Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Data Integrator (for Admins) is a point-to-point integration service used to integrate data into Dataverse. It supports integrating data between finance and operations apps and Dataverse. It also supports integrating data into finance and operations apps and Dynamics 365 Sales. This service is generally available since July 2017.
Note
We highly recommend customers start using dual-write, which provides tightly coupled, bidirectional integration between finance and operations apps and Dataverse. Any data change in finance and operations apps causes writes to Dataverse, and any data change in Dataverse causes writes to finance and operations apps. This automated data flow provides an integrated user experience across the apps.
Tip
Check out the blog: Data Integrator Updates – New features with an intuitive user interface providing a fluent experience.
Use the Data Integrator for your business
The Data Integrator (for Admins) also supports process-based integration scenarios like Prospect to Cash that provide direct synchronization between finance and operations apps and Dynamics 365 Sales. The Prospect to Cash templates that are available with the data integration feature enable the flow of data for accounts, contacts, products, sales quotations, sales orders, and sales invoices between finance and operations apps and Sales. While data is flowing between finance and operations apps and Sales, you can perform sales and marketing activities in Sales, and you can handle order fulfillment by using inventory management in finance and operations apps.

The Prospect to Cash integration enables sellers to handle and monitor their sales processes with the strengths from Dynamics 365 Sales, while all aspects of fulfillment and invoicing happen using the rich functionality in finance and operations apps. With Microsoft Dynamics 365 Prospect to Cash integration, you get the combined power from both systems.
For more information about the Prospect to Cash integration, see the documentation on the Prospect to Cash solution.
Field Service integration and PSA (Project Service Automation) integration are also supported for data integration.
Data Integrator platform
The Data Integrator (for Admins) consists of the Data Integration platform, out-of-the-box templates provided by our application teams (for example, finance and operations apps and Dynamics 365 Sales) and custom templates created by our customers and partners. We have built an application-agnostic platform that can scale across various sources. At the core of it, you create connections (to integration end points), choose one of the customizable templates with predefined mappings (that you can further customize), and create and execute the data integration project.
Integration templates serve as a blueprint with predefined entities and field mappings to enable flow of data from source to destination. It also allows you to transform the data before importing it. Many times, the schema between the source and destinations apps can be different and a template with predefined entities and field mappings serves as a great starting point for an integration project.
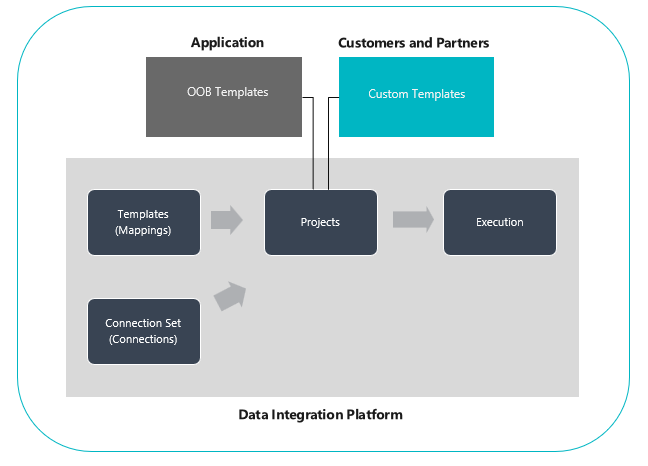
Set up a data integration project
There are three primary steps:
Create a connection (provide credentials to data sources).
Create a connection set (identify environments for connections you created in the previous step).
Create a data integration project using a template (create or use predefined mappings for one or more entities).
After you create an integration project, you get the option to run the project manually and also set up a schedule-based refresh for the future. The rest of this article expands on these three steps.
Note
The user interface for Data Integrator project management is hosted at https://dataintegrator.trafficmanager.net. Your organization policies might require adding this site to your allowlist to access the interface.
Create a connection
Before you can create a data integration project, you must provision a connection for each system that you intend to work with in the Microsoft Power Apps portal. Think of these connections as your points of integration.
Go to Power Apps.
On the left navigation pane, select Connections, and then select New connection. If the item isn't in the left navigation pane, select More to find it.
You can either select a connection from the list of connections or search for your connection.
After you select your connection, select Create. Then you're prompted for credentials.
After you provide your credentials, the connection will be listed under your connections.
Note
Make sure that the account you specify for each connection has access to entities for the corresponding applications. Additionally, the account for each connection can be in a different tenant. After you provide your credentials, the connection is listed under your connections.
Note
Make sure that the account you specify for each connection has access to entities for the corresponding applications. Additionally, the account for each connection can be in a different tenant.
Create a connection set
Connection sets are a collection of two connections, environments for the connections, organization mapping information, and integration keys that can be reused among projects. You can start using a connection set for development and then switch to a different one for production. One key piece of information that is stored with a connection set is organization unit mappings—for example, mappings between the finance and operations apps legal entity (or company) and Dynamics 365 Sales organization or business units. You can store multiple organization mappings in a connection set.
Sign in to the Power Platform admin center.
Select Manage in the navigation pane.
In the Manage pane, select Data integration. The Data integration page is displayed.
Select the Connection sets tab and select New connection set. The New connection set pane is displayed.
Provide a name for your connection set.
Choose the connection you created earlier and select the appropriate environment.
Repeat the previous step by choosing your next connection and enivironment.
Specify the organization to business unit mapping (if you're integrating between finance and operations apps and Sales systems).
Note
You can specify multiple mappings for each connection set.
After you complete all the fields, select Save.
You see the new connection set you created under the Connection sets tab. Your connection set is ready to be used across various integration projects.
Create a data integration project
Projects enable the flow of data between systems. A project contains mappings for one or more entities. Mappings indicate which fields map to which other fields. To create a data integration project, perform the following steps:
Select the Data integration tab in the left navigation pane.
While in the Projects tab, select New project.
Provide a name for your integration project.
Select one of the available templates (or create your own template).
Select Next and choose a connection set you created earlier (or create a new connection set).
Make sure you chose the right one by confirming the connection and environment names.
Review and accept the privacy notice and consent on the next screen.
Select Next and then choose the legal entity to business unit mappings.
Review and accept the privacy notice and consent on the next screen.
Proceed to create the project and then run the project, which in turn executes the project.
You'll see several tabs—Scheduling and Execution history—along with some buttons—Add task, Refresh entities, and Advanced Query—that are described later in this article.
View execution history
Anytime you execute a project, manually or schedule based, it generates a detailed log, which shows project name, last updated timestamp along with status. You can view this under the execution history for each project. Project execution history is maintained for 45 days after which it's automatically purged.
Execution history also shows the status of execution along with the number of upserts and any errors.
For execution failures, you can drill down to view the root cause.
If the project execution is in 'ERROR' state, then it retries execution at the next scheduled run.
If the project execution is in 'WARNING' state, then you must fix the issues on the source. The project retries execution at the next scheduled run.
Example of successful execution, showing status as completed with # of upserts. (Update Insert is a logic to either update the record, if it already exists, or to insert new record.)
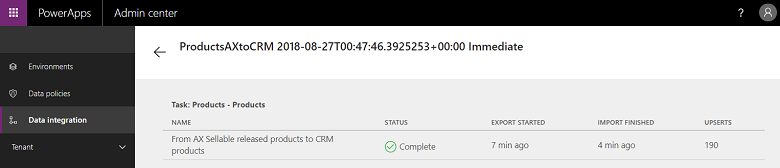
For execution failures, you can drill down to see the root cause.
Here's an example of a failure with project validation errors. In this case, the project validation error is due to missing source fields in the entity mappings.
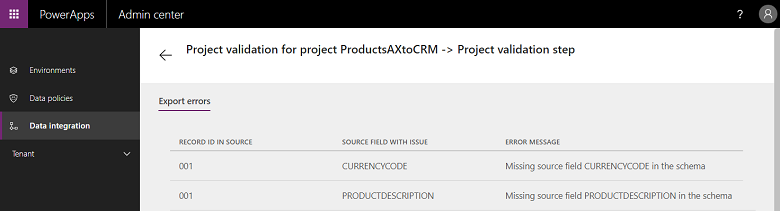
If the project execution is in 'ERROR' state, then it retries execution at the next scheduled run.
If the project execution is in 'WARNING' state, then you need to fix the issues on the source. It retries execution at the next scheduled run.
In either case, you could also choose to manually 'rerun execution.'
Note
Anytime you execute a project, manually or schedule based, it generates a detailed log, which shows project name, last updated timestamp along with status. You can view this under the execution history for each project. Project execution history is maintained for 45 days after which it's automatically purged.
Set up a schedule-based refresh
Two types of executions/writes are available:
Manual writes (execute and refresh project manually)
Schedule-based writes (autorefresh)
After you create an integration project, you can run it manually or configure schedule-based writes, which lets you set up automatic refresh for your projects.
To set up schedule-based writes follow these steps:
- Go to Power Platform admin center.
- Select Manage in the navigation pane.
- In the Manage pane, select Data integration. The Data integration page is displayed.
- Select the Projects tab, select the project, and then select the Context menu icon (...) and Schedule.
- On the Scheduling tab,
- Select the toggle so that Recur every is displayed and complete all the fields.
- Select Save schedule.
You can set a frequency as often as one minute or have it recur some hours, days, weeks, or months. The next refresh won't start until the previous project task completes its run.
Also note that under Notifications, you can opt in for email-based alert notifications, which alerts you on job executions that either completed with warnings or failed due to errors. You can provide multiple recipients, including groups separated by commas.
Note
- You can schedule 50 integration projects at any given time per paid tenant. However you can create more projects and run them interactively. For trial tenants, there's an additional limitation that a scheduled project can only run for the first 50 executions.
- While you can schedule projects to run every minute, this tactic might put much stress on your apps and impact overall performance. We highly encourage users to test project executions under true load conditions and optimize for performance with less frequent refreshes. In production environments, we don't recommend running more than five projects per minute per tenant.
- To optimize performance and not overload the apps, project executions are limited to 500-K rows per execution per project.
- Anytime you execute a project, manually or schedule based, it generates a detailed log, which shows project name, last updated timestamp along with status. You can view the logs under the execution history for each project. Project execution history is maintained for 45 days after which it's automatically purged.
Customize projects, templates, and mappings
You use a template to create a data integration project. A template commoditizes the movement of data that in turn helps a business user or administrator expedite integrating data from sources to destination and reduces overall burden and cost. A business user or administrator can start with an out-of-the-box template published by Microsoft or its partner and then further customize it before creating a project. You can then save the project as a template and share with your organization and/or create a new project.
A template provides you with source, destination, and direction of data flow. You need to keep this fact in mind while customizing or creating your own template.
You can customize projects and templates in these ways:
- Customize field mappings.
- Customize a template by adding an entity of your choice.
Customize field mappings
To create a connection set, follow these steps:
- Go to Power Platform admin center.
- Select Manage in the navigation pane.
- In the Manage pane, select Data integration. The Data integration page is displayed.
- Select the Projects tab, select the project for which you want to customize field mappings, and then select the Context menu icon (...) and Connection set details.
- Select the Go to connection set details link.
- Select the Organizations tab, and then select + Add mapping.
- After you customize your field mappings, select Save on the command bar.
Create your own template
Create your own template by modifying existing templates
Sign in to Power Platform admin center.
Select Manage > Data integration on the left navigation pane.
On the Templates tab, create a project by selecting an existing template that matches your choice of source and destination and direction of flow.
Choose the appropriate connection.
Before you save or run the project, select Add task on the command bar.
The Add task dialog opens.
Provide a meaningful task name and add source and destination entities of your choice.
A dropdown list shows you all your source and destination entities.
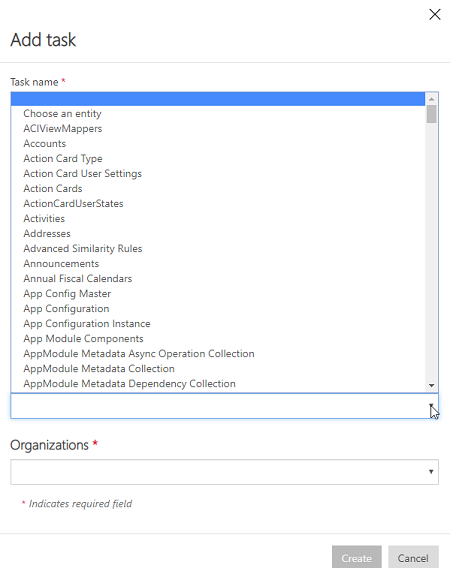
In this case, a new task was created to sync User entity from SalesForce to Users entity in Dataverse.
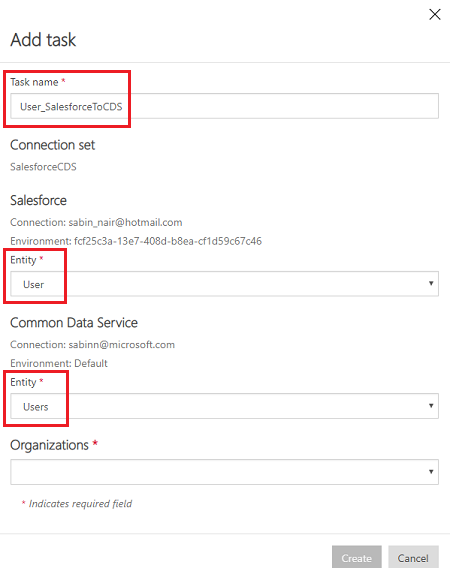
After you create the task, you can view your new task listed and you can delete the original task.
You just created a new template—in this case, a template to pull User entity data from SalesForce to Dataverse. Select Save to save your customization.
Follow the steps to customize field mappings for this new template. You could run this project and save the project as a template from the Project tab. When saving as a template, provide a name and description. You can also share the template with everyone in your organization.
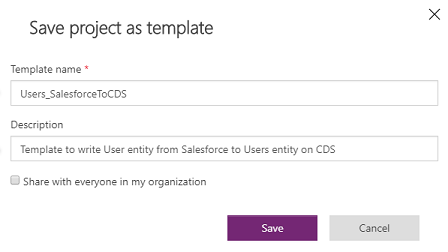
Create your own template from a blank template
Sign in to Power Platform admin center.
Go to Manage > Data integration on the left navigation pane.
Select New project and provide a name for your project. For example, Demo_CreateYourOwnTemplate project.
In the Select a template list page, pick a generic blank template. For this example, choose the Sales to Fin and Ops template since we want to move data from finance and operations apps to Dynamics 365 Sales.
Follow steps 6 through 9 in How to create another data integration project to create the data integration project you want. Then, select Save.
The Tasks page appears, which is empty since it's a blank template, without any tasks. Select Add task to pick an entity from the drop-down list and add a new task.
In this case, for demo purposes, we create an Activities Sales to Fin and Ops task by picking the Activities entity for finance and operations apps and Dynamics 365 Sales. Select Create.
Notice a new task is added Activities Sales to Fin and Ops. Select Save to save your changes.
The project is created. On the Projects tab, select the project, and then select ... > Save as template.
Provide a name and description, then select Save. Additionally, select Share with everyone in my organization to share this template.
The newly created template appears on the Templates list page.
Additionally, after creating a new integration project, when you choose Select a template you'll notice your newly created template in the Templates tab.
Advanced data transformation and filtering
With Power Query support, advanced filtering and data transformation of source data is available. Power Query enables users to reshape data to fit their needs, with an easy-to-use, engaging, and no-code user experience. You can enable this on a project-by-project basis.
Enable advanced query and filtering
Go to Power Platform admin center.
Select Manage > Data integration on the left navigation pane.
On the Projects tab, select the project where you want to enable advanced query, select ... > Project Details. Then select Advanced query on the command bar.
You receive a warning that enabling advanced query is a one-way operation and can't be undone. Select OK to proceed and then select the source and destination mapping arrow.
You're presented with the familiar entity mapping page with a link to open Advanced Query and Filtering.
Select to link to launch the Advanced Query and Filtering user interface, which gives you source field data in Microsoft Excel-type columns.
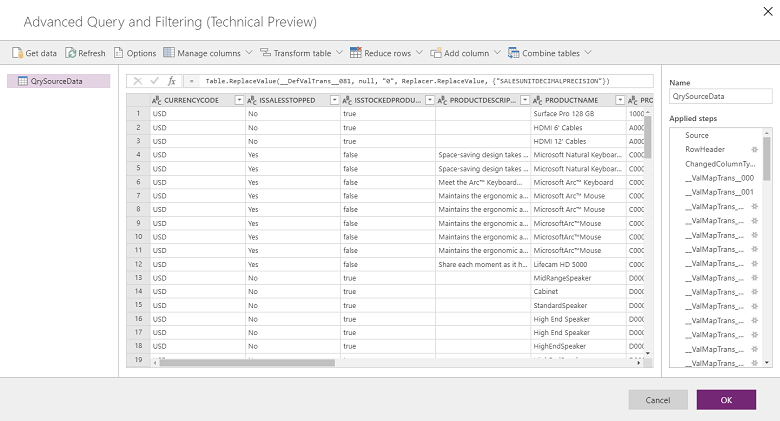
From the top menu, you have several options for transforming data such as Add conditional column, Duplicate column, and Extract.
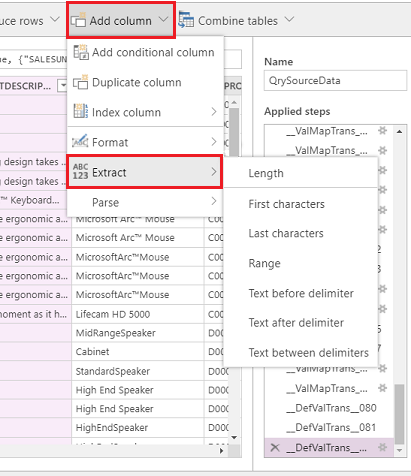
You can also right-click any column for more options such as Remove columns, Remove duplicates, and Split column.
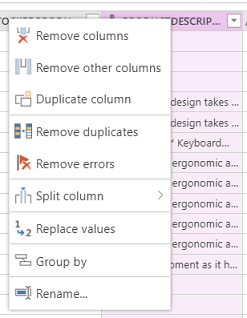
You also can filter by selecting each column and using Excel-type filters.
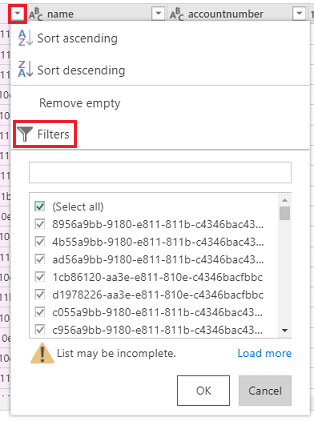
Default value transforms can be achieved using the conditional column. To do this, from the Add Column dropdown list, select Add Conditional Column and enter the name of the new column. Fill in both Then and Else with what should be the default value, using any field and value for If and equal to.
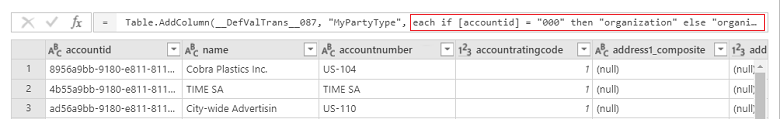
Notice the each clause in the fx editor, at the top.

Fix the each clause in the fx editor and select OK.
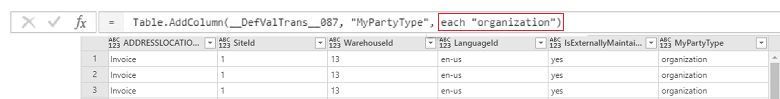
Each time you make a change, you apply a step. You can see the applied steps on the right-hand pane (scroll to the bottom to see the latest step). You can undo a step in case you need to edit. Additionally, you can go to the Advanced editor by right-clicking the QrySourceData on the left pane, at the top to view the M language that gets executed behind the scenes, with the same steps.
Select OK to close the Advanced Query and Filtering interface and then, on the mapping task page, select the newly created column as the source to create the mapping you want.
For more information about Power Query, go to Power Query documentation.
Note
Once Advanced Query and Filtering is enabled, transforms via Fn aren't supported, and instead should be defined using Advanced Query and Filtering.
Doing joins across multiple data sources (either via the Get data button or M query) isn't supported with Advanced Query and Filtering.
If you encounter Power Query evaluation limits with the error:
The power query job failed with error: Exception ExceptionType:MashupEvaluationException, ExceptionMessage:EvaluationQuotaReached, EvaluationResponse:{"ResultType":"ErrorCode,""Code":"EvaluationQuotaReached"
Review the guidance on Power Query Online Limits.
Modifying the url directly in the mashup editor isn't supported. Only the filter applied using the mashup editor UI or specified in source filter edit field on mapping page is used.
Factors that impact performance tuning
There are several factors that impact the performance of an integration scenario. Performance is highly dependent on:
- Which applications you're integrating: finance and operations apps and Dataverse.
- Which entities are used: the entities' shape, validation, and business logic (standard and customizations).
The Data Integrator takes the data from the source application and pushes it into the target application. The main performance considerations are on how source and target applications scale with the concerned entities. It uses the best available technologies to pull/push data in a performant manner.
Finance and operations apps use the data management framework, which provides a way to pull and push data in the most performant fashion. The data management framework is used to manage data entities and data entity packages in finance and operations apps.
Dynamics 365 apps with Dataverse use OData APIs along with parallelism to maximize the performance.
You can use the following settings to tune the performance of finance and operations apps based on load, entity, and resources.
Exporting data from finance and operations apps
- Direct export (skip Staging On): Make sure the entities used for integration support direct export (skip Staging On). This allows export to run in bulk and the staging table is bypassed. If you run with Skip Staging Off, then it falls back to row by row calls and data is inserted in the staging table.
- Enable change tracking for entities: Change tracking enables incremental export of data from finance and operations apps by using data management. In an incremental export, only records that are changed are exported. To enable incremental export, you must enable change tracking on entities. Without change tracking, you do full exports, which can affect performance. For complex scenarios, use custom queries for change tracking.
Importing data to finance and operations apps
- Make sure the entity itself is performant. If possible, create set-based entities.
- If the number of rows to be imported are high and the entity doesn't support set operations: Data management can be configured to import the entity with parallel tasks. This can be configured in data management (parameters), by configuring the entity execution parameters. This uses batch framework to create parallel tasks, which is based on resource availability to run in parallel.
- Turning off validations (optional): While the Data Integrator doesn't bypass any business logic and validations, you might optionally turn off the ones that aren't required to improve performance.
Import/Export data to/from customer engagement apps
Ensure indexes are defined for integration keys.