Hi @Bogdan Carjac ,
Thanks for reaching out.
I understood, you are able to get the access token using Authorization code flow and now using this access token you can call any protected API/WebAPI or Microsoft Graph API.
Here, first need to understand two different validations of Access Token:
1.Access token is a JWT that contains claims that you can use to identify the granted permissions to your APIs. .An access token contains claims such as scopes, roles and audience that you can use in Azure Active Directory to identify the granted permissions to your APIs. Your application/API must validate claims in the token to prove that it is valid.
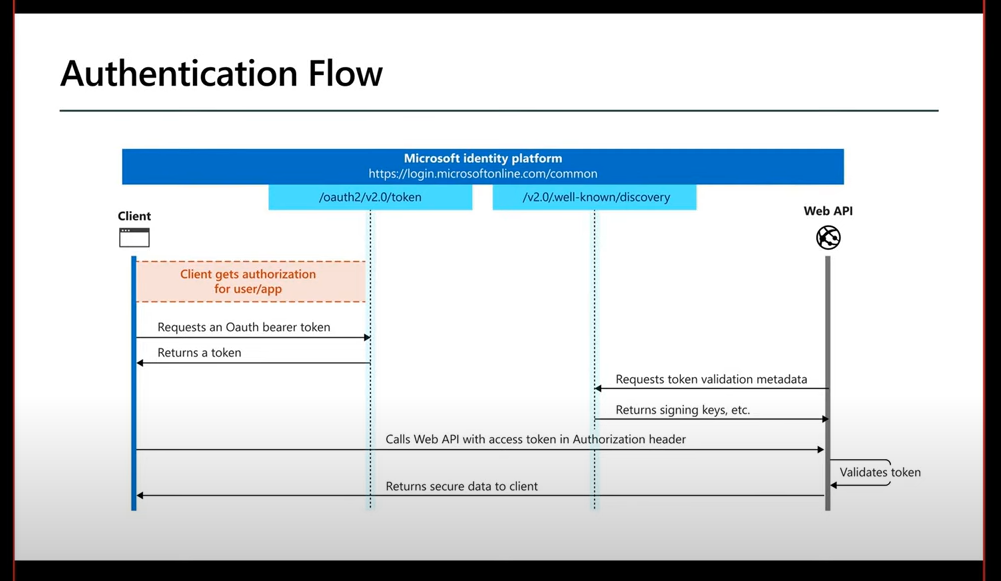
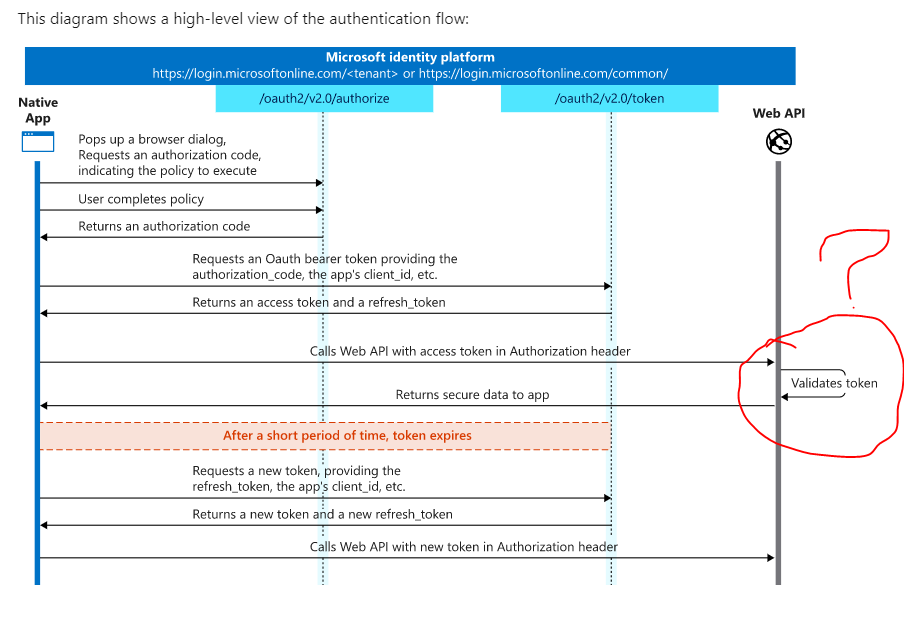
There are different flows to get the access token based on application types and their scenarios. The flow you mentioned above is Authorization Code Flow and there are two steps to get the access token in this flow.
a. Authorize Endpoint- to acquire the code
b. Token Endpoint - to acquire the token in exchange of the code
and then this access token can be used to call the Web API . eg You can use the access token to call Graph API endpoint provided by Microsoft Identity Provider https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/me to get the user details. To get the user's details token must have User.Read scope with Graph API audience.
Access token should have valid scopes or audience to call any API. Access token with Graph API scopes User.Read cannot be used to call API which is reading user's email. These scopes we need to define while registering the application based on the scenario. Refer here
Refer :https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/scenario-web-app-call-api-overview
2.Another validation is access tokens are signed by Azure Active Directory.
When your internal application receives an access token, it must validate the signature to prove that the token is authentic.
To Verify the JWT token that it has not been tampered by an attacker.
Verify that the JWT contains three segments, separated by two period ('.') characters.
Parse the JWT to extract its three components. The first segment is the Header, the second is the Payload, and the third is the Signature. Each segment is base64url encoded.
Signature contains the digital signature of the token that was generated by Azure AD’s private key and verify that the token was signed by the sender.
To validate the authenticity of the JWT token’s data is by using Azure AD’s public key to verify the signature.
You can obtain public key by calling the public Azure AD OpenID configuration endpoint:
https://login.microsoftonline.com/{tenant_id}/discovery/keys?appid={client_id} and verify against the private key generated by Azure AD token. For validation, developers can decode JWTs using jwt.ms and verify against "kid" claim.
If it works, you know the contents were signed with the private key. If not, you can’t be sure of it so you should treat the JWT token as an invalid token.
Hope this will help.
Thanks,
Shweta
-------------------------------------
Please remember to "Accept Answer" if answer helped you.