Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Creating the optimal model for your business can be a rather iterative process. Results can vary depending on the configurations you set and the training data you provide. Updating these factors can improve the performance of your model. In some cases, however, performance might be degraded. Each AI model type has a set of guidelines to help you with the process of creating the best model, tailored to your needs.
Evaluate your model
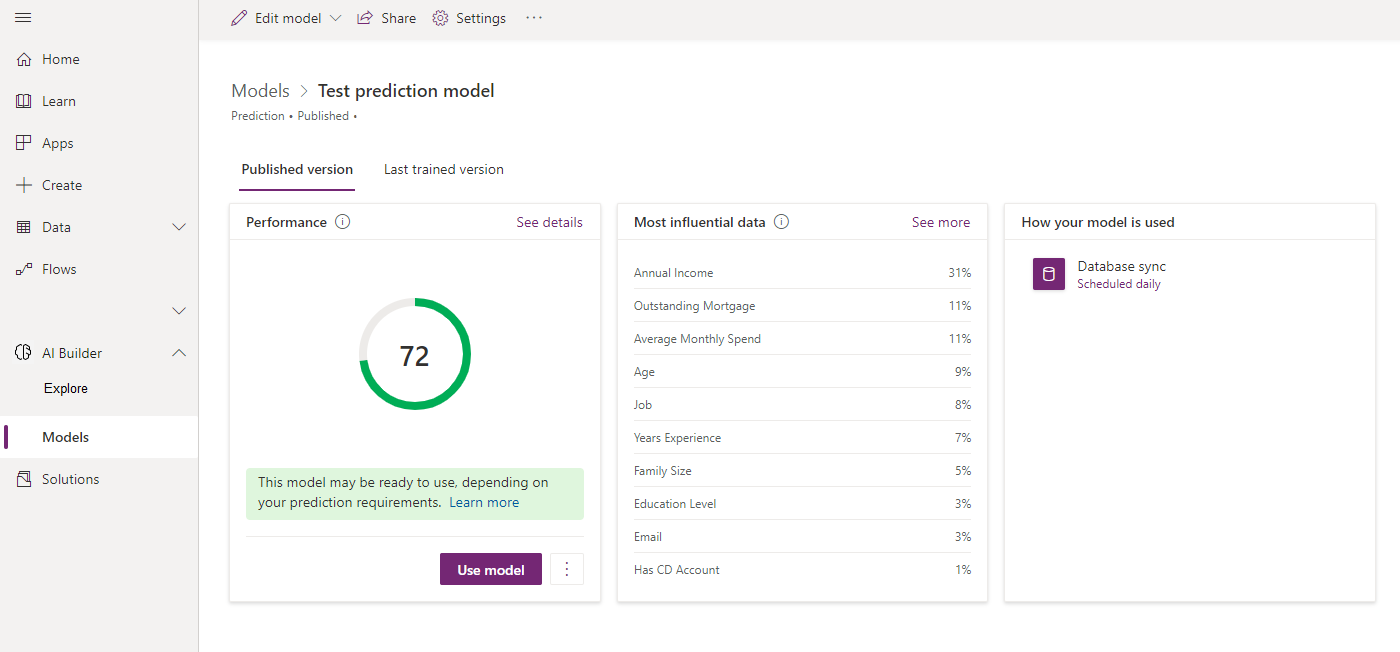
After you train your model for the first time, you can evaluate its performance and quality on its details page.
Depending on your AI model type, a performance score might appear for each trained version. You can use this score to quickly compare two versions of the same model. However, remember that the score is based on the configuration for that training. Make sure you take any changes you made between versions into consideration when you compare scores.
Each AI model type has a different explanation for how the score is calculated and how the score should be interpreted. View the tooltip next to Performance to learn more.
Some AI model types include a feature to quickly test the performance for your trained version with real data of your choosing. Select Quick test to see your model in action.
After you finish evaluating your newly trained model, you have two options:
- Publish your model: For more information about when to publish a model, see When should I publish my model?.
- Create a new version: For more information about when to create a new version, see When should I create a new version?.
Underfit models
An underfit model is a model that actually performs worse than a random guess. If your model consistently performs poorly, it's probably an indication that there's a problem with your training data. Are the fields you're using relevant to the type of determination that your model is intended to make? Are there data input errors or other problems that are leading your model astray?
Overfit models
An overfit model appears to perform very well—if not perfectly—when run on your training data. That can be because there's a column in your training data that directly corresponds to outcome. For example, let's say you have a prediction model that predicts whether a shipment will arrive on time. If your historical data includes the actual delivery date, your model would predict perfectly when run against your historical data. It probably wouldn't do so well when run on real data in your business environment, because the delivery date column wouldn't be populated yet.
Edit the model name
- At the top of the page, select Settings.
- In the Model settings panes on the right, under Name, enter a different name. Depending on your AI model type, you might need to first select the General section.
- Select Save.
Create a new version
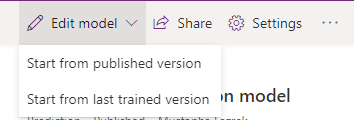
To create a new version, select Edit model at the top of the page.
You can have up to two trained versions available at a time: one Published version and one Last trained version that isn't published. If you train a new version when a last trained version already exists, the existing last trained version is overwritten.
When you create a new version, your model is based on the configuration from an existing version—your published version, or your last trained version. If you have both, you have to choose which one you want to create the new version from.
A new version is created only after you've successfully trained it. If you leave without finishing your changes and training your model, your progress is saved as a draft. Certain actions, such as creating a new version or retraining, might be disabled until you train or discard your draft. You can only have one draft available at a time, so you have to select either Resume draft to pick up where you left off or Discard draft to get rid of the changes before you can continue.
After training, your training results appear under the Last trained version section of the Details page.
If you're satisfied with your last trained version, you can publish your model to make it available. Otherwise, you can always create a new version.
When should I create a new version?
You can create a new version of your model to help improve the model performance or quality. This depends on the AI model type: some models can be improved by updating the configuration, and some models can be improved by updating the training data.
Due to the experimental nature of machine learning, not all new versions you create will result in an increase in model performance. If you aren't satisfied with your model, you can create a new version to try to yield better results.
If you're satisfied with your model, you can publish it to make it available. Because you can only have two trained versions available at a time, you might want to publish a model that you don't want to be overwritten by a new version.
For more information about the nuances of improving your model performance, see the message underneath your accuracy score.
Retrain and republish existing models
Whereas training creates a new version by updating your configuration, retraining creates a new version that uses the same configuration as your current version. The benefit of retraining is that it will study any new data so that your model stays accurate over time. This action is only applicable to certain AI model types.
Sign in to Power Apps.
On the left pane, select AI Builder > Models.
Follow the steps for your model type.
For prediction and category classification models, in the Performance section, select the (…) menu, and then select Retrain now.
This replaces your last trained version. If you're ready, publish this version.
Perform these steps on each of your AI Builder models to get your AI models up and running again.
Next step
Publish your model in AI Builder