Σημείωση
Η πρόσβαση σε αυτή τη σελίδα απαιτεί εξουσιοδότηση. Μπορείτε να δοκιμάσετε να συνδεθείτε ή να αλλάξετε καταλόγους.
Η πρόσβαση σε αυτή τη σελίδα απαιτεί εξουσιοδότηση. Μπορείτε να δοκιμάσετε να αλλάξετε καταλόγους.
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
A pipeline in an Azure Data Factory or Synapse Analytics workspace processes data in linked storage services by using linked compute services. It contains a sequence of activities where each activity performs a specific processing operation. This article describes the Data Lake Analytics U-SQL Activity that runs a U-SQL script on an Azure Data Lake Analytics compute linked service.
Create an Azure Data Lake Analytics account before creating a pipeline with a Data Lake Analytics U-SQL Activity. To learn about Azure Data Lake Analytics, see Get started with Azure Data Lake Analytics.
Add a U-SQL activity for Azure Data Lake Analytics to a pipeline with UI
To use a U-SQL activity for Azure Data Lake Analytics in a pipeline, complete the following steps:
Search for Data Lake in the pipeline Activities pane, and drag a U-SQL activity to the pipeline canvas.
Select the new U-SQL activity on the canvas if it is not already selected.
Select the ADLA Account tab to select or create a new Azure Data Lake Analytics linked service that will be used to execute the U-SQL activity.
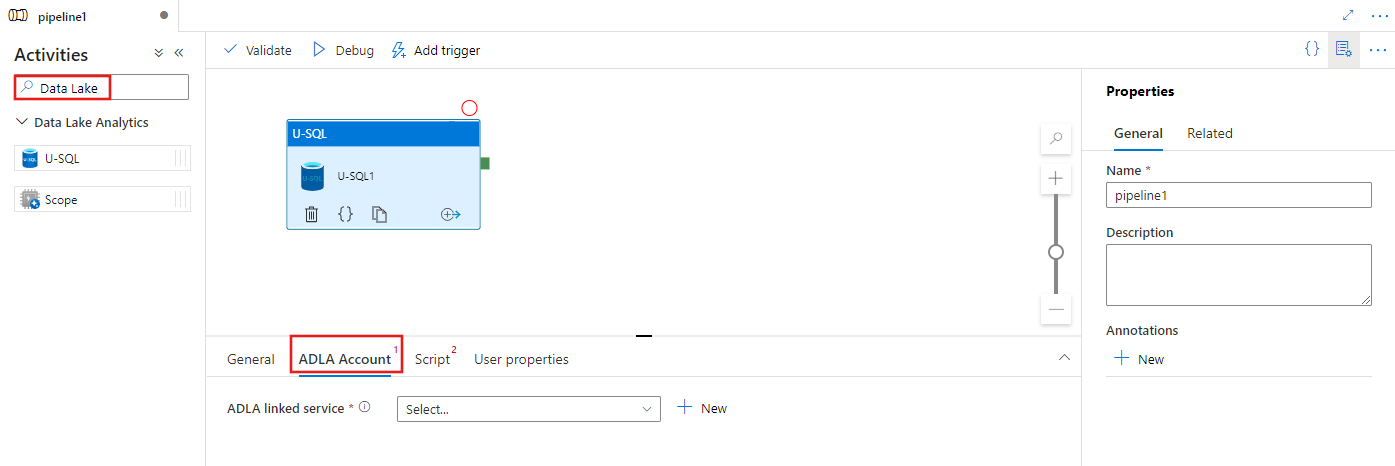
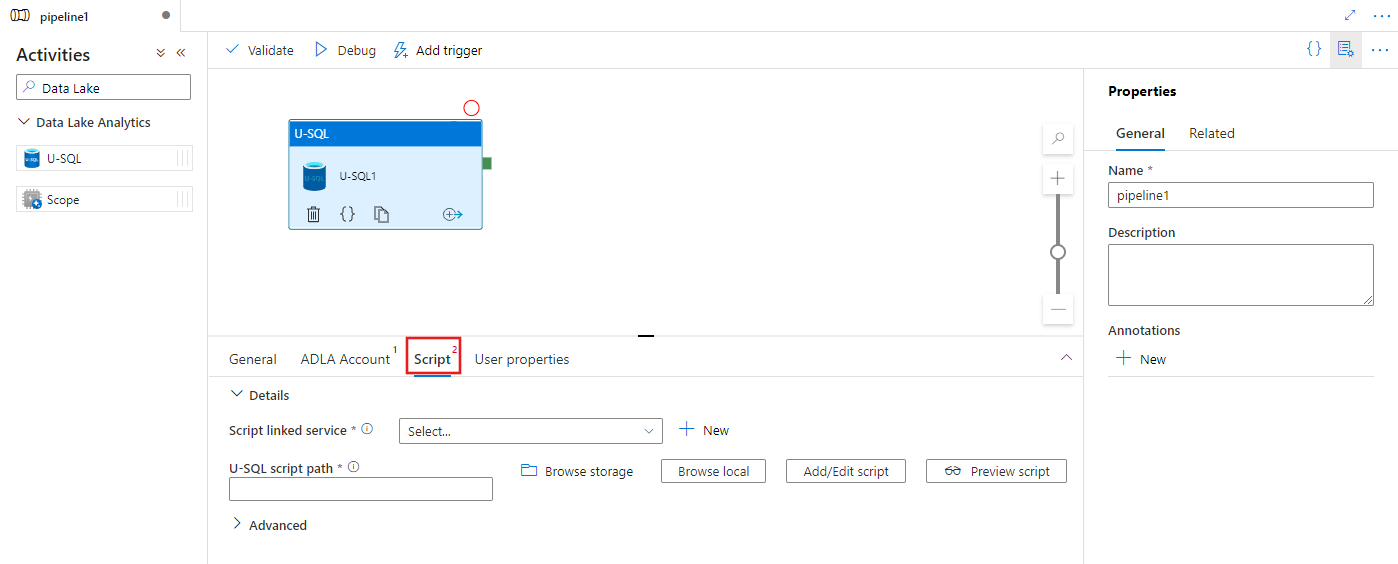
Select the Script tab to select or create a new storage linked service, and a path within the storage location, which will host the script.
Azure Data Lake Analytics linked service
You create an Azure Data Lake Analytics linked service to link an Azure Data Lake Analytics compute service to an Azure Data Factory or Synapse Analytics workspace. The Data Lake Analytics U-SQL activity in the pipeline refers to this linked service.
The following table provides descriptions for the generic properties used in the JSON definition.
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property should be set to: AzureDataLakeAnalytics. | Yes |
| accountName | Azure Data Lake Analytics Account Name. | Yes |
| dataLakeAnalyticsUri | Azure Data Lake Analytics URI. | No |
| subscriptionId | Azure subscription ID | No |
| resourceGroupName | Azure resource group name | No |
Service principal authentication
The Azure Data Lake Analytics linked service requires a service principal authentication to connect to the Azure Data Lake Analytics service. To use service principal authentication, register an application entity in Microsoft Entra ID and grant it the access to both the Data Lake Analytics and the Data Lake Store it uses. For detailed steps, see Service-to-service authentication. Make note of the following values, which you use to define the linked service:
- Application ID
- Application key
- Tenant ID
Grant service principal permission to your Azure Data Lake Analytics using the Add User Wizard.
Use service principal authentication by specifying the following properties:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| servicePrincipalId | Specify the application's client ID. | Yes |
| servicePrincipalKey | Specify the application's key. | Yes |
| tenant | Specify the tenant information (domain name or tenant ID) under which your application resides. You can retrieve it by hovering the mouse in the upper-right corner of the Azure portal. | Yes |
Example: Service principal authentication
{
"name": "AzureDataLakeAnalyticsLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureDataLakeAnalytics",
"typeProperties": {
"accountName": "<account name>",
"dataLakeAnalyticsUri": "<azure data lake analytics URI>",
"servicePrincipalId": "<service principal id>",
"servicePrincipalKey": {
"value": "<service principal key>",
"type": "SecureString"
},
"tenant": "<tenant info, e.g. microsoft.onmicrosoft.com>",
"subscriptionId": "<optional, subscription id of ADLA>",
"resourceGroupName": "<optional, resource group name of ADLA>"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
To learn more about the linked service, see Compute linked services.
Data Lake Analytics U-SQL Activity
The following JSON snippet defines a pipeline with a Data Lake Analytics U-SQL Activity. The activity definition has a reference to the Azure Data Lake Analytics linked service you created earlier. To execute a Data Lake Analytics U-SQL script, the service submits the script you specified to the Data Lake Analytics, and the required inputs and outputs is defined in the script for Data Lake Analytics to fetch and output.
{
"name": "ADLA U-SQL Activity",
"description": "description",
"type": "DataLakeAnalyticsU-SQL",
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "<linked service name of Azure Data Lake Analytics>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"typeProperties": {
"scriptLinkedService": {
"referenceName": "<linked service name of Azure Data Lake Store or Azure Storage which contains the U-SQL script>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"scriptPath": "scripts\\kona\\SearchLogProcessing.txt",
"degreeOfParallelism": 3,
"priority": 100,
"parameters": {
"in": "/datalake/input/SearchLog.tsv",
"out": "/datalake/output/Result.tsv"
}
}
}
The following table describes names and descriptions of properties that are specific to this activity.
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| name | Name of the activity in the pipeline | Yes |
| description | Text describing what the activity does. | No |
| type | For Data Lake Analytics U-SQL activity, the activity type is DataLakeAnalyticsU-SQL. | Yes |
| linkedServiceName | Linked Service to Azure Data Lake Analytics. To learn about this linked service, see Compute linked services article. | Yes |
| scriptPath | Path to folder that contains the U-SQL script. Name of the file is case-sensitive. | Yes |
| scriptLinkedService | Linked service that links the Azure Data Lake Store or Azure Storage that contains the script | Yes |
| degreeOfParallelism | The maximum number of nodes simultaneously used to run the job. | No |
| priority | Determines which jobs out of all that are queued should be selected to run first. The lower the number, the higher the priority. | No |
| parameters | Parameters to pass into the U-SQL script. | No |
| runtimeVersion | Runtime version of the U-SQL engine to use. | No |
| compilationMode | Compilation mode of U-SQL. Must be one of these values: Semantic: Only perform semantic checks and necessary sanity checks, Full: Perform the full compilation, including syntax check, optimization, code generation, etc., SingleBox: Perform the full compilation, with TargetType setting to SingleBox. If you don't specify a value for this property, the server determines the optimal compilation mode. |
No |
See SearchLogProcessing.txt for the script definition.
Sample U-SQL script
@searchlog =
EXTRACT UserId int,
Start DateTime,
Region string,
Query string,
Duration int,
Urls string,
ClickedUrls string
FROM @in
USING Extractors.Tsv(nullEscape:"#NULL#");
@rs1 =
SELECT Start, Region, Duration
FROM @searchlog
WHERE Region == "en-gb";
@rs1 =
SELECT Start, Region, Duration
FROM @rs1
WHERE Start <= DateTime.Parse("2012/02/19");
OUTPUT @rs1
TO @out
USING Outputters.Tsv(quoting:false, dateTimeFormat:null);
In above script example, the input and output to the script is defined in @in and @out parameters. The values for @in and @out parameters in the U-SQL script are passed dynamically by the service using the ‘parameters’ section.
You can specify other properties such as degreeOfParallelism and priority as well in your pipeline definition for the jobs that run on the Azure Data Lake Analytics service.
Dynamic parameters
In the sample pipeline definition, in and out parameters are assigned with hard-coded values.
"parameters": {
"in": "/datalake/input/SearchLog.tsv",
"out": "/datalake/output/Result.tsv"
}
It is possible to use dynamic parameters instead. For example:
"parameters": {
"in": "/datalake/input/@{formatDateTime(pipeline().parameters.WindowStart,'yyyy/MM/dd')}/data.tsv",
"out": "/datalake/output/@{formatDateTime(pipeline().parameters.WindowStart,'yyyy/MM/dd')}/result.tsv"
}
In this case, input files are still picked up from the /datalake/input folder and output files are generated in the /datalake/output folder. The file names are dynamic based on the window start time being passed in when pipeline gets triggered.
Related content
See the following articles that explain how to transform data in other ways: