What is Azure Automation?
Automation is needed in three broad areas of cloud operations:
- Deploy and manage - Deliver repeatable and consistent infrastructure as code.
- Response - Create event-based automation to diagnose and resolve issues.
- Orchestrate - Orchestrate and integrate your automation with other Azure or third party services and products.
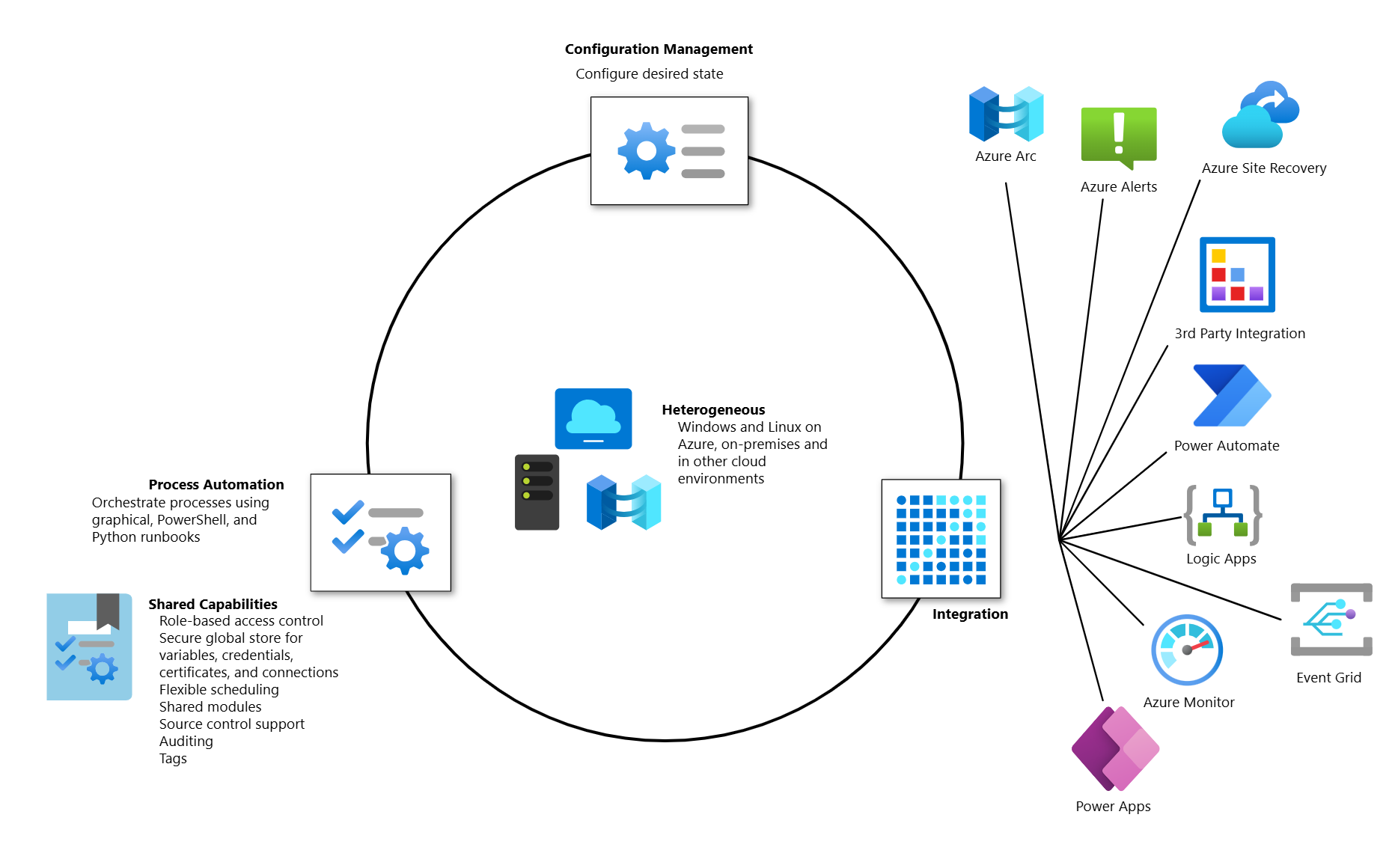
Azure Automation delivers a cloud-based automation, operating system updates, and configuration service that supports consistent management across your Azure and non-Azure environments. It includes process automation, configuration management, update management, shared capabilities, and heterogeneous features.
There are several Azure services that can deliver the above requirements, where each service includes a set of capabilities and serves a role as a programmable platform to build cloud solutions. For example, Azure Bicep and Resource Manager provide a language to develop repeatable and consistent deployment templates for Azure resources. Azure Automation can process that template to deploy an Azure resource and then process a set of post-deployment configuration tasks.
Automation gives you complete control during deployment, operations, and decommissioning of enterprise workloads and resources.
Process Automation
Process Automation in Azure Automation allows you to automate frequent, time-consuming, and error-prone management tasks. This service helps you focus on work that adds business value. By reducing errors and boosting efficiency, it also helps to lower your operational costs. The process automation operating environment is detailed in Runbook execution in Azure Automation.
Process automation supports the integration of Azure services and other third party systems required in deploying, configuring, and managing your end-to-end processes. The service allows you to author graphical, PowerShell and Python runbooks. To run runbooks directly on the Windows or Linux machine or against resources in the on-premises or other cloud environment to manage those local resources, you can deploy a Hybrid Runbook Worker to the machine.
Webhooks let you fulfill requests and ensure continuous delivery and operations by triggering automation from Azure Logic Apps, Azure Function, ITSM product or service, DevOps, and monitoring systems.
Configuration Management
Configuration Management in Azure Automation is supported by Azure Automation State Configuration capability.
Azure Automation State Configuration
Azure Automation State Configuration is a cloud-based feature for PowerShell desired state configuration (DSC) that provides services for enterprise environments. Using this feature, you can manage your DSC resources in Azure Automation and apply configurations to virtual or physical machines from a DSC pull server in the Azure cloud.
Shared capabilities
Azure Automation provides a number of shared capabilities, including shared resources, role-based access control, flexible scheduling, source control integration, auditing, and tagging.
Shared resources
Azure Automation consists of a set of shared resources that make it easier to automate and configure your environments at scale.
- Schedules - Trigger Automation operations at predefined times.
- Modules - Manage Azure and other systems. You can import modules into the Automation account for Microsoft, third-party, community, and custom-defined cmdlets and DSC resources.
- Modules gallery - Supports native integration with the PowerShell Gallery to let you view runbooks and import them into the Automation account. The gallery allows you to quickly get started integrating and authoring your processes from PowerShell gallery and Microsoft Script Center.
- Python 2 and 3 packages - Support Python 2 and 3 runbooks for your Automation account.
- Credentials - Securely store sensitive information that runbooks and configurations can use at runtime.
- Connections - Store name-value pairs of common information for connections to systems. The module author defines connections in runbooks and configurations for use at runtime.
- Certificates - Define information to be used in authentication and securing of deployed resources when accessed by runbooks or DSC configurations at runtime.
- Variables - Hold content that can be used across runbooks and configurations. You can change variable values without having to modify any of the runbooks or configurations that reference them.
Role-based access control
Azure Automation supports Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) to regulate access to the Automation account and its resources. To learn more about configuring Azure RBAC on your Automation account, runbooks, and jobs, see Role-based access control for Azure Automation.
Source control integration
Azure Automation supports source control integration. This feature promotes configuration as code where runbooks or configurations can be checked into a source control system.
Heterogeneous support (Windows and Linux)
Automation is designed to work across Windows and Linux physical servers and virtual machines outside of Azure, on your corporate network, or other cloud provider. It delivers a consistent way to automate and configure deployed workloads and the operating systems that run them. The Hybrid Runbook Worker feature of Azure Automation enables running runbooks directly on the non-Azure physical server or virtual machine hosting the role, and against resources in the environment to manage those local resources.
Through Arc-enabled servers, it provides a consistent deployment and management experience for your non-Azure machines. It enables integration with the Automation service using the VM extension framework to deploy the Hybrid Runbook Worker role, and simplify onboarding to Update Management and Change Tracking and Inventory.
Common scenarios
Azure Automation supports management throughout the lifecycle of your infrastructure and applications. Common scenarios include:
- Schedule tasks - stop VMs or services at night and turn on during the day, weekly or monthly recurring maintenance workflows.
- Build and deploy resources - Deploy virtual machines across a hybrid environment using runbooks and Azure Resource Manager templates. Integrate into development tools, such as Jenkins and Azure DevOps.
- Periodic maintenance - to execute tasks that need to be performed at set timed intervals like purging stale or old data, or reindexing a SQL database.
- Respond to alerts - Orchestrate a response when cost-based, system-based, service-based, and/or resource utilization alerts are generated.
- Hybrid automation - Manage or automate on-premises servers and services like SQL Server, Active Directory, SharePoint Server, etc.
- Azure resource lifecycle management - for IaaS and PaaS services.
- Resource provisioning and deprovisioning.
- Add correct tags, locks, NSGs, UDRs per business rules.
- Resource group creation, deletion & update.
- Start container group.
- Register DNS record.
- Encrypt Virtual machines.
- Configure disk (disk snapshot, delete old snapshots).
- Subscription management.
- Start-stop resources to save cost.
- Monitoring & integrate with 1st party (through Azure Monitor) or 3rd party external systems.
- Ensure resource creation\deletion operations are captured to SQL.
- Send resource usage data to web API.
- Send monitoring data to ServiceNow, Event Hubs, New Relic and so on.
- Collect and store information about Azure resources.
- Perform SQL monitoring checks & reporting.
- Check website availability.
- Dev/test automation scenarios - Stop and start resources, scale resources, etc.
- Governance related automation - Automatically apply or update tags, locks, etc.
- Azure Site Recovery - orchestrate pre/post scripts defined in a Site Recovery DR workflow.
- Azure Virtual Desktop - orchestrate scaling of VMs or start/stop VMs based on utilization.
- Configure VMs - Assess and configure Windows and Linux machines with configurations for the infrastructure and application.
- Retrieve inventory - Get a complete inventory of deployed resources for targeting, reporting, and compliance.
- Find changes - Identify and isolate machine changes that can cause misconfiguration and improve operational compliance. Remediate or escalate them to management systems.
Depending on your requirements, one or more of the following Azure services integrate with or complement Azure Automation to help fulfill them:
- Azure Arc-enabled servers enables simplified onboarding of hybrid machines to Update Management, Change Tracking and Inventory, and the Hybrid Runbook Worker role.
- Azure Alerts action groups can initiate an Automation runbook when an alert is raised.
- Azure Monitor to collect metrics and log data from your Automation account for further analysis and take action on the telemetry. Automation features such as Update Management and Change Tracking and Inventory rely on the Log Analytics workspace to deliver elements of their functionality.
- Azure Policy includes initiative definitions to help establish and maintain compliance with different security standards for your Automation account.
- Azure Site Recovery can use Azure Automation runbooks to automate recovery plans.
These Azure services can work with Automation job and runbook resources using an HTTP webhook or API method:
Note
This service supports Azure Lighthouse, which lets service providers sign in to their own tenant to manage subscriptions and resource groups that customers have delegated.
Pricing for Azure Automation
Process automation includes runbook jobs and watchers. Billing for jobs is based on the number of job run time minutes used in the month, and for watchers, it is on the number of hours used in a month. The charges for process automation are incurred whenever a job or watcher runs. You create Automation accounts with a Basic SKU, wherein the first 500 job run time minutes are free per subscription. You are billed only for minutes/hours that exceed the 500 mins free included units.
You can review the prices associated with Azure Automation on the pricing page.