I'd suggest starting a case here with product support.
https://support.serviceshub.microsoft.com/supportforbusiness
--please don't forget to Accept as answer if the reply is helpful--
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Hi everyone, I hope you are doing well.
for the past few months, our clients have been using the Routing and RAS service to access our windows server 2016 via VPN. The VPN service has been configured as described in https://www.starwindsoftware.com/blog/how-to-install-vpn-access-on-windows-server-2016.
Since last week, we are having problems with the Routing and RAS service: The server has not been reachable anymore as the network/ethernet connection broke. After a restart, the server is reachable again - but only until the routing and ras service starts. We have tried several settings in the Routing and RAS configuration but nothing worked for us. The only way to get everything working again, was to deactivate, delete and re-configure the routing and ras service with multiple restarts in between. After that, the server connection + vpn service works fine again. After ~8 days, the exact same problem occurred again.
The event log does not show any anomalies. We only have one NIC (if this information is important). The network configuration, however, shows that whenever the problem occurs, the RAS Dial interface is not showing up as usual (in the success case):
PPP-Adapter RAS (Dial In) Interface:
Verbindungsspezifisches DNS-Suffix:
Beschreibung. . . . . . . . . . . : RAS (Dial In) Interface
Physische Adresse . . . . . . . . :
DHCP aktiviert. . . . . . . . . . : Nein
Autokonfiguration aktiviert . . . : Ja
IPv4-Adresse . . . . . . . . . . : 10.0.0.1(Bevorzugt)
Subnetzmaske . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.255
Standardgateway . . . . . . . . . :
NetBIOS über TCP/IP . . . . . . . : Aktiviert
Do you have any idea what could be the reason for this problem and how we could fix it?
Best Regards
Kevin
I'd suggest starting a case here with product support.
https://support.serviceshub.microsoft.com/supportforbusiness
--please don't forget to Accept as answer if the reply is helpful--
Thank you. Maybe someone else ran into the same problem before and can help us to fix the issue.
If not, we will start a case with the product support.
Best,
Kevin

Hello Kevin,
Is this a correct understanding of the situation when the problem is active:
Gary
Hi Gary,
thanks for your help!
Yes, this understanding is (almost) correct:
One thing that we could observe (I dont know if that is important) was that the IP ROUTING has flipped from non-active to active again, after deactivating the RRAS service again. However, the local network connection still did not work anymore until the server got restarted. In the following you can see the ipconfig /all in the error case (with flipping IP Routing):
C:\Users\Administrator>ipconfig /all
Windows-IP-Konfiguration
Hostname . . . . . . . . . . . . : WIN-XY
Primäres DNS-Suffix . . . . . . . :
Knotentyp . . . . . . . . . . . . : Hybrid
IP-Routing aktiviert . . . . . . : Nein
WINS-Proxy aktiviert . . . . . . : Nein
Ethernet-Adapter Ethernet:
Verbindungsspezifisches DNS-Suffix:
Beschreibung. . . . . . . . . . . : Red Hat VirtIO Ethernet Adapter
Physische Adresse . . . . . . . . : FA-16-3E-FF-0B-C6
DHCP aktiviert. . . . . . . . . . : Ja
Autokonfiguration aktiviert . . . : Ja
Verbindungslokale IPv6-Adresse . : fe80::48b7:6382:f01e:aa57%15(Bevorzugt)
IPv4-Adresse . . . . . . . . . . : X.Y.Z.W(Bevorzugt)
Subnetzmaske . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Lease erhalten. . . . . . . . . . : Sonntag, 6. Dezember 2020 11:13:21
Lease läuft ab. . . . . . . . . . : Montag, 7. Dezember 2020 11:13:21
Standardgateway . . . . . . . . . : X.Y.Z.1
DHCP-Server . . . . . . . . . . . : 46.243.90.4
DHCPv6-IAID . . . . . . . . . . . : 55727104
DHCPv6-Client-DUID. . . . . . . . : 00-01-00-01-26-61-D4-67-FA-16-3E-FF-0B-C6
DNS-Server . . . . . . . . . . . : 109.237.142.6
109.237.143.6
NetBIOS über TCP/IP . . . . . . . : Aktiviert
Tunneladapter isatap.{E3FE5266-8B89-4659-B781-EDF5349AC86D}:
Medienstatus. . . . . . . . . . . : Medium getrennt
Verbindungsspezifisches DNS-Suffix:
Beschreibung. . . . . . . . . . . : Microsoft ISATAP Adapter
Physische Adresse . . . . . . . . : 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-E0
DHCP aktiviert. . . . . . . . . . : Nein
Autokonfiguration aktiviert . . . : Ja
Tunneladapter Teredo Tunneling Pseudo-Interface:
Verbindungsspezifisches DNS-Suffix:
Beschreibung. . . . . . . . . . . : Teredo Tunneling Pseudo-Interface
Physische Adresse . . . . . . . . : 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-E0
DHCP aktiviert. . . . . . . . . . : Nein
Autokonfiguration aktiviert . . . : Ja
IPv6-Adresse. . . . . . . . . . . : 2001:0:2851:782c:24b0:3ca9:4deb:9b6f(Bevorzugt)
Verbindungslokale IPv6-Adresse . : fe80::24b0:3ca9:4deb:9b6f%5(Bevorzugt)
Standardgateway . . . . . . . . . : ::
DHCPv6-IAID . . . . . . . . . . . : 134217728
DHCPv6-Client-DUID. . . . . . . . : 00-01-00-01-26-61-D4-67-FA-16-3E-FF-0B-C6
NetBIOS über TCP/IP . . . . . . . : Deaktiviert
C:\Users\Administrator>ipconfig /all
Windows-IP-Konfiguration
Hostname . . . . . . . . . . . . : WIN-XY
Primäres DNS-Suffix . . . . . . . :
Knotentyp . . . . . . . . . . . . : Hybrid
IP-Routing aktiviert . . . . . . : Ja
WINS-Proxy aktiviert . . . . . . : Nein
Ethernet-Adapter Ethernet:
Verbindungsspezifisches DNS-Suffix:
Beschreibung. . . . . . . . . . . : Red Hat VirtIO Ethernet Adapter
Physische Adresse . . . . . . . . : FA-16-3E-FF-0B-C6
DHCP aktiviert. . . . . . . . . . : Ja
Autokonfiguration aktiviert . . . : Ja
Verbindungslokale IPv6-Adresse . : fe80::48b7:6382:f01e:aa57%15(Bevorzugt)
IPv4-Adresse . . . . . . . . . . : X.Y.Z.W(Bevorzugt)
Subnetzmaske . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Lease erhalten. . . . . . . . . . : Sonntag, 6. Dezember 2020 11:13:21
Lease läuft ab. . . . . . . . . . : Montag, 7. Dezember 2020 11:13:21
Standardgateway . . . . . . . . . : X.Y.Z.1
DHCP-Server . . . . . . . . . . . : 46.243.90.4
DHCPv6-IAID . . . . . . . . . . . : 55727104
DHCPv6-Client-DUID. . . . . . . . : 00-01-00-01-26-61-D4-67-FA-16-3E-FF-0B-C6
DNS-Server . . . . . . . . . . . : 109.237.142.6
109.237.143.6
NetBIOS über TCP/IP . . . . . . . : Aktiviert
Tunneladapter isatap.{E3FE5266-8B89-4659-B781-EDF5349AC86D}:
Medienstatus. . . . . . . . . . . : Medium getrennt
Verbindungsspezifisches DNS-Suffix:
Beschreibung. . . . . . . . . . . : Microsoft ISATAP Adapter
Physische Adresse . . . . . . . . : 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-E0
DHCP aktiviert. . . . . . . . . . : Nein
Autokonfiguration aktiviert . . . : Ja
Tunneladapter Teredo Tunneling Pseudo-Interface:
Verbindungsspezifisches DNS-Suffix:
Beschreibung. . . . . . . . . . . : Teredo Tunneling Pseudo-Interface
Physische Adresse . . . . . . . . : 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-E0
DHCP aktiviert. . . . . . . . . . : Nein
Autokonfiguration aktiviert . . . : Ja
IPv6-Adresse. . . . . . . . . . . : 2001:0:2851:782c:24b0:3ca9:4deb:9b6f(Bevorzugt)
Verbindungslokale IPv6-Adresse . : fe80::24b0:3ca9:4deb:9b6f%5(Bevorzugt)
Standardgateway . . . . . . . . . : ::
DHCPv6-IAID . . . . . . . . . . . : 134217728
DHCPv6-Client-DUID. . . . . . . . : 00-01-00-01-26-61-D4-67-FA-16-3E-FF-0B-C6
NetBIOS über TCP/IP . . . . . . . : Deaktiviert
Please Note: Whenever this problem occurred (yesterday and last week), the only way to get the RRAS service working again without breaking the local network was to disable and re-configure the RRAS service (with the same settings) and restarting the entire server multiple times in between (to empty the cache).
I really appreciate your help!
Best
Kevin

Hello Kevin,
The first difficulty is to know/decide what to investigate first: the total loss of IP connectivity or anomalies in the RRAS.
There are many things that might need to be checked to understand the IP connectivity problem, so it might be best to start with a focussed look at the behaviour of RRAS.
I would suggest using Event Tracing for Windows (ETW) to trace the Microsoft-Windows-RRAS provider, starting the trace before the RemoteAccess service is started.
This can be done a number of ways; for example:
The type of data recorded looks something like this:
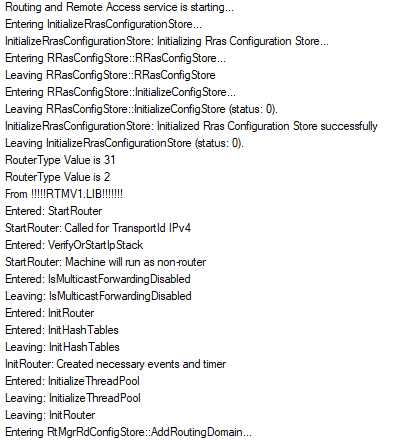
Check what you can capture and see whether anything stands out in the trace data as the onset of a problem. If you need to know what could be expected at a particular point in the trace then let us know and we can see if we can find the corresponding point in the trace of a working system.
Gary