Balancing host pools
Azure Virtual Desktop supports two load-balancing methods. Each method determines which session host will host a user's session when they connect to a resource in a host pool.
The following load-balancing methods are available in Azure Virtual Desktop:
- Breadth-first load balancing allows you to evenly distribute user sessions across the session hosts in a host pool.
- Depth-first load balancing allows you to saturate a session host with user sessions in a host pool. Once the first session reaches its session limit threshold, the load balancer directs any new user connections to the next session host in the host pool until it reaches its limit, and so on.
Each host pool can only configure one type of load-balancing specific to it. However, both load-balancing methods share the following behaviors no matter which host pool they're in:
- If a user already has a session in the host pool and is reconnecting to that session, the load balancer will successfully redirect them to the session host with their existing session. This behavior applies even if that session host's AllowNewConnections property is set to False.
- If a user doesn't already have a session in the host pool, then the load balancer won't consider session hosts whose AllowNewConnections property is set to False during load balancing.
Breadth-first load-balancing method
The breadth-first load-balancing method allows you to distribute user connections to optimize for this scenario. This method is ideal for organizations that want to provide the best experience for users connecting to their pooled virtual desktop environment.
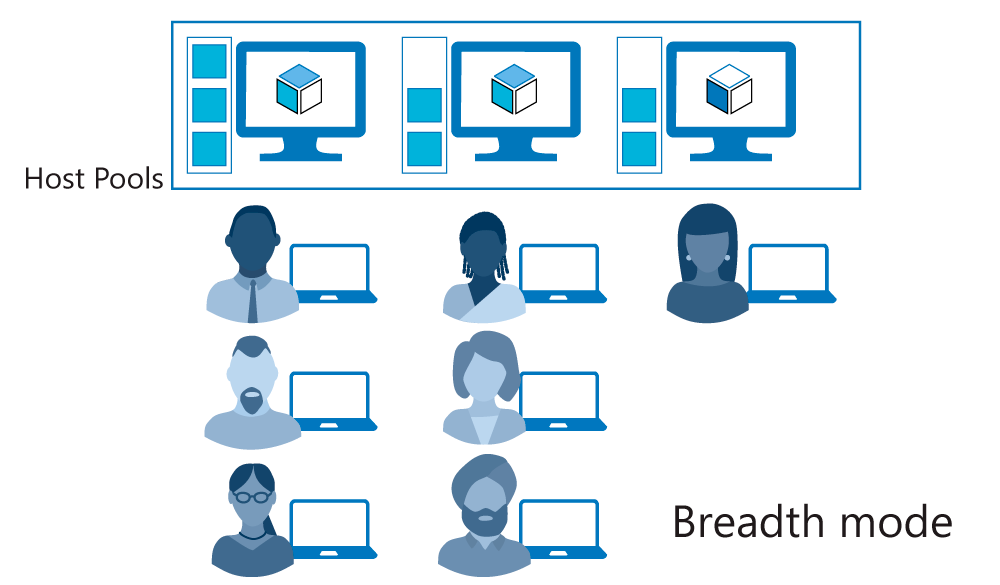
The breadth-first method first queries session hosts that allow new connections. The method then selects a session host randomly from half the set of session hosts with the least number of sessions. For example, if there are nine machines with 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19 sessions, a new session you create won't automatically go to the first machine. Instead, it can go to any of the first five machines with the lowest number of sessions (11, 12, 13, 14, 15).
Depth-first load-balancing method
The depth-first load-balancing method allows you to saturate one session host at a time to optimize for this scenario. This method is ideal for cost-conscious organizations that want more granular control on the number of virtual machines they've allocated for a host pool.
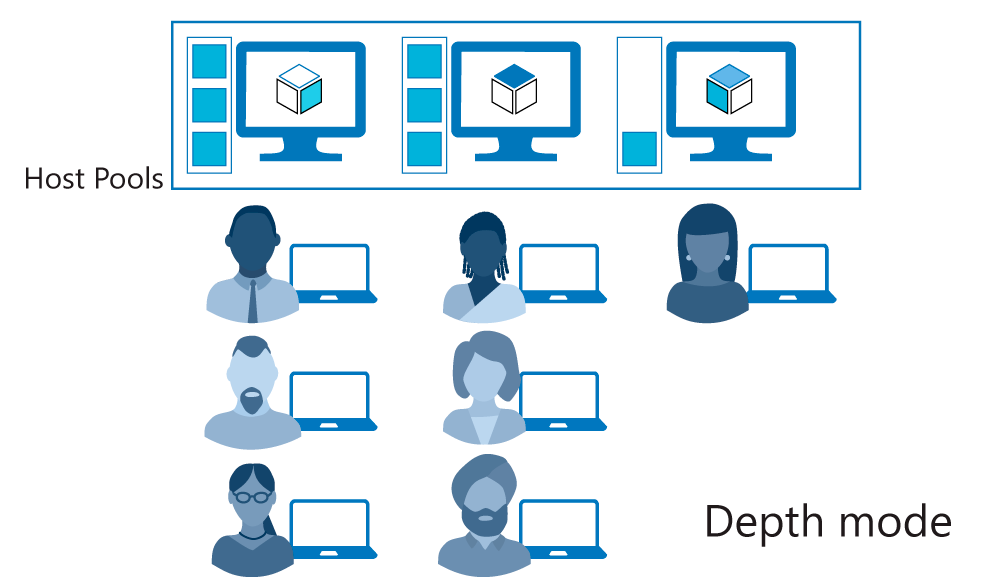
The depth-first method first queries session hosts that allow new connections and haven't gone over their maximum session limit. The method then selects the session host with highest number of sessions. If there's a tie, the method selects the first session host in the query.
The depth-first load-balancing algorithm distributes sessions to session hosts based on the maximum session host limit. This parameter is required when you use the depth-first load-balancing algorithm. For the best possible user experience, make sure to change the maximum session host limit parameter to a number that best suits your environment.