Tutorial: Device Update for Azure IoT Hub using the Ubuntu (18.04 x64) simulator reference agent
Device Update for Azure IoT Hub supports image-based, package-based, and script-based updates.
Image updates provide a higher level of confidence in the end state of the device. It's typically easier to replicate the results of an image update between a preproduction environment and a production environment because it doesn't pose the same challenges as packages and their dependencies. Because of their atomic nature, you can also adopt an A/B failover model easily.
This tutorial walks you through the steps to complete an end-to-end image-based update by using Device Update for IoT Hub.
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to:
- Download and install an image.
- Add a tag to your IoT device.
- Import an update.
- Create a device group.
- Deploy an image update.
- Monitor the update deployment.
Prerequisites
If you haven't already done so, create a Device Update account and instance and configure an IoT hub.
Download the zip file named Tutorial_Simulator.zip from Release Assets in the latest release, and unzip it.
Add a device to Azure IoT Hub
After the Device Update agent is running on an IoT device, you must add the device to IoT Hub. From within IoT Hub, a connection string is generated for a particular device.
From the Azure portal, start the Device Update for IoT Hub.
Create a new device.
On the left pane, go to Devices. Then select New.
Under Device ID, enter a name for the device. Ensure that the Autogenerate keys checkbox is selected.
Select Save.
Now, you're returned to the Devices page and the device you created should be in the list. Select that device.
In the device view, select the Copy icon next to Primary Connection String.
Paste the copied characters somewhere for later use in the following steps:
This copied string is your device connection string.
Install a Device Update agent to test it as a simulator
Follow the instructions to install the Azure IoT Edge runtime.
Note
The Device Update agent doesn't depend on IoT Edge. But it does rely on the IoT Identity Service daemon that's installed with IoT Edge (1.2.0 and higher) to obtain an identity and connect to IoT Hub.
Although not covered in this tutorial, the IoT Identity Service daemon can be installed standalone on Linux-based IoT devices. The sequence of installation matters. The Device Update package agent must be installed after the IoT Identity Service. Otherwise, the package agent won't be registered as an authorized component to establish a connection to IoT Hub.
Then, install the Device Update agent .deb packages.
sudo apt-get install deviceupdate-agent deliveryoptimization-plugin-aptEnter your IoT device's module (or device, depending on how you provisioned the device with Device Update) primary connection string in the configuration file by running the following command:
sudo nano /etc/adu/du-config.jsonSet up the agent to run as a simulator. Run the following command on the IoT device so that the Device Update agent invokes the simulator handler to process a package update with APT ('microsoft/apt:1'):
sudo /usr/bin/AducIotAgent --register-content-handler /var/lib/adu/extensions/sources/libmicrosoft_simulator_1.so --update-type 'microsoft/apt:1'To register and invoke the simulator handler, use the following format, filling in the placeholders:
sudo /usr/bin/AducIotAgent --register--content-handler <full path to the handler file> --update-type <update type name>You will need the file
sample-du-simulator-data.jsonfrom the downloadedTutorial_Simulator.zipin the prerequisites.Open the file
sample-du-simulator-data.jsonand copy contents to clipboard:nano sample-du-simulator-data.jsonSelect the contents of the file and press Ctrl+C. Press Ctrl+X to close the file and don't save changes.
Run the following command to create and edit the
du-simulator-data.jsonfile in the tmp folder:sudo nano /tmp/du-simulator-data.jsonPress Ctrl+V to paste the contents into the editor. Select Ctrl+X to save the changes, and then Y.
Change permissions:
sudo chown adu:adu /tmp/du-simulator-data.json sudo chmod 664 /tmp/du-simulator-data.jsonIf /tmp doesn't exist, then:
sudo mkdir/tmp sudo chown root:root/tmp sudo chmod 1777/tmpRestart the Device Update agent by running the following command:
sudo systemctl restart adu-agent
Device Update for Azure IoT Hub software is subject to the following license terms:
Read the license terms prior to using the agent. Your installation and use constitutes your acceptance of these terms. If you don't agree with the license terms, don't use the Device Update for IoT Hub agent.
Note
After your testing with the simulator, run the following command to invoke the APT handler and deploy over-the-air package updates:
# sudo /usr/bin/AducIotAgent --register-content-handler /var/lib/adu/extensions/sources/libmicrosoft_apt_1.so --update-type 'microsoft/a pt:1'
Add a tag to your device
Sign in to the Azure portal and go to the IoT hub.
From Devices on the left pane, find your IoT device and go to the device twin or module twin.
In the module twin of the Device Update agent module, delete any existing Device Update tag values by setting them to null. If you're using the device identity with a Device Update agent, make these changes on the device twin.
Add a new Device Update tag value, as shown:
"tags": { "ADUGroup": "<CustomTagValue>" }
Import the update
You will need the files
TutorialImportManifest_Sim.importmanifest.jsonandadu-update-image-raspberrypi3.swufrom the downloadedTutorial_Simulator.zipin the prerequisites. The update file is reused from the Raspberry Pi tutorial. Because the update in this tutorial is simulated, the specific file content doesn't matter.Sign in to the Azure portal and go to your IoT hub with Device Update. On the left pane, under Automatic Device Management, select Updates.
Select the Updates tab.
Select + Import New Update.
Select + Select from storage container. Select an existing account or create a new account by using + Storage account. Then select an existing container or create a new container by using + Container. This container will be used to stage your update files for importing.
Note
We recommend that you use a new container each time you import an update to avoid accidentally importing files from previous updates. If you don't use a new container, be sure to delete any files from the existing container before you finish this step.
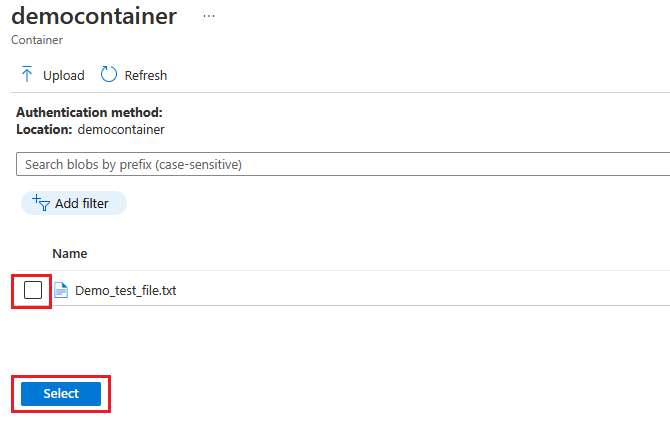
In your container, select Upload and go to the files you downloaded in step 1. After you've selected all your update files, select Upload. Then select the Select button to return to the Import update page.
This screenshot shows the import step. File names might not match the ones used in the example.
On the Import update page, review the files to be imported. Then select Import update to start the import process.
The import process begins, and the screen switches to the Import History section. When the Status column indicates the import has succeeded, select the Available updates header. You should see your imported update in the list now.
Learn more about how to import updates.
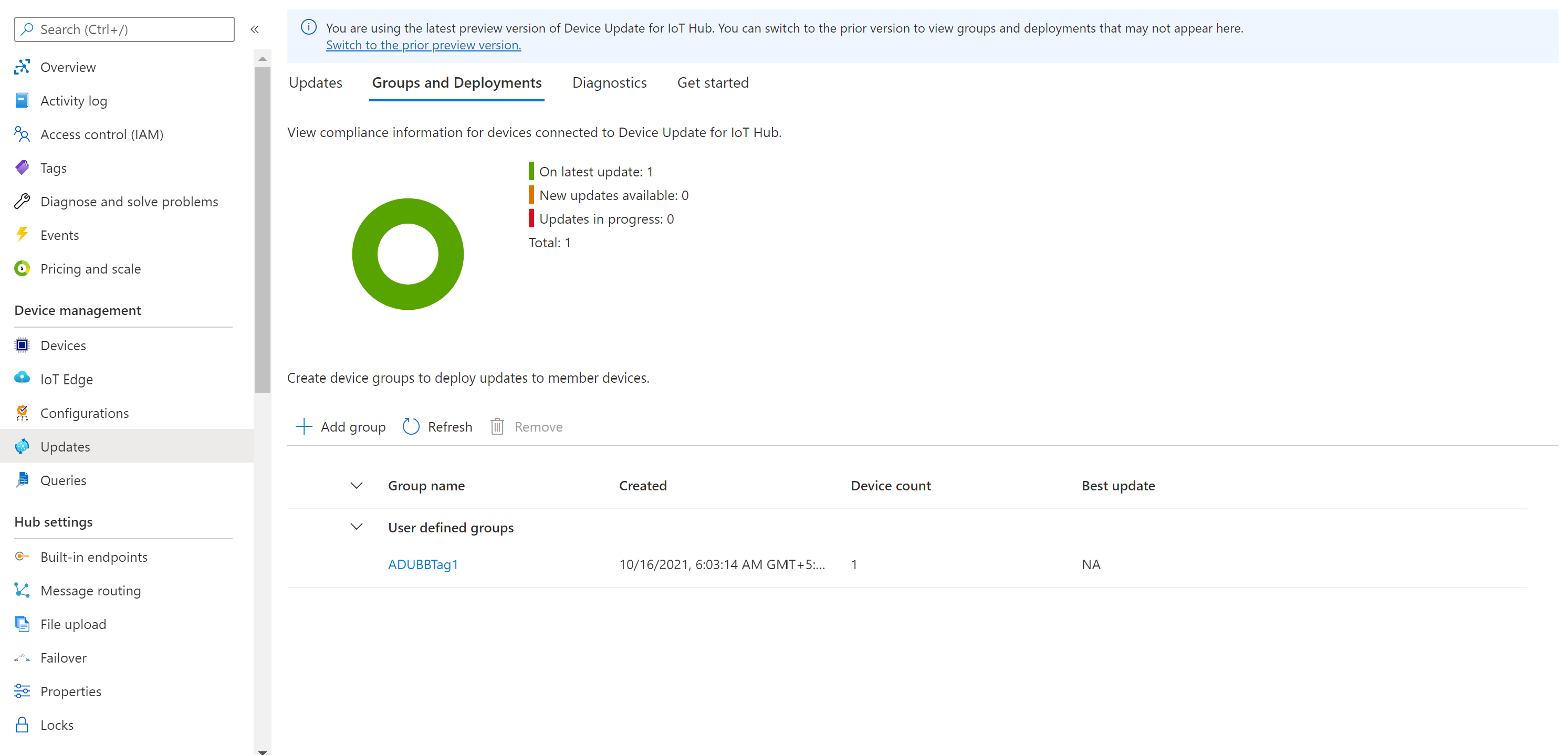
Create an update group
Go to the Groups and Deployments tab at the top of the page.
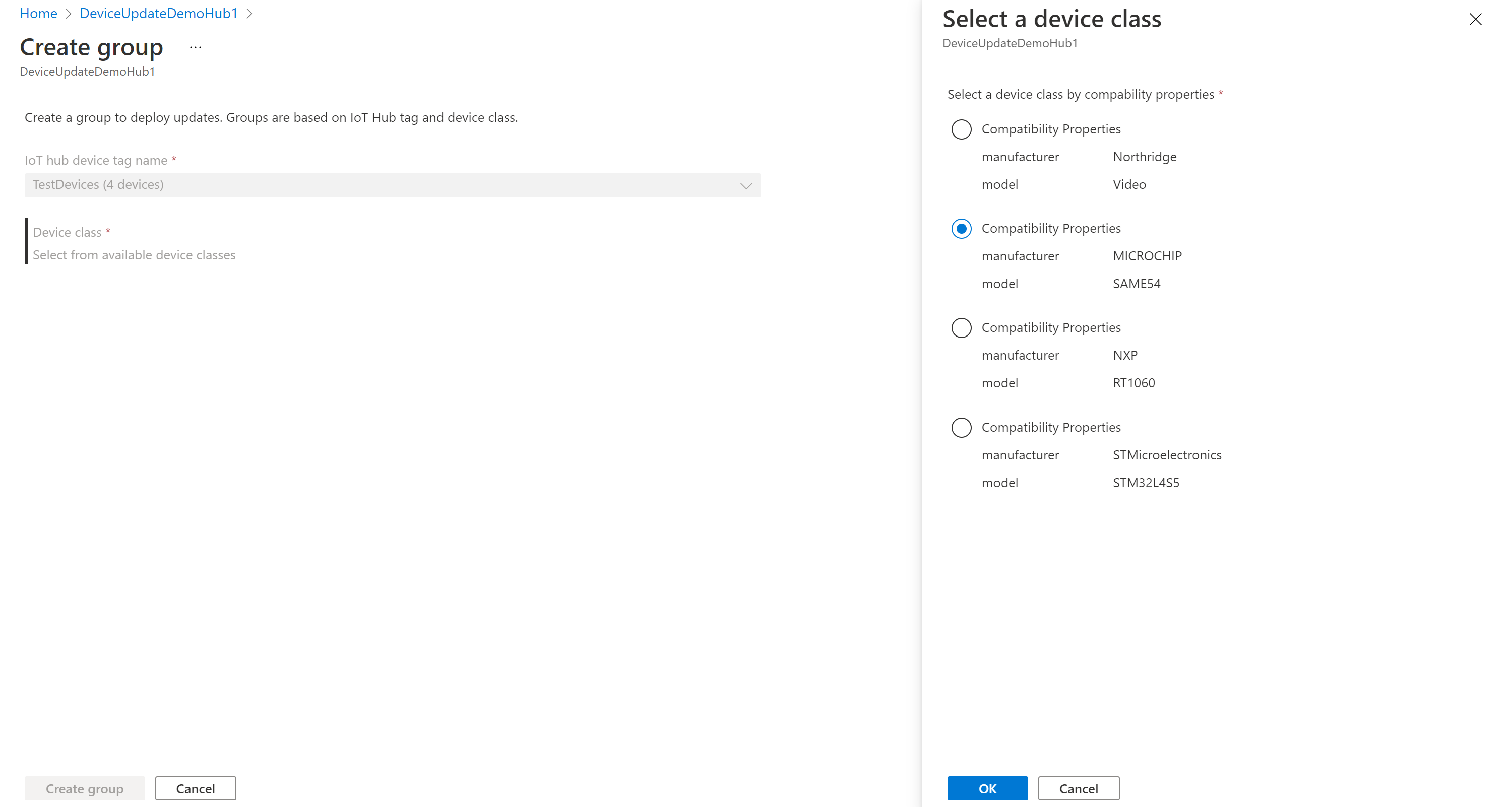
Select Add group to create a new group.
Select an IoT Hub tag and Device Class from the list. Then select Create group.
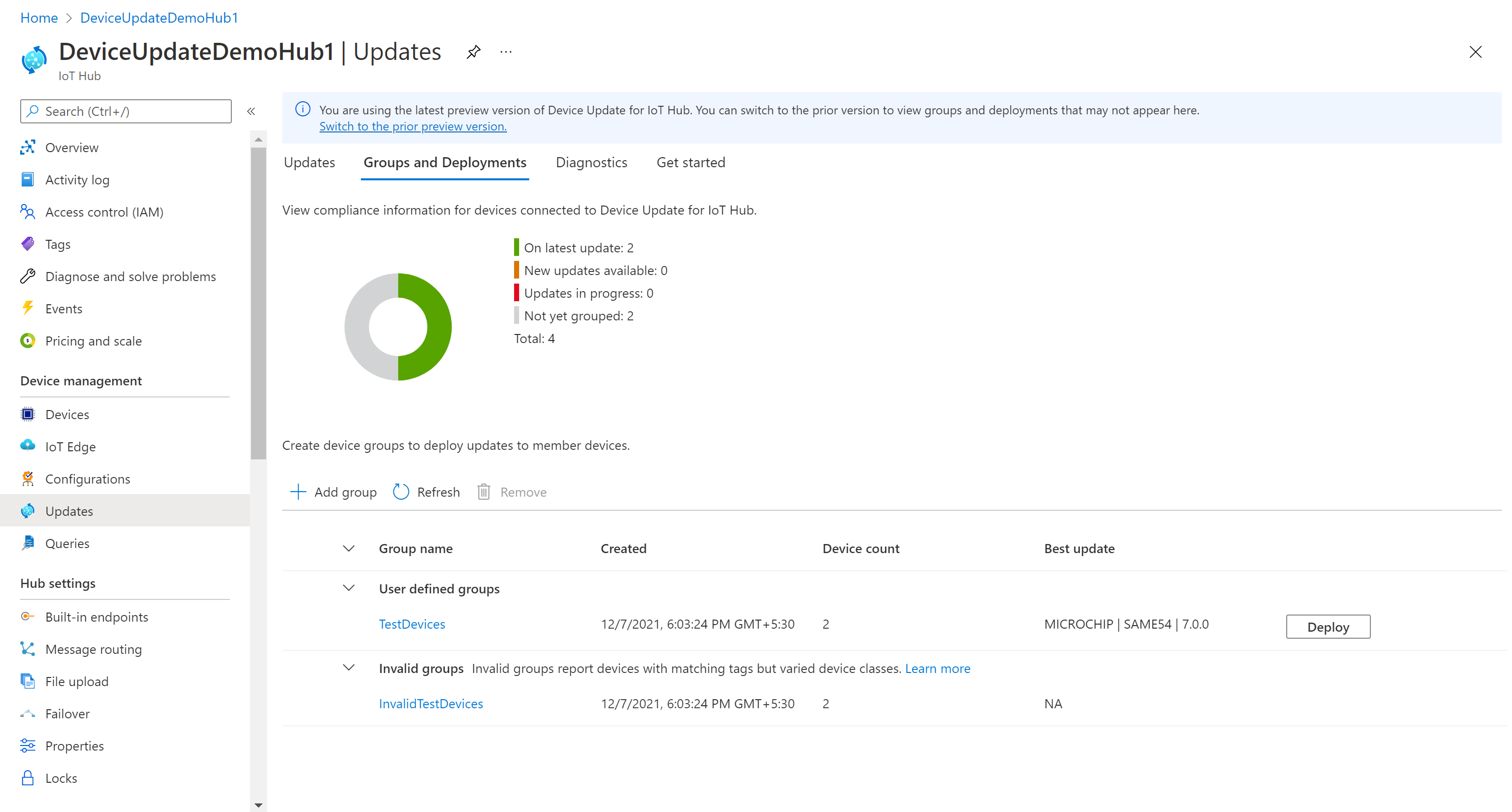
After the group is created, the update compliance chart and groups list are updated. The update compliance chart shows the count of devices in various states of compliance: On latest update, New updates available, and Updates in progress. Learn about update compliance.
You should see your newly created group and any available updates for the devices in the new group. If there are devices that don't meet the device class requirements of the group, they'll show up in a corresponding invalid group. To deploy the best available update to the new user-defined group from this view, select Deploy next to the group.
Learn more about how to add tags and create update groups.
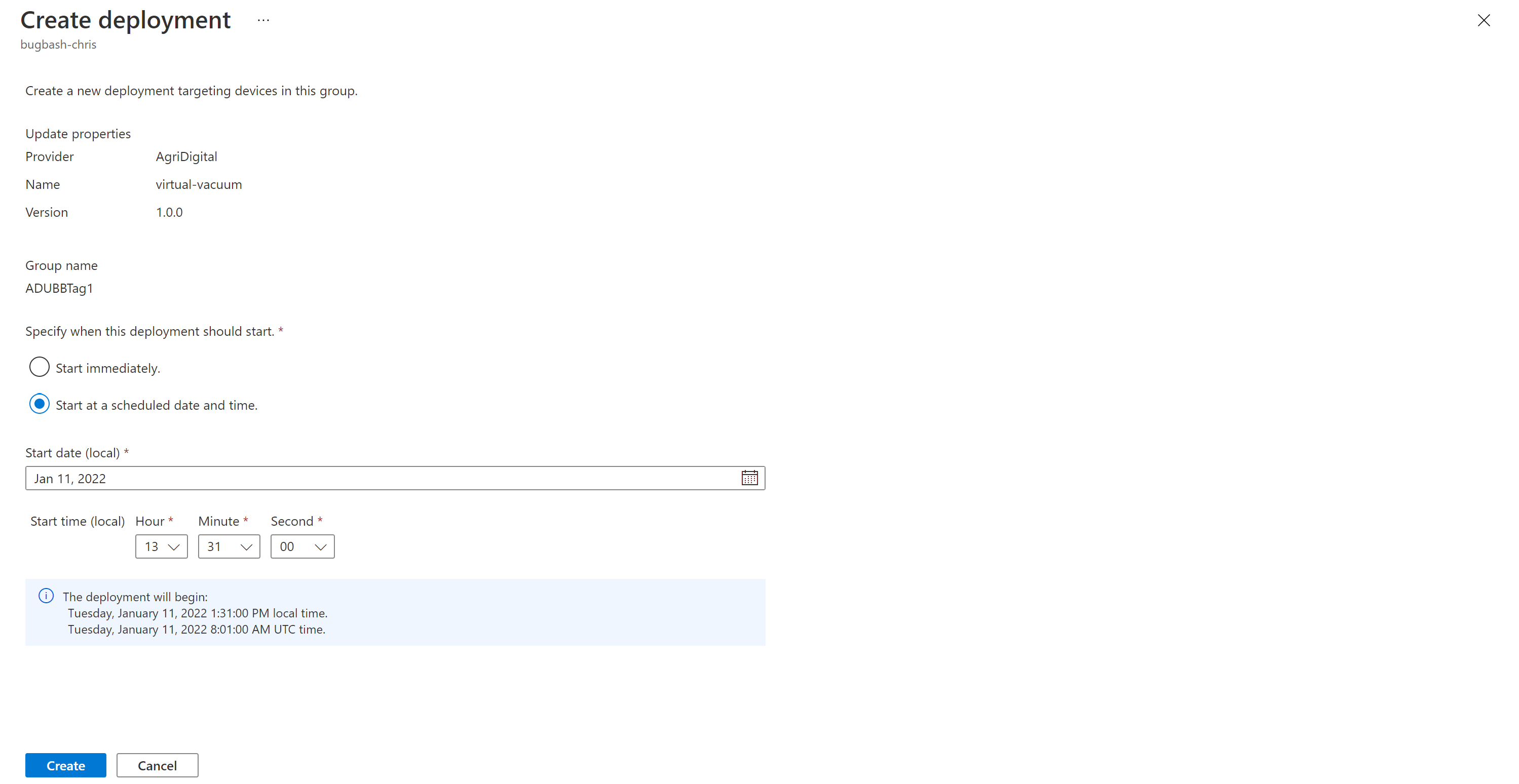
Deploy the update
After the group is created, you should see a new update available for your device group. A link to the update should be under Best update. You might need to refresh once. Learn more about update compliance.
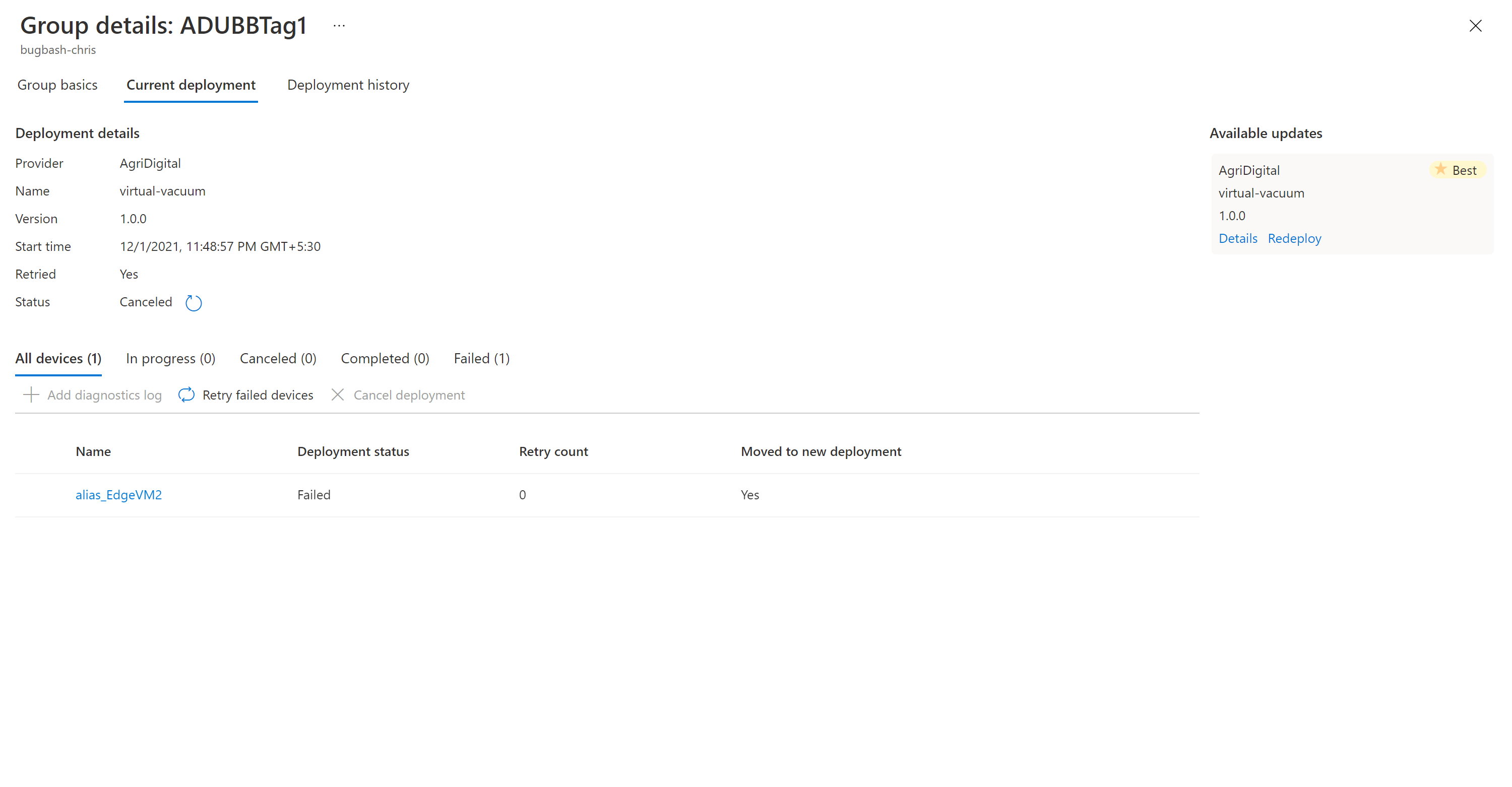
Select the target group by selecting the group name. You're directed to Group details under Group basics.
To start the deployment, go to the Current deployment tab. Select the deploy link next to the desired update from the Available updates section. The best available update for a given group is denoted with a Best highlight.
Schedule your deployment to start immediately or in the future. Then select Create.
Under Deployment details, Status turns to Active. The deployed update is marked with (deploying).
View the compliance chart to see that the update is now in progress.
After your device is successfully updated, you see that your compliance chart and deployment details updated to reflect the same.
Monitor the update deployment
Select the Deployment history tab at the top of the page.
Select Details next to the deployment you created.
Select Refresh to view the latest status details.
You've now completed a successful end-to-end image update by using Device Update for IoT Hub using the Ubuntu (18.04 x64) simulator reference agent.
Clean up resources
When no longer needed, clean up your Device Update account, instance, IoT hub, and IoT device.