Events
31 Mar, 11 pm - 2 Apr, 11 pm
The biggest Fabric, Power BI, and SQL learning event. March 31 – April 2. Use code FABINSIDER to save $400.
Register todayThis browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
Follow this article when you want to parse the Parquet files or write the data into Parquet format.
Parquet format is supported for the following connectors:
For a list of supported features for all available connectors, visit the Connectors Overview article.
Important
For copy empowered by Self-hosted Integration Runtime e.g. between on-premises and cloud data stores, if you are not copying Parquet files as-is, you need to install the 64-bit JRE 8 (Java Runtime Environment), JDK 23 (Java Development Kit), or OpenJDK on your IR machine. Check the following paragraph with more details.
For copy running on Self-hosted IR with Parquet file serialization/deserialization, the service locates the Java runtime by firstly checking the registry (SOFTWARE\JavaSoft\Java Runtime Environment\{Current Version}\JavaHome) for JRE, if not found, secondly checking system variable JAVA_HOME for OpenJDK.
JAVA_HOME system variable to the root folder of the JDK 23 installation i.e. C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-23, and add the path to both the C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-23\bin and C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-23\bin\server folders to the Path system variable.Tip
If you copy data to/from Parquet format using Self-hosted Integration Runtime and hit error saying "An error occurred when invoking java, message: java.lang.OutOfMemoryError:Java heap space", you can add an environment variable _JAVA_OPTIONS in the machine that hosts the Self-hosted IR to adjust the min/max heap size for JVM to empower such copy, then rerun the pipeline.
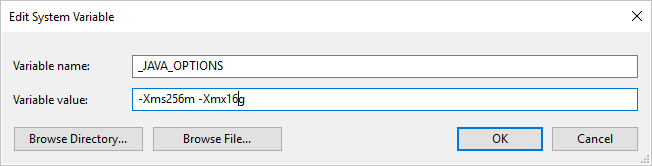
Example: set variable _JAVA_OPTIONS with value -Xms256m -Xmx16g. The flag Xms specifies the initial memory allocation pool for a Java Virtual Machine (JVM), while Xmx specifies the maximum memory allocation pool. This means that JVM will be started with Xms amount of memory and will be able to use a maximum of Xmx amount of memory. By default, the service uses min 64 MB and max 1G.
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining datasets, see the Datasets article. This section provides a list of properties supported by the Parquet dataset.
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the dataset must be set to Parquet. | Yes |
| location | Location settings of the file(s). Each file-based connector has its own location type and supported properties under location. See details in connector article -> Dataset properties section. |
Yes |
| compressionCodec | The compression codec to use when writing to Parquet files. When reading from Parquet files, Data Factories automatically determine the compression codec based on the file metadata. Supported types are "none", "gzip", "snappy" (default), and "lzo". Note currently Copy activity doesn't support LZO when read/write Parquet files. |
No |
Note
White space in column name is not supported for Parquet files.
Below is an example of Parquet dataset on Azure Blob Storage:
{
"name": "ParquetDataset",
"properties": {
"type": "Parquet",
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "<Azure Blob Storage linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"schema": [ < physical schema, optional, retrievable during authoring > ],
"typeProperties": {
"location": {
"type": "AzureBlobStorageLocation",
"container": "containername",
"folderPath": "folder/subfolder",
},
"compressionCodec": "snappy"
}
}
}
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining activities, see the Pipelines article. This section provides a list of properties supported by the Parquet source and sink.
The following properties are supported in the copy activity *source* section.
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the copy activity source must be set to ParquetSource. | Yes |
| storeSettings | A group of properties on how to read data from a data store. Each file-based connector has its own supported read settings under storeSettings. See details in connector article -> Copy activity properties section. |
No |
The following properties are supported in the copy activity *sink* section.
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the copy activity sink must be set to ParquetSink. | Yes |
| formatSettings | A group of properties. Refer to Parquet write settings table below. | No |
| storeSettings | A group of properties on how to write data to a data store. Each file-based connector has its own supported write settings under storeSettings. See details in connector article -> Copy activity properties section. |
No |
Supported Parquet write settings under formatSettings:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type of formatSettings must be set to ParquetWriteSettings. | Yes |
| maxRowsPerFile | When writing data into a folder, you can choose to write to multiple files and specify the max rows per file. | No |
| fileNamePrefix | Applicable when maxRowsPerFile is configured.Specify the file name prefix when writing data to multiple files, resulted in this pattern: <fileNamePrefix>_00000.<fileExtension>. If not specified, file name prefix will be auto generated. This property does not apply when source is file-based store or partition-option-enabled data store. |
No |
In mapping data flows, you can read and write to parquet format in the following data stores: Azure Blob Storage, Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1, Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 and SFTP, and you can read parquet format in Amazon S3.
The below table lists the properties supported by a parquet source. You can edit these properties in the Source options tab.
| Name | Description | Required | Allowed values | Data flow script property |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Format | Format must be parquet |
yes | parquet |
format |
| Wild card paths | All files matching the wildcard path will be processed. Overrides the folder and file path set in the dataset. | no | String[] | wildcardPaths |
| Partition root path | For file data that is partitioned, you can enter a partition root path in order to read partitioned folders as columns | no | String | partitionRootPath |
| List of files | Whether your source is pointing to a text file that lists files to process | no | true or false |
fileList |
| Column to store file name | Create a new column with the source file name and path | no | String | rowUrlColumn |
| After completion | Delete or move the files after processing. File path starts from the container root | no | Delete: true or false Move: [<from>, <to>] |
purgeFiles moveFiles |
| Filter by last modified | Choose to filter files based upon when they were last altered | no | Timestamp | modifiedAfter modifiedBefore |
| Allow no files found | If true, an error is not thrown if no files are found | no | true or false |
ignoreNoFilesFound |
The below image is an example of a parquet source configuration in mapping data flows.
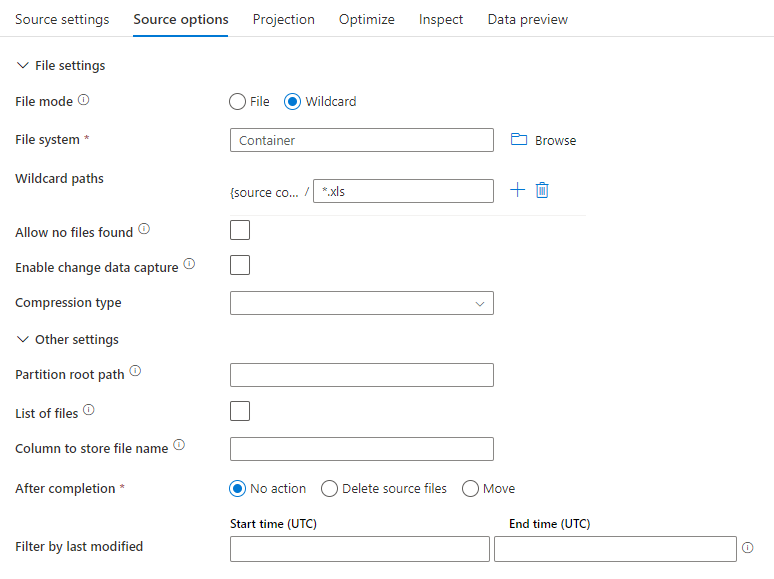
The associated data flow script is:
source(allowSchemaDrift: true,
validateSchema: false,
rowUrlColumn: 'fileName',
format: 'parquet') ~> ParquetSource
The below table lists the properties supported by a parquet sink. You can edit these properties in the Settings tab.
| Name | Description | Required | Allowed values | Data flow script property |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Format | Format must be parquet |
yes | parquet |
format |
| Clear the folder | If the destination folder is cleared prior to write | no | true or false |
truncate |
| File name option | The naming format of the data written. By default, one file per partition in format part-#####-tid-<guid> |
no | Pattern: String Per partition: String[] As data in column: String Output to single file: ['<fileName>'] |
filePattern partitionFileNames rowUrlColumn partitionFileNames |
The below image is an example of a parquet sink configuration in mapping data flows.
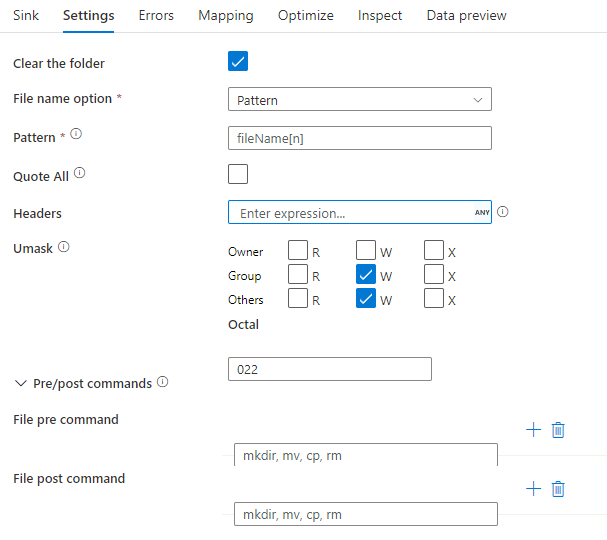
The associated data flow script is:
ParquetSource sink(
format: 'parquet',
filePattern:'output[n].parquet',
truncate: true,
allowSchemaDrift: true,
validateSchema: false,
skipDuplicateMapInputs: true,
skipDuplicateMapOutputs: true) ~> ParquetSink
Parquet complex data types (e.g. MAP, LIST, STRUCT) are currently supported only in Data Flows, not in Copy Activity. To use complex types in data flows, do not import the file schema in the dataset, leaving schema blank in the dataset. Then, in the Source transformation, import the projection.
Events
31 Mar, 11 pm - 2 Apr, 11 pm
The biggest Fabric, Power BI, and SQL learning event. March 31 – April 2. Use code FABINSIDER to save $400.
Register todayTraining
Module
Petabyte-scale ingestion with Azure Data Factory - Training
Petabyte-scale ingestion with Azure Data Factory or Azure Synapse Pipeline