Conditional Access authentication strength
Authentication strength is a Conditional Access control that specifies which combinations of authentication methods can be used to access a resource. Users can satisfy the strength requirements by authenticating with any of the allowed combinations.
For example, an authentication strength can require that only phishing-resistant authentication methods be used to access a sensitive resource. To access a nonsensitive resource, administrators can create another authentication strength that allows less secure multifactor authentication (MFA) combinations, such as password + text message.
Authentication strength is based on the Authentication methods policy, where administrators can scope authentication methods for specific users and groups to be used across Microsoft Entra ID federated applications. Authentication strength allows further control over the usage of these methods based upon specific scenarios such as sensitive resource access, user risk, location, and more.
Scenarios for authentication strengths
Authentication strengths can help customers address these scenarios:
- Require specific authentication methods to access a sensitive resource.
- Require a specific authentication method when a user takes a sensitive action within an application (in combination with Conditional Access authentication context).
- Require users to use a specific authentication method when they access sensitive applications outside of the corporate network.
- Require more secure authentication methods for users at high risk.
- Require specific authentication methods from guest users who access a resource tenant (in combination with cross-tenant settings).
Authentication strengths
Administrators can specify an authentication strength to access a resource by creating a Conditional Access policy with the Require authentication strength control. They can choose from three built-in authentication strengths: Multifactor authentication strength, Passwordless MFA strength, and Phishing-resistant MFA strength. They can also create a custom authentication strength based on the authentication method combinations they want to allow.
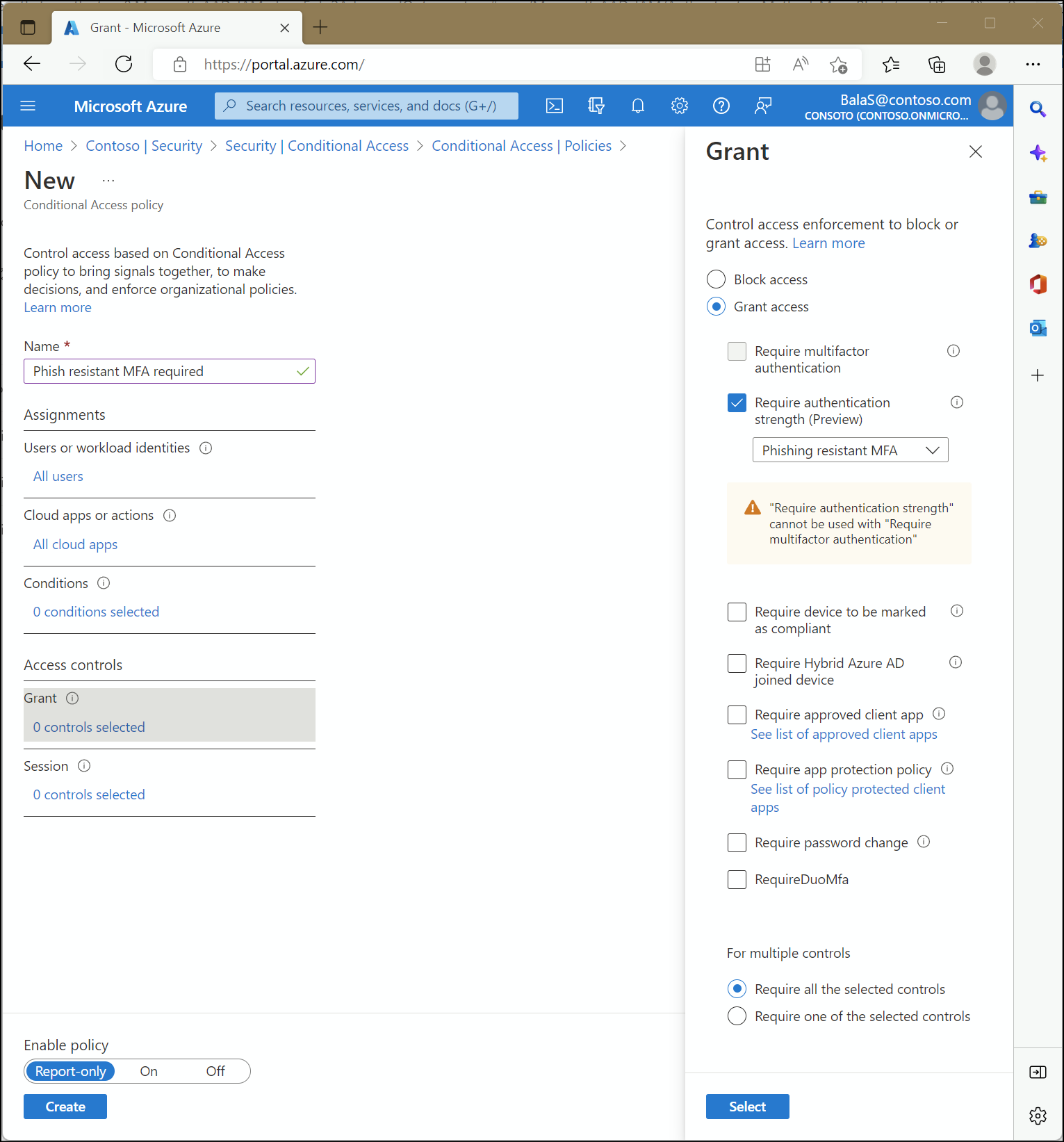
Built-in authentication strengths
Built-in authentication strengths are combinations of authentication methods that are predefined by Microsoft. Built-in authentication strengths are always available and can't be modified. Microsoft will update built-in authentication strengths when new methods become available.
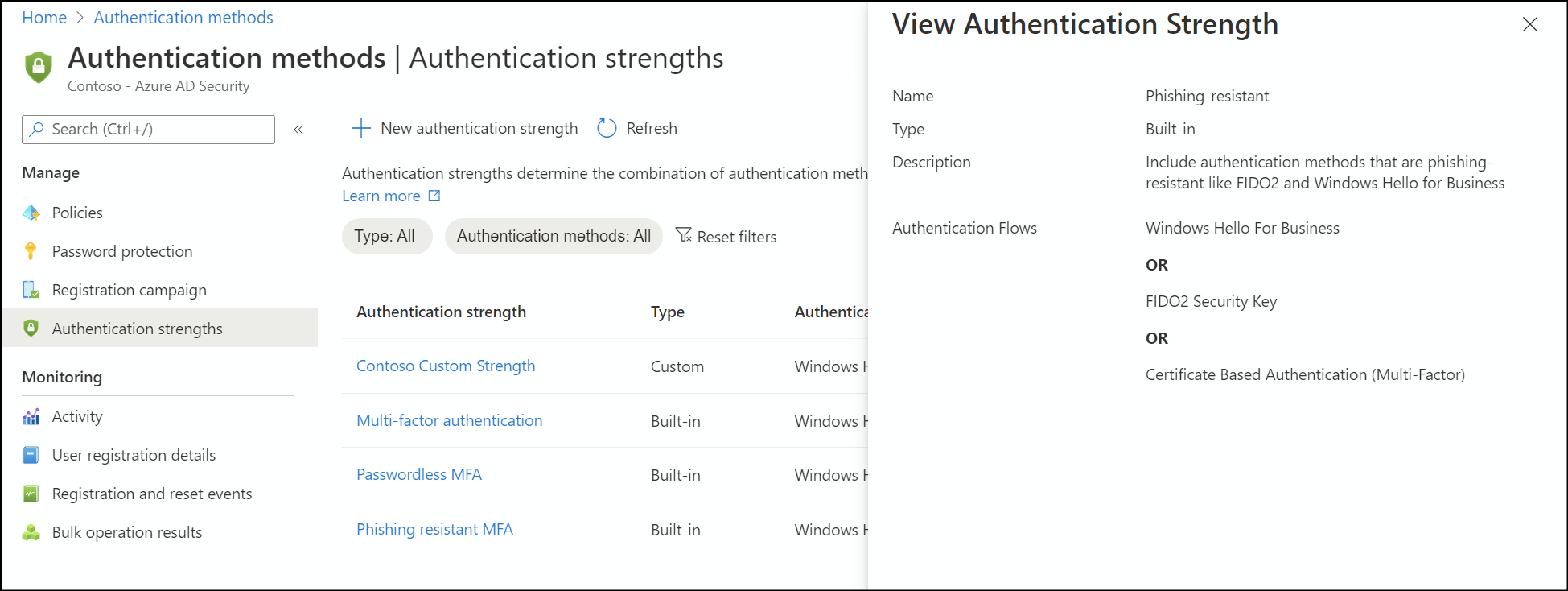
For an example, the built-in Phishing-resistant MFA strength allows the following combinations:
Windows Hello for Business
Or
FIDO2 security key
Or
Microsoft Entra certificate-based authentication (Multifactor)
The combinations of authentication methods for each built-in authentication strength are listed in the following table. These combinations include methods that need to be registered by users and enabled in the Authentication methods policy or the legacy MFA settings policy.
- MFA strength - the same set of combinations that could be used to satisfy the Require multifactor authentication setting.
- Passwordless MFA strength - includes authentication methods that satisfy MFA but don't require a password.
- Phishing-resistant MFA strength - includes methods that require an interaction between the authentication method and the sign-in surface.
| Authentication method combination | MFA strength | Passwordless MFA strength | Phishing-resistant MFA strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIDO2 security key | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Windows Hello for Business | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Certificate-based authentication (Multi-Factor) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Microsoft Authenticator (Phone Sign-in) | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Temporary Access Pass (One-time use AND Multi-use) | ✅ | ||
| Password + something you have1 | ✅ | ||
| Federated single-factor + something you have1 | ✅ | ||
| Federated Multi-Factor | ✅ | ||
| Certificate-based authentication (single-factor) | |||
| SMS sign-in | |||
| Password | |||
| Federated single-factor |
1 Something you have refers to one of the following methods: text message, voice, push notification, software OATH token, or hardware OATH token.
The following API call can be used to list definitions of all the built-in authentication strengths:
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/identity/conditionalAccess/authenticationStrength/policies?$filter=policyType eq 'builtIn'
Conditional Access Administrators can also create custom authentication strengths to exactly suit their access requirements. For more information, see Custom Conditional Access authentication strengths.
Limitations
Conditional Access policies are only evaluated after the initial authentication - As a result, authentication strength doesn't restrict a user's initial authentication. Suppose you are using the built-in phishing-resistant MFA strength. A user can still type in their password, but they are required to sign in with a phishing-resistant method such as FIDO2 security key before they can continue.
Require multifactor authentication and Require authentication strength can't be used together in the same Conditional Access policy - These two Conditional Access grant controls can't be used together because the built-in authentication strength Multifactor authentication is equivalent to the Require multifactor authentication grant control.
Authentication methods that aren't currently supported by authentication strength - The Email one-time pass (Guest) authentication method isn't included in the available combinations.
Windows Hello for Business – If the user signed in with Windows Hello for Business as their primary authentication method, it can be used to satisfy an authentication strength requirement that includes Windows Hello for Business. However, if the user signed in with another method like password as their primary authentication method, and the authentication strength requires Windows Hello for Business, they aren't prompted to sign in with Windows Hello for Business. The user needs to restart the session, choose Sign-in options, and select a method required by the authentication strength.
Known issue
FIDO2 security key Advanced options - Advanced options aren't supported for external users with a home tenant that is located in a different Microsoft cloud than the resource tenant.
Authentication strength blade double representation - The Authentication Strength blade currently represents both Platform Credential for macOS and Windows Hello For Business with the same Authentication method name, Windows Hello For Business. Work is in progress to represent Platform Credential for macOS separately. While configuring custom authentication strength that needs to use Platform Credential for macOS, please use "Windows Hello For Business" until this is fixed.
FAQ
Should I use authentication strength or the Authentication methods policy?
Authentication strength is based on the Authentication methods policy. The Authentication methods policy helps to scope and configure authentication methods to be used across Microsoft Entra ID by specific users and groups. Authentication strength allows another restriction of methods for specific scenarios, such as sensitive resource access, user risk, location, and more.
For example, the administrator of Contoso wants to allow their users to use Microsoft Authenticator with either push notifications or passwordless authentication mode. The administrator goes to the Microsoft Authenticator settings in the Authentication methods policy, scopes the policy for the relevant users, and sets the Authentication mode to Any.
Then for Contoso's most sensitive resource, the administrator wants to restrict the access to only passwordless authentication methods. The administrator creates a new Conditional Access policy, using the built-in Passwordless MFA strength.
As a result, users in Contoso can access most of the resources in the tenant using password + push notification from the Microsoft Authenticator OR only using Microsoft Authenticator (phone sign-in). However, when the users in the tenant access the sensitive application, they must use Microsoft Authenticator (phone sign-in).
Prerequisites
- Microsoft Entra ID P1 - Your tenant needs to have Microsoft Entra ID P1 license to use Conditional Access. If needed, you can enable a free trial.
- Enable combined registration - Authentication strengths are supported when using combined MFA and SSPR registration. Using the legacy registration will result in poor user experience as the user may register methods that aren't required by the Authentication methods policy.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for