Thanks for reaching out.
To use application permissions with your own API (as opposed to Microsoft Graph), you must first expose the API by defining scopes in the API's app registration in the Azure portal. Then, configure access to the API by selecting those permissions in your client application's app registration. If you haven't exposed any scopes in your API's app registration, you won't be able to specify application permissions to that API in your client application's app registration in the Azure portal.
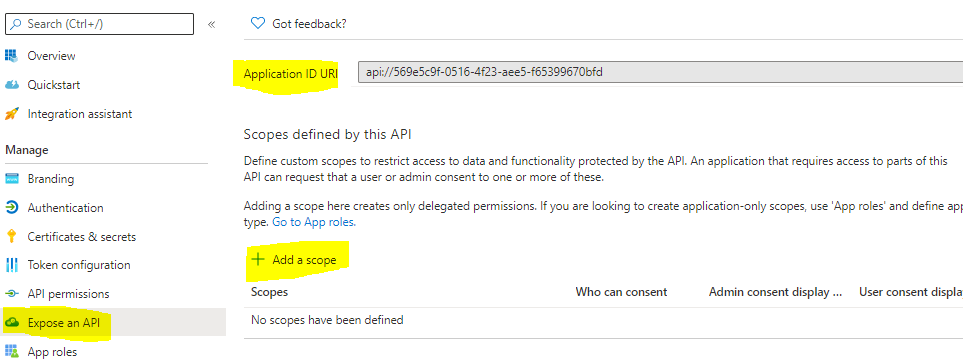
For an example, if I sent scope parameter with custom name like https://testwebapp.in/.default without configuring same as application ID URI in Azure AD then is an expected behavior and you get error AADSTS500011.
scope parameter in the request should be the resource identifier (application ID URI) of the resource you want, affixed with the .default suffix. For the Microsoft Graph example, the value is https://graph.microsoft.com/.default. This value tells the Microsoft identity platform that of all the direct application permissions you have configured for your app, the endpoint should issue a token for the ones associated with the resource you want to use.
Hope this helps
------
Please "Accept the answer" if the information helped you. This will help us and others in the community as well.