Move data to Azure SQL Database
While there are methods available for migrating an entire schema and its data, there are also cases where only a subset of the database is needed. Fortunately, many of the methods we’ve seen support partial data migration, and we’ll learn about a few others.
In our bicycle manufacturer scenario, suppose the company has an on-premises SQL Server database that contains several years’ worth of sales, customer, and product data. The company wants to migrate to an Azure SQL Database to take advantage of the scalability and flexibility of the cloud. However, they only need to migrate the customer and product tables, as they want to keep their sales data on-premises for security reasons.
SQL Data Sync
The Data Sync feature allows you to incrementally synchronize data across multiple databases running on Azure SQL Database or on-premises SQL Server. You can also use Data Sync to keep your source and target databases in sync after migrations. Data Sync tracks changes using insert, update, and delete triggers. The changes are recorded in a side table in the user database.
Due to its ability to synchronize data in both directions, this feature is a great choice for hybrid applications. It's particularly appealing to customers considering moving to the cloud, as it allows them to transition some of their applications to Azure quickly.
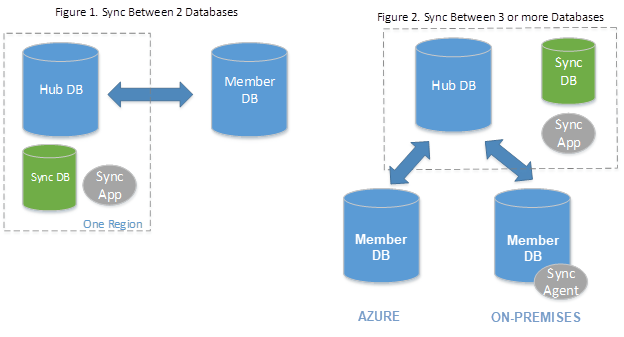
Data Sync is based on a hub topology, where you define one of the databases in the sync group to work as a hub database. The sync group can have multiple members, and you can only synchronize changes between the hub database and individual databases. Data Sync tracks changes using INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE triggers through a historical table created on the user database.
When compared to transactional replication, which has lower latency, one disadvantage of Data Sync is its higher performance impact. This means that changes made to one database requires more resources when using Data Sync.
When you create a sync group, it asks you to provide a database responsible to store the sync group metadata. The metadata location can be either a new database or an existing database as long it resides in the same region as your sync group.
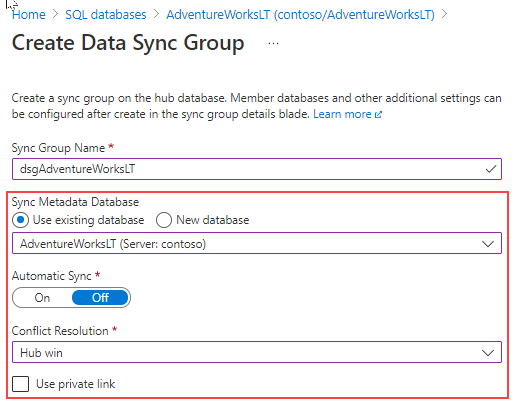
You can specify sync group properties like the schedule synchronization, the conflict resolution option, and the use of a private link if needed.
For more information about how to configure SQL Data Sync, see Tutorial: Set up SQL Data Sync between databases in Azure SQL Database and SQL Server.
Bulk copy
The bcp utility allows bulk exporting of data from a SQL Server table into a data file and vice versa. The utility is versatile, enabling data transfer between SQL Server and other programs or databases.
Understanding the schema and data types of the table is essential for using the bcp command effectively, unless a pre-existing format file is available.
Azure Data Factory
You can use Azure Data Factory for data migration rather than entire database migration. Azure Data Factory can migrate and transform data from source SQL Server databases, and it's commonly used for business intelligence workloads (BI).