if event should be consumed or continue bubble up.
return false;
}, layer.getId()); //Limit this event to the symbol layer.
//Add a feature click event to the map.
map.events.add(OnFeatureClick { features: List<Feature> ->
//Retrieve the title property of the feature as a string.
val msg = features[0].getStringProperty("title")
//Display a toast message with the title information.
Toast.makeText(this, msg, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
//Return a boolean indicating if event should be consumed or continue bubble up.
return false
}, layer.getId()) //Limit this event to the symbol layer.
Neben Popupmeldungen gibt es aber auch noch verschiedene andere Möglichkeiten, um die Metadateneigenschaften eines Merkmals zu präsentieren:
- Snackbar-Widget:
Snackbarsliefern einfaches Feedback zu einem Vorgang. Sie zeigen eine kurze Meldung am unteren Bildschirmrand (Mobilgeräte) bzw. links unten (größere Geräte) an.Snackbarswerden im Vordergrund über allen anderen Bildschirmelementen eingeblendet, und es kann immer nur eine einzelne Snackbar angezeigt werden. - Dialogfelder: Ein Dialogfeld ist ein kleines Fenster, in dem der Benutzer zu einer Entscheidung oder zur Eingabe zusätzlicher Informationen aufgefordert wird. Ein Dialogfeld füllt nicht den gesamten Bildschirm aus und wird in der Regel für modale Ereignisse verwendet, bei denen der Benutzer eine Aktion ausführen muss, damit ein Vorgang fortgesetzt wird.
- Fügen Sie der aktuellen Aktivität ein Fragment hinzu.
- Navigieren Sie zu einer anderen Aktivität oder Ansicht.
Anzeigen eines Popups
Das Azure Maps Android SDK bietet eine Popup-Klasse, mit der Anmerkungselemente auf der Benutzeroberfläche, die an einer Position auf der Karte verankert sind, auf einfache Weise erstellt werden können. Für Popups müssen Sie eine Ansicht mit einem relativen Layout in der Option content des Popups übergeben. Hier ist ein Beispiel für ein einfaches Layout, bei dem dunkler Text auf einem hellen Hintergrund angezeigt wird.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#ffffff"
android:layout_margin="8dp"
android:padding="10dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/message"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text=""
android:textSize="18dp"
android:textColor="#222"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:width="200dp"/>
</RelativeLayout>
Angenommen, das obige Layout ist in einer Datei mit dem Namen popup_text.xml im Ordner res -> layout einer App gespeichert, dann wird mit dem folgenden Code ein Popup erstellt und der Karte hinzugefügt. Beim Klicken auf ein Feature wird die Eigenschaft title mit dem Layout von popup_text.xml angezeigt, wobei die untere Mitte des Layouts an der angegebenen Position auf der Karte verankert ist.
//Create a popup and add it to the map.
Popup popup = new Popup();
map.popups.add(popup);
map.events.add((OnFeatureClick)(feature) -> {
//Get the first feature and it's properties.
Feature f = feature.get(0);
JsonObject props = f.properties();
//Retrieve the custom layout for the popup.
View customView = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.popup_text, null);
//Access the text view within the custom view and set the text to the title property of the feature.
TextView tv = customView.findViewById(R.id.message);
tv.setText(props.get("title").getAsString());
//Get the position of the clicked feature.
Position pos = MapMath.getPosition((Point)cluster.geometry());
//Set the options on the popup.
popup.setOptions(
//Set the popups position.
position(pos),
//Set the anchor point of the popup content.
anchor(AnchorType.BOTTOM),
//Set the content of the popup.
content(customView)
//Optionally, hide the close button of the popup.
//, closeButton(false)
//Optionally offset the popup by a specified number of pixels.
//pixelOffset(new Pixel(10, 10))
);
//Open the popup.
popup.open();
//Return a boolean indicating if event should be consumed or continue bubble up.
return false;
});
//Create a popup and add it to the map.
val popup = Popup()
map.popups.add(popup)
map.events.add(OnFeatureClick { feature: List<Feature> ->
//Get the first feature and it's properties.
val f = feature[0]
val props = f.properties()
//Retrieve the custom layout for the popup.
val customView: View = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.popup_text, null)
//Access the text view within the custom view and set the text to the title property of the feature.
val tv: TextView = customView.findViewById(R.id.message)
tv.text = props!!["title"].asString
//Get the position of the clicked feature.
val pos = MapMath.getPosition(f.geometry() as Point?);
//Set the options on the popup.
popup.setOptions(
//Set the popups position.
position(pos),
//Set the anchor point of the popup content.
anchor(AnchorType.BOTTOM),
//Set the content of the popup.
content(customView)
//Optionally, hide the close button of the popup.
//, closeButton(false)
//Optionally offset the popup by a specified number of pixels.
//pixelOffset(Pixel(10, 10))
)
//Open the popup.
popup.open()
//Return a boolean indicating if event should be consumed or continue bubble up.
false
})
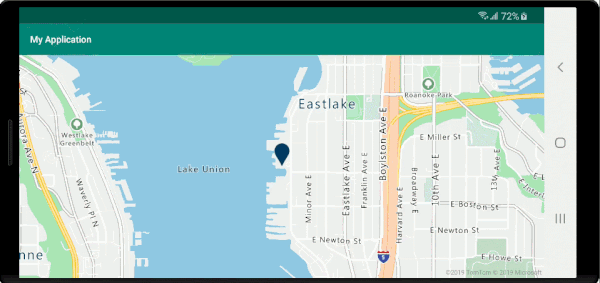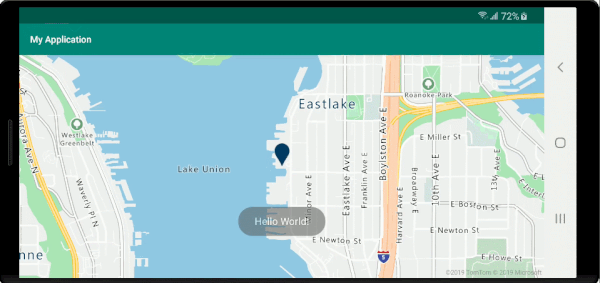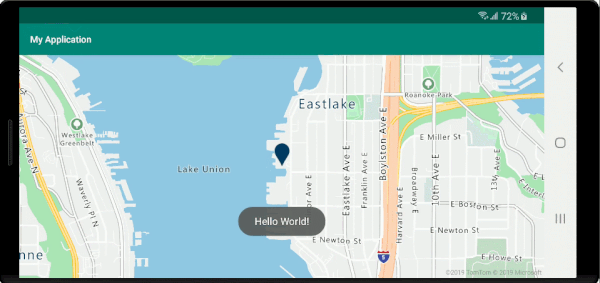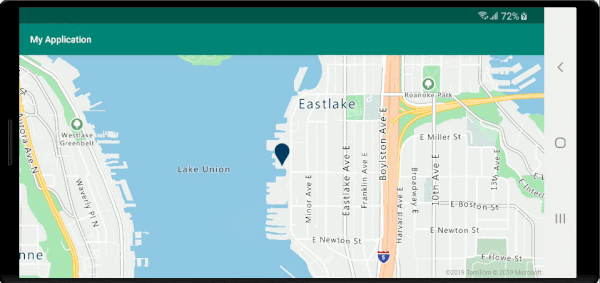
Der folgende Screenshot zeigt Popups, die beim Klicken auf Features angezeigt und beim Verschieben der Karte an der angegebenen Position verankert bleiben.
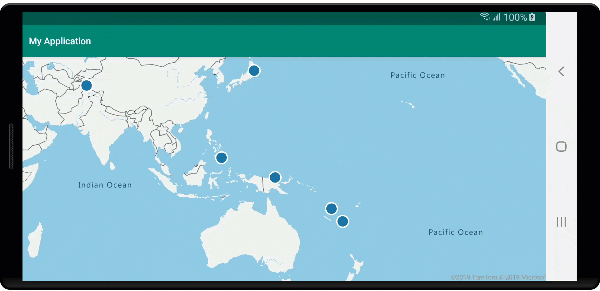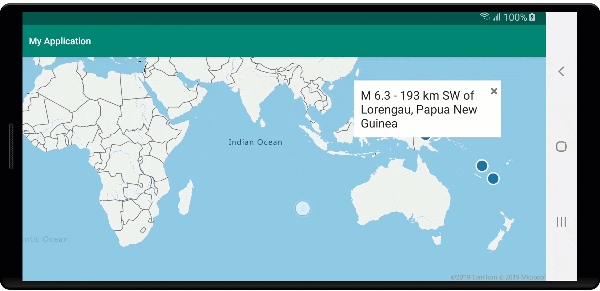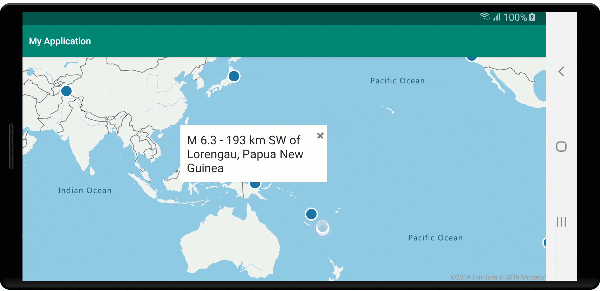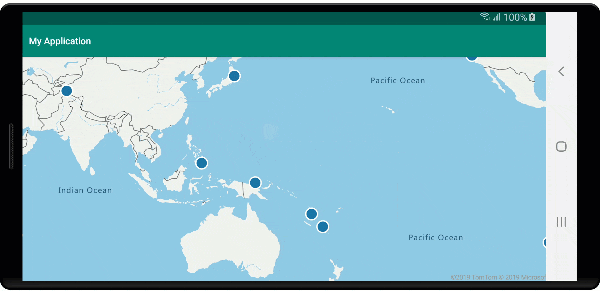
Nächste Schritte
So fügen Sie Ihrer Karte weitere Daten hinzu:
Feedback
Bald verfügbar: Im Laufe des Jahres 2024 werden wir GitHub-Issues stufenweise als Feedbackmechanismus für Inhalte abbauen und durch ein neues Feedbacksystem ersetzen. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Feedback senden und anzeigen für