Hinweis
Für den Zugriff auf diese Seite ist eine Autorisierung erforderlich. Sie können versuchen, sich anzumelden oder das Verzeichnis zu wechseln.
Für den Zugriff auf diese Seite ist eine Autorisierung erforderlich. Sie können versuchen, das Verzeichnis zu wechseln.
Gilt für: SQL Server 2019 (15.x)
Important
Die Big Data Cluster von Microsoft SQL Server 2019 werden eingestellt. Der Support für SQL Server 2019 Big Data Cluster endete am 28. Februar 2025. Weitere Informationen finden Sie im Ankündigungsblogbeitrag und den Big Data-Optionen auf der Microsoft SQL Server-Plattform.
Sie können Python- und R-Skripts auf der Masterinstanz eines SQL Server-Big Data-Clusters mit Machine Learning Services ausführen.
Note
Sie können Java-Code auch mithilfe der Java-Spracherweiterung in der Masterinstanz von SQL Server-Big Data-Cluster ausführen. Wenn Sie die folgenden Schritte ausführen, werden auch die SQL Server-Spracherweiterungen aktiviert.
Aktivieren von Machine Learning Services
Machine Learning Services wird standardmäßig in Big Data-Clustern von SQL Server 2019 installiert und erfordert keine separate Installation.
Führen Sie diese Anweisung auf der Masterinstanz aus, um Machine Learning Services zu aktivieren:
EXEC sp_configure 'external scripts enabled', 1
RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE
GO
Sie können nun Python- und R-Skripts auf der Masterinstanz von Big Data-Clustern ausführen. Informationen zum Ausführen Ihres ersten Skripts finden Sie in den Schnellstarts unter Nächste Schritte.
Note
Die Konfigurationseinstellung kann nicht für die Verbindung eines Verfügbarkeitsgruppenlisteners festgelegt werden. Wenn Big Data-Cluster mit Hochverfügbarkeit bereitgestellt werden, legen Sie external scripts enabled für alle Replikate fest. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter Aktivierung für Cluster mit Hochverfügbarkeit.
Aktivierung für Cluster mit Hochverfügbarkeit
Wenn Sie SQL Server-Big Data-Cluster mit Hochverfügbarkeit bereitstellen, erstellt die Bereitstellung eine Verfügbarkeitsgruppe für die Masterinstanz. Legen Sie external scripts enabled für alle Instanzen der Verfügbarkeitsgruppe fest, um Machine Learning Services zu aktivieren. Für einen Big Data-Cluster müssen Sie sp_configure auf allen Replikaten der SQL Server-Masterinstanz ausführen.
Im folgenden Abschnitt wird beschrieben, wie Sie externe Skripts für alle Instanzen aktivieren.
Erstellen eines externen Lastenausgleichs für jede Instanz
Erstellen Sie für jedes Replikat in der Verfügbarkeitsgruppe einen Lastenausgleich, damit Sie eine Verbindung mit der Instanz herstellen können.
kubectl expose pod <pod-name> --port=<connection port number> --name=<load-balancer-name> --type=LoadBalancer -n <kubernetes namespace>
In den Beispielen dieses Artikels werden die folgenden Werte verwendet:
-
<pod-name>:master-# -
<connection port number>:1533 -
<load-balancer-name>:mymaster-# -
<kubernetes namespace>:mssql-cluster
Aktualisieren Sie das folgende Skript für Ihre Umgebung, und führen Sie die Befehle aus:
kubectl expose pod master-0 --port=1533 --name=mymaster-0 --type=LoadBalancer -n mssql-cluster
kubectl expose pod master-1 --port=1533 --name=mymaster-1 --type=LoadBalancer -n mssql-cluster
kubectl expose pod master-2 --port=1533 --name=mymaster-2 --type=LoadBalancer -n mssql-cluster
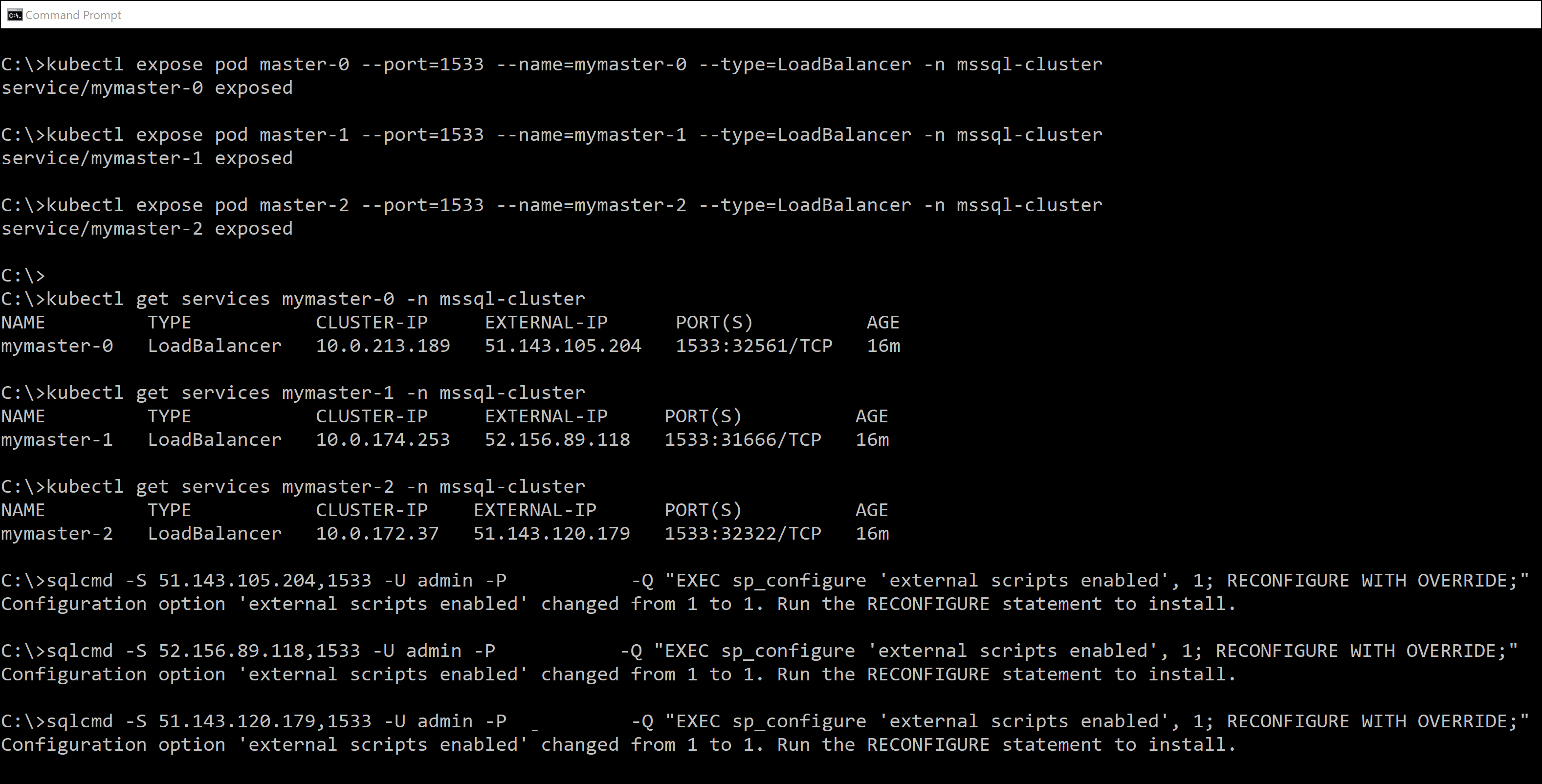
kubectl gibt die folgende Ausgabe zurück.
service/mymaster-0 exposed
service/mymaster-1 exposed
service/mymaster-2 exposed
Bei jedem Lastenausgleich handelt es sich um einen Masterreplikatendpunkt.
Aktivieren der Skriptausführung auf allen Replikaten
Rufen Sie die IP-Adresse für den Masterreplikatendpunkt ab.
Der folgende Befehl gibt die externe IP-Adresse für den Replikatendpunkt zurück.
kubectl get services <load-balancer-name> -n <kubernetes namespace>Führen Sie die folgenden Befehle aus, um die externe IP-Adresse für alle Replikate dieses Szenarios abzurufen:
kubectl get services mymaster-0 -n mssql-cluster kubectl get services mymaster-1 -n mssql-cluster kubectl get services mymaster-2 -n mssql-clusterNote
Es kann einige Zeit dauern, bis die externe IP-Adresse verfügbar ist. Führen Sie das obige Skript regelmäßig aus, bis jeder Endpunkt eine externe IP-Adresse zurückgibt.
Stellen Sie eine Verbindung mit dem Masterreplikatendpunkt her, und aktivieren Sie die Skriptausführung.
Führen Sie diese Anweisung aus:
EXEC sp_configure 'external scripts enabled', 1 RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE GOSie können den obigen Befehl beispielsweise mit
sqlcmdausführen. Im folgenden Beispiel wird eine Verbindung mit dem Masterreplikatendpunkt hergestellt und die Skriptausführung wird aktiviert. Ersetzen Sie die Werte im Skript durch die Werte Ihrer Umgebung.sqlcmd -S <IP address>,1533 -U <user name> -P <password> -Q "EXEC sp_configure 'external scripts enabled', 1; RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE;"Wiederholen Sie den Schritt für alle Replikate.
Demonstration
Die folgende Abbildung veranschaulicht diesen Prozess.
Sie können nun Python- und R-Skripts auf der Masterinstanz von Big Data-Clustern ausführen. Informationen zum Ausführen Ihres ersten Skripts finden Sie in den Schnellstarts unter Nächste Schritte.
Löschen der Masterreplikatendpunkte
Löschen Sie die Endpunkte der Replikate im Kubernetes-Cluster. Der in Kubernetes zur Verfügung gestellte Endpunkt ist ein Lastenausgleichsdienst.
Mit dem folgenden Befehl wird der Lastenausgleichsdienst gelöscht.
kubectl delete svc <load-balancer-name> -n mssql-cluster
Führen Sie die folgenden Befehle aus, um die Beispiele dieses Artikels abzurufen.
kubectl delete svc mymaster-0 -n mssql-cluster
kubectl delete svc mymaster-1 -n mssql-cluster
kubectl delete svc mymaster-2 -n mssql-cluster
Schnellstart für maschinelles Lernen mit Big Data-Clustern von SQL Server
Python quickstarts
- Ausführen von Python-Skripts
- Datenstrukturen und -objekte
- Python functions
- Trainieren und Bewerten eines Modells
R quickstarts
Tutorials für maschinelles Lernen für Big Data-Cluster von SQL Server
Python tutorial
Skiverleih (lineare Regression)
Kategorisierung von Kunden (C steht für Clustering)
NYC-Taxitrinkgelder (Klassifizierung)
- 1: Einführung
- 2: Durchsuchen von Daten
- 3 – Featureentwicklung
- 4: Trainieren und Bereitstellen
- 5: Vorhersagen
R tutorials
Skiverleih (Entscheidungsbaum)
Kategorisierung von Kunden (C steht für Clustering)
NYC-Taxitrinkgelder (Klassifizierung)
- 1: Einführung
- 2: Durchsuchen von Daten
- 3 – Featureentwicklung
- 4: Trainieren und Bereitstellen
- 5: Vorhersagen
Schrittanleitungen für maschinelles Lernen für Big Data-Cluster von SQL Server
Durchsuchen und Modellieren von Daten
- Anzeigen eines Histogramms in Python
- Importieren von Daten in einen Pandas-Datenrahmen
- Einfügen eines Datenrahmens in SQL
Datentypkonvertierungen
Deploy
Predictions
Package management
Installieren neuer Python-Pakete
Installieren neuer R-Pakete
- Abrufen von R-Paketinformationen
- Installieren mit sqlmlutils
- Erstellen eines miniCRAN-Repositorys
- Tipps für die Verwendung von R-Paketen
Monitor
Security
Spark-Maschinenlernen
- Verwenden von Machine Learning mit Spark
- Data Wrangling mithilfe von PROSE Code Accelerator
- Machine Learning-Modelle mit MLeap in Apache Spark
Next steps
- Ausführen einfacher Python-Skripts mit SQL Server Machine Learning Services
- Schnellstart: Erstellen und Bewerten eines Vorhersagemodells in Python mit SQL Server Machine Learning Services
- Ausführen einfacher R-Skripts mit SQL Server Machine Learning Services
- Schnellstart: Erstellen und Bewerten eines Vorhersagemodells in R mit SQL Machine Learning