Denial of Service - overwhelming the system
Denial of service occurs when an attacker causes the system to be unavailable.
Examples include:
- Flooding the network with requests.
- Absorbing memory and CPU processes.
- Crashing data stores with an overwhelming number of requests.
Elements and interactions at risk from denial of service
Element
| Name | Shape | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Process | 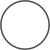 |
Activity that modifies or redirects input to an output |
| Data store |  |
Permanent or temporary data storage |
| Data-flow | 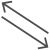 |
Data movement between elements |
Interaction
| Name | Interaction | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Process -> Process | 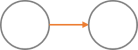 |
A task sends data to another task |
| Process <-> External Entity | 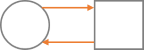 |
A task sends or receives data to or from a user |
| Process <-> Data Store |  |
A task sends or receives data to or from a data store |
| Data Flow <-> Trust Boundary |  |
Data is transmitted from a trusted environment to someone over the internet (and vice-versa) |
How to prevent denial of service
Availability ensures your system is up and running for users. Examples include:
- Using network access-control lists to control incoming and outgoing traffic.
- Using elastic resources to manage growing or shrinking usage.
- Monitoring the system to detect anomalies.
- Enabling operating-system flags to handle memory and CPU processes.
Common security controls to reduce or eliminate risk
- Access control lists (ACL)
- Filtering
- Quotas
- Authorization
- High availability
Tip
Good question to ask: Are there areas where my service is resource-limited?