Describe Microsoft Entra Verified ID
Microsoft Entra Verified ID is a managed verifiable credentials service based on open standards. Verified ID automates verification of identity credentials and enables privacy-protected interactions between organizations and users.
Why do we need it?
In the digital world, transactions are increasingly done over the web and often require individuals to make claims or assertions that organizations can digitally verify. The current process of obtaining and presenting a digital credential that can make the minimum required claims and that can be verified can be difficult and cumbersome. A digital credential serves as a digital identity. Once you use that online digital identity to access the desired service or make an online transaction, it’s common you begin to get targeted advertisements and emails for services for which you never signed up. That’s because it’s hard to retain control of your identity once you've shared it in exchange for access to a service. Individuals and businesses need a way to express their qualifications and/or personal information, that is, our digital identities, over the web in a manner that is cryptographically secure, compliant to privacy requirements, and machine readable for verification. Additionally, individuals and organizations want to be able to control how and when their digital identities are used and shared. Verifiable credentials help address these challenges.
How it works
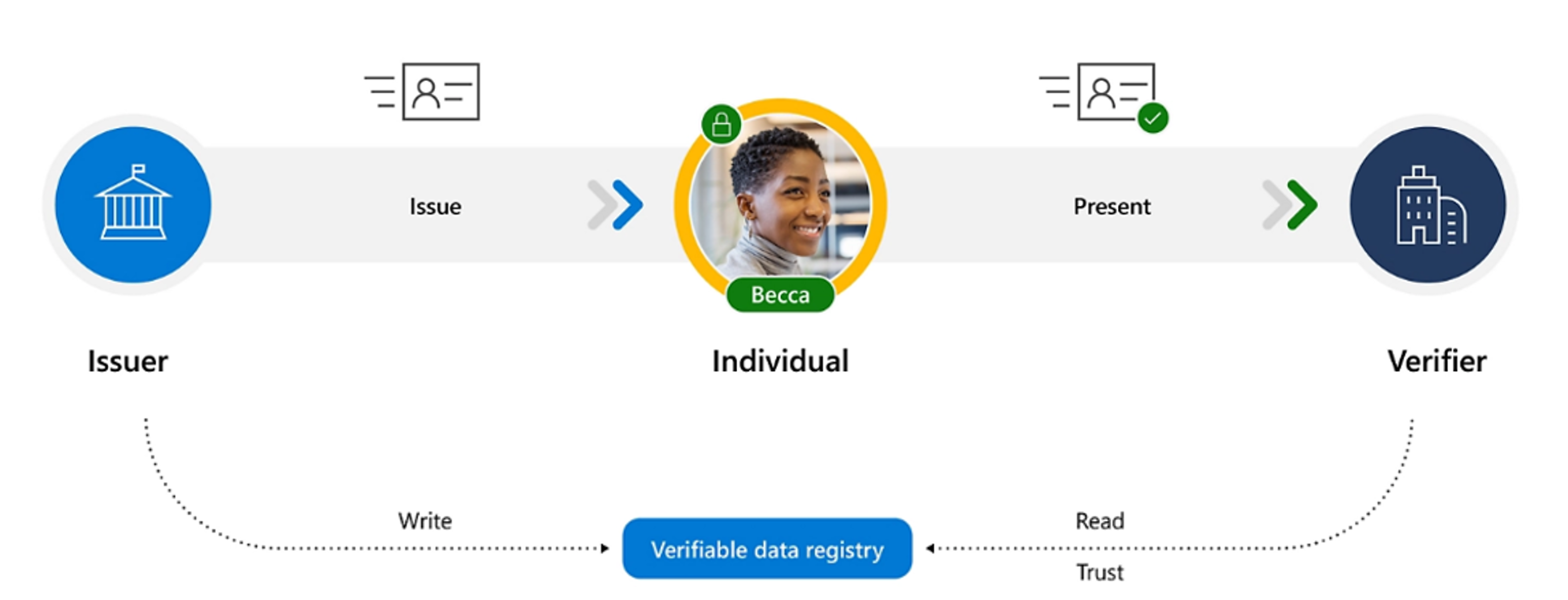
This diagram illustrates the participation of three parties in a verifiable credential’s interaction. This solution automates verification of identity credentials and claims.
- The issuer is an organization that attests to claims and grants digitally signed credentials to the user. An issuer can be an identity verification provider, a government agency, an employer, a university, or any other organization that can provide proof of the user’s credential.
- The user receives and approves the credentials obtained from the issuer, stores and manages credentials in their digital wallet, and presents it to the verifier. The credential claims are cryptographically signed with the user’s private key.
- The verifier is an organization that requests proof and, upon receipt, verifies that the claims in the credentials satisfy requirements. A verifier could be a prospective employer, and airline, mortgage company, or any organization that is requesting proof of the user’s credential.
Supporting it all is a verifiable data registry. The underlying verifiable data registry is a collection of systems involved in creating and recording meta data that are used with verifiable credentials, including public keys. These systems are usually distributed networks, such as distributed ledgers, blockchains, distributed file systems, or other trusted data storage. The way to think about the verifiable data registry is as an underlying network that represents a trust system. The verifier interacts with the data registry to read the meta-data associated with the credential to then verify the credential that presented by the user.
A common scenario with any credential is that the credential may expire, or the issuer may need to revoke that credential. The standard for verifiable credentials includes property fields in the credential to account for these scenarios.
Visit https://aka.ms/vcdemo for a more complete demonstration of an onboarding verifiable credential scenario. Also, the summary and resources section of this module includes a link to the training content that describes concepts behind Microsoft Entra Verified ID.