Tutorial: Load GeoJSON data into Azure Maps Android SDK
This tutorial guides you through the process of importing a GeoJSON file of location data into the Azure Maps Android SDK. In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Add Azure Maps to an Android application.
- Create a data source and load in a GeoJSON file from a local file or the web.
- Display the data on the map.
- Interact with the data on the maps to view its details.
Note
Azure Maps Android SDK retirement
The Azure Maps Native SDK for Android is now deprecated and will be retired on 3/31/25. To avoid service disruptions, migrate to the Azure Maps Web SDK by 3/31/25. For more information, see The Azure Maps Android SDK migration guide.
Prerequisites
- Complete the Quickstart: Create an Android app. This tutorial extends the code used in that quickstart.
- Download the Sample Points of Interest GeoJSON file.
Import GeoJSON data from web or assets folder
Most GeoJSON files wrap all data within a FeatureCollection. With this scenario in mind, if the GeoJSON files are loaded into the application as a string, they can be passed into the feature collection's static fromJson method, which deserializes the string into a GeoJSON FeatureCollection object that can be added to the map.
The following steps show you how to import a GeoJSON file into the application and deserialize it as a GeoJSON FeatureCollection object.
- Complete the Quickstart: Create an Android app as the following steps build on top of this application.
- In the project panel of Android studio, right-click on the app folder and go to
New > Folder > Assets Folder. - Drag and drop the Sample Points of Interest GeoJSON file into the assets folder.
- Go into the MainActivity.java file and add the following code inside the callback for the
mapControl.onReadyevent, inside theonCreatemethod. This code loads the SamplePoiDataSet.json file from the assets folder into a data source usingimportDataFromUrlmethod and then adds it to the map.
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
DataSource source = new DataSource();
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
source.importDataFromUrl("asset://SamplePoiDataSet.json");
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source);
- Go into the MainActivity.kt file and add the following code inside the callback for the
mapControl.onReadyevent, inside theonCreatemethod. This code loads the SamplePoiDataSet.json file from the assets folder into a data source usingimportDataFromUrlmethod and then adds it to the map.
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
DataSource source = new DataSource();
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
source.importDataFromUrl("asset://SamplePoiDataSet.json");
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source);
- Using the code to load the GeoJSON data a data source, we now need to specify how that data should be displayed on the map. There are several different rendering layers for point data; Bubble layer, Symbol layer, and Heat map layer are the most commonly used layers. Add the following code to render the data in a bubble layer in the callback for the
mapControl.onReadyevent after the code for importing the data.
//Create a layer and add it to the map.
BubbleLayer layer = new BubbleLayer(source);
map.layers.add(layer);
//Create a layer and add it to the map.
val layer = new BubbleLayer(source)
map.layers.add(layer)
- In the project panel of Android studio, right-click on the layout folder under the path
app > res > layoutand go toNew > File. Create a new file called popup_text.xml. - Open the popup_text.xml file. If the file opens in a designer view, right-click on the screen and select Go to XML. Copy and paste the following XML into this file. This XML creates a simple layout that can be used with a popup and contains a text view.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#ffffff"
android:layout_margin="8dp"
android:padding="10dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/message"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text=""
android:textSize="18dp"
android:textColor="#222"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:width="200dp"/>
</RelativeLayout>
- Go back into the MainActivity.java file and after the code for the bubble layer, add the following code to create a reusable popup.
//Create a popup and add it to the map.
Popup popup = new Popup();
map.popups.add(popup);
//Close it initially.
popup.close();
- Go back into the MainActivity.kt file and after the code for the bubble layer, add the following code to create a reusable popup.
//Create a popup and add it to the map.
val popup = Popup()
map.popups.add(popup)
//Close it initially.
popup.close()
- Add the following code to attach a
clickevent to the bubble layer. When a bubble in the bubble layer is tapped, the event fires and retrieves details from the properties of the selected feature, create a view using the popup_text.xml layout file, pass it in as content into the popup, then show the popup at the features position.
//Add a click event to the layer.
map.events.add((OnFeatureClick)(feature) -> {
//Get the first feature and it's properties.
Feature f = feature.get(0);
JsonObject props = f.properties();
//Retrieve the custom layout for the popup.
View customView = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.popup_text, null);
//Display the name and entity type information of the feature into the text view of the popup layout.
TextView tv = customView.findViewById(R.id.message);
tv.setText("%s\n%s",
f.getStringProperty("Name"),
f.getStringProperty("EntityType")
);
//Get the position of the clicked feature.
Position pos = MapMath.getPosition((Point)f.geometry());
//Set the options on the popup.
popup.setOptions(
//Set the popups position.
position(pos),
//Set the anchor point of the popup content.
anchor(AnchorType.BOTTOM),
//Set the content of the popup.
content(customView)
);
//Open the popup.
popup.open();
//Return a boolean indicating if event should be consumed or continue to bubble up.
return false;
}, layer);
//Add a click event to the layer.
map.events.add(OnFeatureClick { feature: List<Feature> ->
//Get the first feature and it's properties.
val f = feature[0]
val props = f.properties()
//Retrieve the custom layout for the popup.
val customView: View = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.popup_text, null)
//Display the name and entity type information of the feature into the text view of the popup layout.
val tv = customView.findViewById<TextView>(R.id.message)
tv.text = String.format(
"%s\n%s",
f.getStringProperty("Name"),
f.getStringProperty("EntityType")
)
//Get the position of the clicked feature.
val pos = MapMath.getPosition(f.geometry() as Point?)
//Set the options on the popup.
popup.setOptions( //Set the popups position.
position(pos), //Set the anchor point of the popup content.
anchor(AnchorType.BOTTOM), //Set the content of the popup.
content(customView)
)
//Open the popup.
popup.open()
//Return a boolean indicating if event should be consumed or continue to bubble up.
false
} as OnFeatureClick, layer)
Run the application. A map is displayed with bubbles overlaid for each location in the GeoJSON file. Tapping on any bubble displays a popup with the name and entity type of the feature touched.
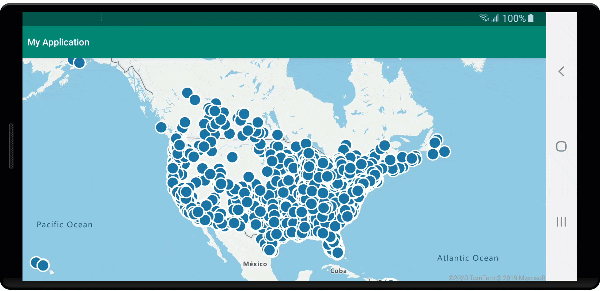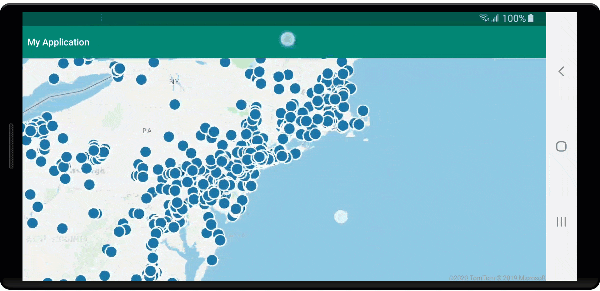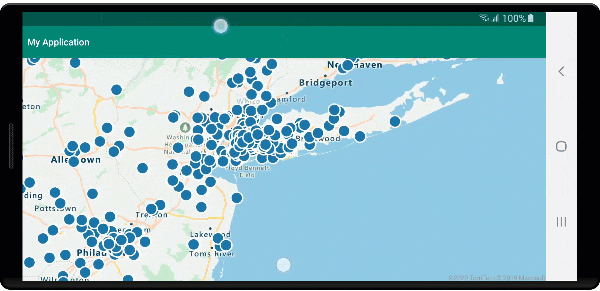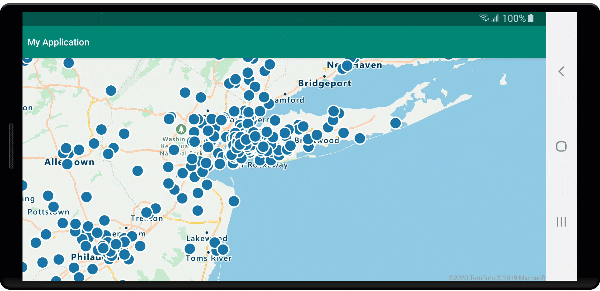
Clean up resources
Take the following steps to clean up the resources from this tutorial:
- Close Android Studio and delete the application you created.
- If you tested the application on an external device, uninstall the application from that device.
Next steps
To see more code examples and an interactive coding experience: