Σημείωση
Η πρόσβαση σε αυτή τη σελίδα απαιτεί εξουσιοδότηση. Μπορείτε να δοκιμάσετε να συνδεθείτε ή να αλλάξετε καταλόγους.
Η πρόσβαση σε αυτή τη σελίδα απαιτεί εξουσιοδότηση. Μπορείτε να δοκιμάσετε να αλλάξετε καταλόγους.
Application Gateway lets you rewrite selected content in requests and responses. With this feature, you can translate URLs, query string parameters, and modify request and response headers. You can also add conditions to ensure that the URL or the specified headers are rewritten only when certain conditions are met. These conditions are based on the request and response information.
The HTTP header and URL rewrite features are only available for the Application Gateway v2 SKU.
Request and response headers
Application Gateway allows you to add, remove, or update HTTP request and response headers while the request and response packets move between the client and backend pools. HTTP headers let a client and server pass extra information with a request or response. By rewriting these headers, you can accomplish important tasks including:
- Adding security-related header fields like HSTS and X-XSS-Protection
- Removing response header fields that might reveal sensitive information
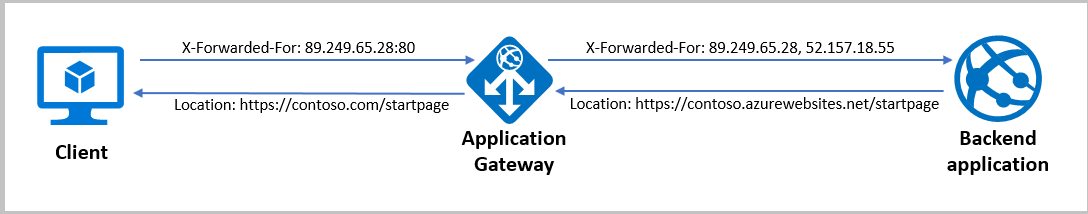
- Removing port information from X-Forwarded-For headers
You can rewrite all headers in requests and responses, except for the Connection and Upgrade headers. You can also use the application gateway to create custom headers and add them to the requests and responses being routed through it. To learn how to rewrite request and response headers with Application Gateway by using Azure portal, see here.
URL path and query string
With URL rewrite capability in Application Gateway, you can:
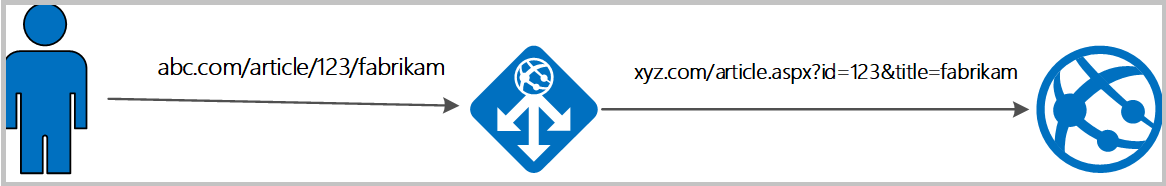
Rewrite the host name, path, and query string of the request URL
Choose to rewrite the URL of all requests on a listener or only those requests that match one or more of the conditions you set. These conditions are based on the request properties (request header and server variables).
Choose to route the request (select the backend pool) based on either the original URL or the rewritten URL
To learn how to rewrite URL with Application Gateway by using Azure portal, see here.
Understanding rewrites in Application Gateway
A rewrite set is a collection of a routing rule, condition, and action.
Request routing rule association: The rewrite configuration associates to a source listener through its routing rule. When you use a routing rule of the type Basic, the rewrite configuration associates with its listener and works as a global rewrite. When you use a Path-based routing rule, you define the rewrite configuration according to the URL path map. In the latter case, it applies only to a specific path area of a site. You can apply a rewrite set to multiple routing rules, but a routing rule can have only one rewrite associated with it.
Rewrite Condition: This configuration is optional. Based on the conditions that you define, the Application Gateway evaluates the contents of the HTTP(S) requests and responses. The subsequent "rewrite action" occurs if the HTTP(S) request or response matches this condition. If you associate more than one condition with an action, the action occurs only when all the conditions are met. In other words, it's a logical AND operation. You can use rewrite conditions to evaluate the content of HTTP(S) requests and responses. This optional configuration enables you to perform a rewrite only when one or more conditions are met. The application gateway uses these types of variables to evaluate the content of requests and responses:
You can choose the following types to look for a condition:
- HTTP header (Request and Response)
- Supported Server variables
A condition lets you evaluate whether a specified header or variable exists by matching their values through text or a Regex pattern. For advanced rewrite configurations, you can also capture the value of header or server variable for later use under Rewrite Action. Learn more about pattern and capturing.
Rewrite Action: Rewrite action set allows you to rewrite headers (request or response) or the URL components.
An action can have the following value types or their combinations:
- Text.
- Request header's value - To use a captured request header's value, specify the syntax as
{http_req_headerName}. - Response header's value - To use a captured response header's value from the preceding condition, specify the syntax as
{http_resp_headerName}. The Rewrite Action block also supports the "Header Value Matcher" field for Set-Cookie header. This optional field lets you match and capture the value of a specific header when multiple Set-Cookie headers with the same name exist. To manipulate that specific cookie's captured value, you can then use{capt_header_value_matcher}. Learn more about capture under Action set. - Server variable - To use a server variable, specify the syntax as
{var_serverVariable}. List of supported Server variables.
Note
The use of Header Value Matcher field {capt_header_value_matcher} isn't currently supported through the portal. Therefore, you need to use a non-portal method for any PUT operations if you use this field.
When you use an action to rewrite a URL, the following operations are supported:
- URL path: The new value to set as the path.
- URL Query String: The new value to which the query string must be rewritten.
- Re-evaluate path map: Specify if the URL path map must be re-evaluated after rewrite. If you don't check this option, the original URL path is used to match the path-pattern in the URL path map. If you set this option to true, the URL path map is re-evaluated to check the match with the rewritten path. Enabling this switch helps in routing the request to a different backend pool post rewrite.
Pattern matching and capturing
Application Gateway supports pattern matching and capturing under Condition and Action. Under Action, it supports pattern matching and capturing only for a specific header.
Pattern matching
Application Gateway uses regular expressions for pattern matching. Use Regular Expression 2 (RE2) compatible expressions when writing your pattern matching syntax.
You can use pattern matching under both Condition and Action.
- Condition: Use this setting to match the values for a Header or Server Variable. To match a pattern under "Conditions," use the "pattern" property.
- Action: Pattern matching under Action Set is available only for the response header
Set-Cookie. To match a pattern forSet-Cookieunder an action, use theHeaderValueMatcherproperty. If captured, its value can be used as{capt_header_value_matcher}. Because there can be multipleSet-Cookieheaders, pattern matching here allows you to look for a specific cookie. For example, for a certain version of user-agent, you want to rewrite theset-cookieresponse header forcookie2withmax-age=3600(one hour). In this case, you can use- Condition - Type: Request header, Header name: user-agent, Pattern to match: *2.0
- Action - Rewrite type: Response header, Action type: Set, Header name: Set-Cookie, Header Value Matcher:
cookie2=(.*), Header value:cookie2={capt_header_value_matcher_1};Max-Age=3600
Note
If you're running an Application Gateway Web Application Firewall (WAF) with Core Rule Set 3.1 or earlier, you might run into issues when using Perl Compatible Regular Expressions (PCRE) while doing lookahead and lookbehind (negative or positive) assertions.
Syntax for capturing
You can use patterns to capture a substring for later use. Put parentheses around a sub-pattern in the regex definition. The first pair of parentheses stores its substring in 1, the second pair in 2, and so on. You can use as many parentheses as you like. Perl defines more numbered variables to represent these captured strings. You can find some examples in this Perl programming guidance.
- (\d)(\d) # Match two digits, capturing them into groups 1 and 2
- (\d+) # Match one or more digits, capturing them all into group 1
- (\d)+ # Match a digit one or more times, capturing the last into group 1
Once captured, you can use them in the Action Set value using the following format:
- For a request header capture, you must use {http_req_headerName_groupNumber}. For example, {http_req_User-Agent_1} or {http_req_User-Agent_2}
- For a response header capture, you must use {http_resp_headerName_groupNumber}. For example, {http_resp_Location_1} or {http_resp_Location_2}. Whereas for a response header Set-Cookie captured through "HeaderValueMatcher" property, you must use {capt_header_value_matcher_groupNumber}. For example, {capt_header_value_matcher_1} or {capt_header_value_matcher_2}.
- For a server variable, you must use {var_serverVariableName_groupNumber}. For example, {var_uri_path_1} or {var_uri_path_2}
Note
- Use of / to prefix and suffix the pattern shouldn't be specified in the pattern to match value. For example, (\d)(\d) will match two digits. /(\d)(\d)/ won't match two digits.
- The case of the condition variable needs to match case of the capture variable. For example, if my condition variable is User-Agent, my capture variable must be for User-Agent (that is {http_req_User-Agent_2}). If my condition variable is defined as user-agent, my capture variable must be for user-agent (that is {http_req_user-agent_2}).
- If you want to use the whole value, you shouldn't mention the number. Simply use the format {http_req_headerName}, etc. without the groupNumber.
Server variables
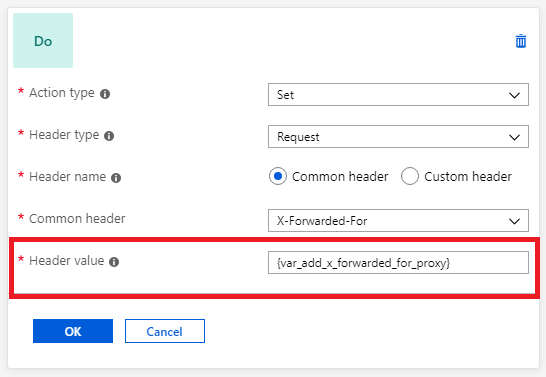
Application Gateway uses server variables to store useful information about the server, the connection with the client, and the current request on the connection. Examples of information stored include the client's IP address and the web browser type. Server variables change dynamically, for example, when a new page loads or when a form is posted. You can use these variables to evaluate rewrite conditions and rewrite headers. In order to use the value of server variables to rewrite headers, you need to specify these variables in the syntax {var_serverVariableName}
Application gateway supports the following server variables:
| Variable name | Description |
|---|---|
| add_x_forwarded_for_proxy | The X-Forwarded-For client request header field with the client_ip variable (see explanation later in this table) appended to it in the format IP1, IP2, IP3, and so on. If the X-Forwarded-For field isn't in the client request header, the add_x_forwarded_for_proxy variable is equal to the $client_ip variable. This variable is useful when you want to rewrite the X-Forwarded-For header set by Application Gateway so that the header contains only the IP address without the port information. |
| ciphers_supported | A list of the ciphers supported by the client. |
| ciphers_used | The string of ciphers used for an established TLS connection. |
| client_ip | The IP address of the client from which the application gateway received the request. If there's a reverse proxy before the application gateway and the originating client, client_ip returns the IP address of the reverse proxy. |
| client_port | The client port. |
| client_tcp_rtt | Information about the client TCP connection. Available on systems that support the TCP_INFO socket option. |
| client_user | When HTTP authentication is used, the user name supplied for authentication. |
| host | In this order of precedence: the host name from the request line, the host name from the Host request header field, or the server name matching a request. Example: In the request http://contoso.com:8080/article.aspx?id=123&title=fabrikam, the host value is contoso.com |
| cookie_name | The name cookie. |
| http_method | The method used to make the URL request. For example, GET or POST. |
| http_status | The session status. For example, 200, 400, or 403. |
| http_version | The request protocol. Usually HTTP/1.0, HTTP/1.1, or HTTP/2.0. |
| query_string | The list of variable/value pairs that follows the ? in the requested URL. Example: In the request http://contoso.com:8080/article.aspx?id=123&title=fabrikam, query_string value is id=123&title=fabrikam |
| received_bytes | The length of the request (including the request line, header, and request body). |
| request_query | The arguments in the request line. |
| request_scheme | The request scheme: http or https. |
| request_uri | The full original request URI (with arguments). Example: in the request http://contoso.com:8080/article.aspx?id=123&title=fabrikam*, request_uri value is /article.aspx?id=123&title=fabrikam |
| sent_bytes | The number of bytes sent to a client. |
| server_port | The port of the server that accepted a request. |
| ssl_connection_protocol | The protocol of an established TLS connection. |
| ssl_enabled | "On" if the connection operates in TLS mode. Otherwise, an empty string. |
| uri_path | Identifies the specific resource in the host that the web client wants to access. The variable refers to the original URL path before any manipulation. This is the part of the request URI without the arguments. For example, in the request http://contoso.com:8080/article.aspx?id=123&title=fabrikam, the uri_path value is /article.aspx. |
Mutual authentication server variables
Application Gateway supports the following server variables for mutual authentication scenarios. Use these server variables as you would other server variables.
| Variable name | Description |
|---|---|
| client_certificate | The client certificate in PEM format for an established SSL connection. |
| client_certificate_end_date | The end date of the client certificate. |
| client_certificate_fingerprint | The SHA1 fingerprint of the client certificate for an established SSL connection. |
| client_certificate_issuer | The "issuer DN" string of the client certificate for an established SSL connection. |
| client_certificate_serial | The serial number of the client certificate for an established SSL connection. |
| client_certificate_start_date | The start date of the client certificate. |
| client_certificate_subject | The "subject DN" string of the client certificate for an established SSL connection. |
| client_certificate_verification | The result of the client certificate verification: SUCCESS, FAILED:<reason>, or NONE if a certificate wasn't present. |
Common scenarios for header rewrite
Remove port information from the X-Forwarded-For header
Application Gateway inserts an X-Forwarded-For header into all requests before it forwards the requests to the backend. This header is a comma-separated list of IP ports. There might be scenarios in which the backend servers only need the headers to contain IP addresses. You can use header rewrite to remove the port information from the X-Forwarded-For header. One way to do this is to set the header to the add_x_forwarded_for_proxy server variable. Alternatively, you can also use the variable client_ip:
Modify a redirection URL
Modifying a redirect URL can be useful under certain circumstances. For example, you might originally redirect clients to a path like "/blog" but now want to send them to "/updates" due to a change in content structure.
Warning
You might need to modify a redirection URL when you configure Application Gateway to override the hostname toward the backend. In this configuration, the backend sees a different hostname than the browser. The redirect doesn't use the correct hostname. This configuration isn't recommended.
For more information about the limitations and implications of such a configuration, see Preserve the original HTTP host name between a reverse proxy and its backend web application. For the recommended setup for App Service, see "Custom Domain (recommended)" in Configure App Service with Application Gateway. Rewriting the location header on the response as described in the following example should be considered a workaround and doesn't address the root cause.
When the app service sends a redirection response, it uses the same hostname in the location header of its response as the one in the request it receives from the application gateway. So the client makes the request directly to contoso.azurewebsites.net/path2 instead of going through the application gateway (contoso.com/path2). Bypassing the application gateway isn't desirable.
You can resolve this issue by setting the hostname in the location header to the application gateway's domain name.
Here are the steps for replacing the hostname:
Create a rewrite rule with a condition that checks if the location header in the response contains azurewebsites.net. Enter the pattern `(https?)://.azurewebsites.net(.).
Perform an action to rewrite the location header so that it has the application gateway's hostname. Enter
{http_resp_Location_1}://contoso.com{http_resp_Location_2}as the header value. Alternatively, you can also use the server variablehostto set the hostname to match the original request.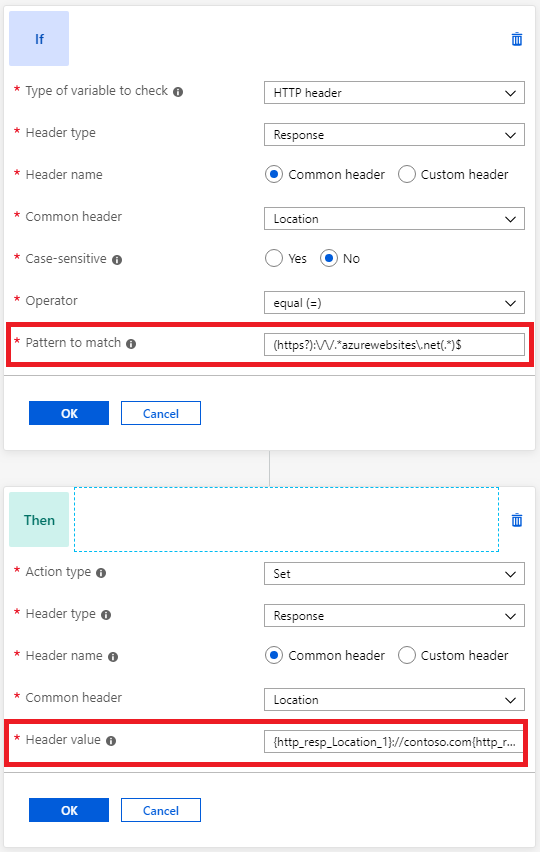
Implement security HTTP headers to prevent vulnerabilities
You can fix several security vulnerabilities by implementing necessary headers in the application response. These security headers include X-XSS-Protection, Strict-Transport-Security, and Content-Security-Policy. You can use Application Gateway to set these headers for all responses.
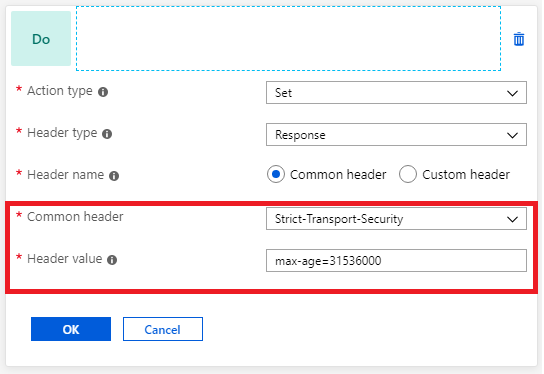
Delete unwanted headers
You might want to remove headers that reveal sensitive information from an HTTP response. For example, you might want to remove information like the backend server name, operating system, or library details. You can use the application gateway to remove these headers:
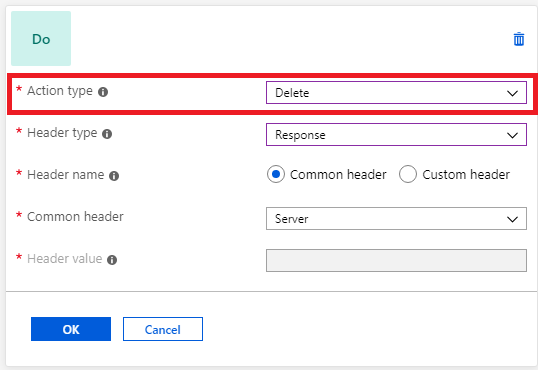
You can't create a rewrite rule to delete the host header. If you attempt to create a rewrite rule with the action type set to delete and the header set to host, it results in an error.
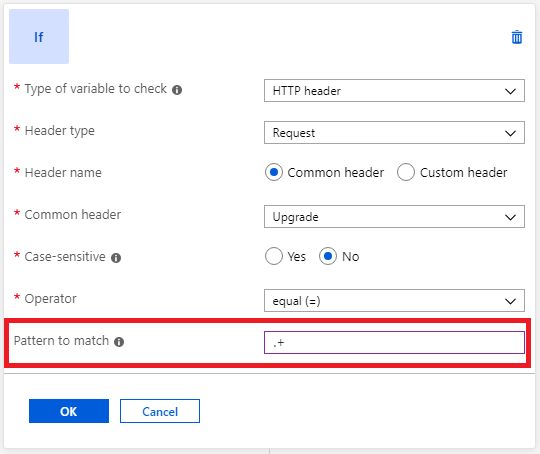
Check for the presence of a header
You can evaluate an HTTP request or response header for the presence of a header or server variable. This evaluation is useful when you want to perform a header rewrite only when a certain header is present.
Common scenarios for URL rewrite
Parameter based path selection
To accomplish scenarios where you want to choose the backend pool based on the value of a header, part of the URL, or query string in the request, use a combination of URL Rewrite capability and path-based routing.
Create a rewrite set with a condition that checks for a specific parameter (query string, header, etc.) and then performs an action where it changes the URL path (ensure Reevaluate path map is enabled). Associate the rewrite set to a path based rule. The path based rule must contain the same URL paths specified in the rewrite set and their corresponding backend pool.
Thus, the rewrite set allows you to check for a specific parameter and assign it a new path, and the path based rule allows you to assign backend pools to those paths. As long as "Reevaluate path map" is enabled, traffic routes based on the path specified in the rewrite set.
For a use case example using query strings, see Route traffic using parameter based path selection in portal.
Rewrite query string parameters based on the URL
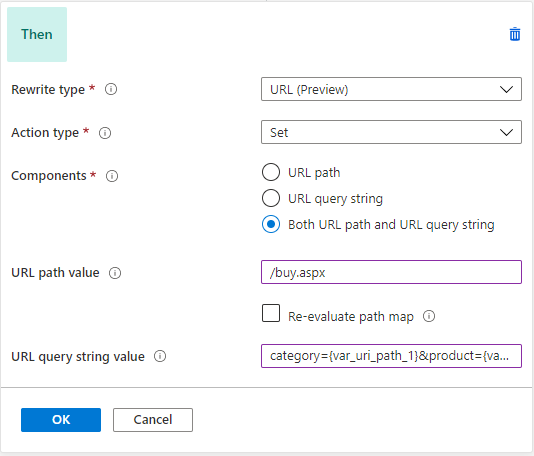
Consider a scenario of a shopping website where the user-visible link is simple and legible, but the backend server needs the query string parameters to show the right content.
In that case, Application Gateway can capture parameters from the URL and add query string key-value pairs from those parameters in the URL. For example, if the user wants to rewrite https://www.contoso.com/fashion/shirts to https://www.contoso.com/buy.aspx?category=fashion&product=shirts, you can achieve this goal through the following URL rewrite configuration.
Condition - If server variable uri_path equals the pattern /(.+)/(.+)
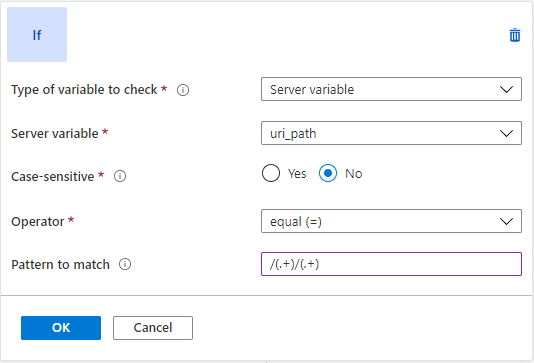
Action - Set URL path to buy.aspx and query string to category={var_uri_path_1}&product={var_uri_path_2}
For a step-by-step guide to achieve the scenario described earlier, see Rewrite URL with Application Gateway using Azure portal.
Rewrite configuration common pitfalls
You can't enable 'Reevaluate path map' for basic request routing rules. This restriction prevents an infinite evaluation loop for a basic routing rule.
For path-based routing rules, you need at least one conditional rewrite rule or one rewrite rule without 'Reevaluate path map' enabled. This requirement prevents an infinite evaluation loop for a path-based routing rule.
If a loop is created dynamically based on client inputs, incoming requests terminate with a 500 error code. Application Gateway continues to serve other requests without any degradation in this scenario.
Using URL rewrite or Host header rewrite with Web Application Firewall (WAF_v2 SKU)
When you configure URL rewrite or host header rewrite, the WAF evaluation happens after the modification to the request header or URL parameters (post-rewrite). When you remove the URL rewrite or host header rewrite configuration on your Application Gateway, the WAF evaluation happens before the header rewrite (pre-rewrite). This order ensures that WAF rules apply to the final request that your backend pool receives.
For example, suppose you have the following header rewrite rule for the header "Accept" : "text/html" - if the value of header "Accept" is equal to "text/html", then rewrite the value to "image/png".
With only header rewrite configured, the WAF evaluation happens on "Accept" : "text/html". But when you configure URL rewrite or host header rewrite, the WAF evaluation happens on "Accept" : "image/png".
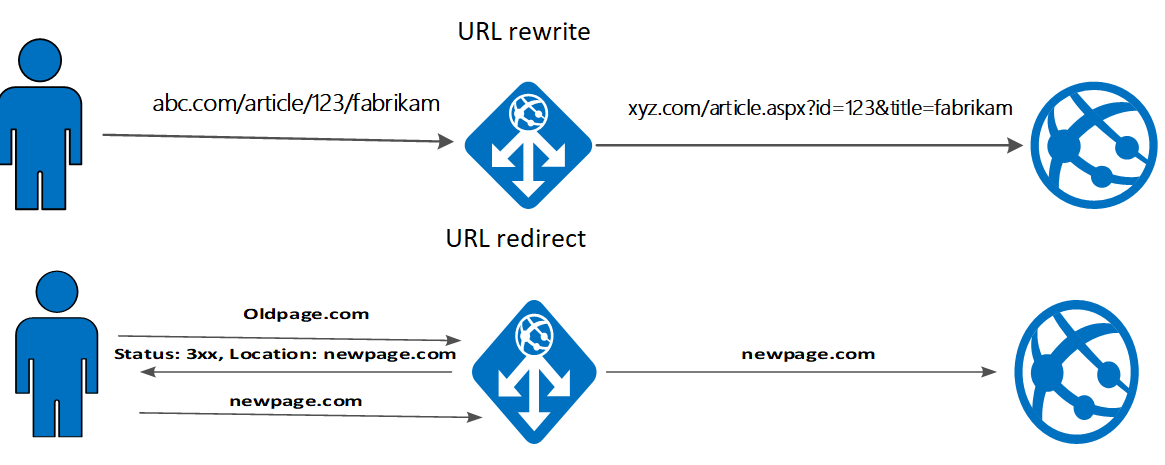
URL rewrite vs URL redirect
For a URL rewrite, Application Gateway rewrites the URL before it sends the request to the backend. This action doesn't change what users see in the browser because the changes are hidden from the user.
For a URL redirect, Application Gateway sends a redirect response to the client with the new URL. That response requires the client to resend its request to the new URL provided in the redirect. The URL that the user sees in the browser updates to the new URL.
Limitations
- Rewrites aren't supported when the application gateway is configured to redirect the requests or to show a custom error page.
- Request header names can contain alphanumeric characters and hyphens. Header names containing other characters are discarded when a request is sent to the backend target.
- Response header names can contain any alphanumeric characters and specific symbols as defined in RFC 7230.
- You can't rewrite
X-Original-Host,Connection, andupgradeheaders. - Rewrites aren't supported for 4xx and 5xx responses generated directly from Application Gateway.