@geek876 , Thank you for your question(s).
I am not sure on the 'Kubernetes Service Address Range' and 'Docker Bridge Address'.
- What should I specify there ?
Kubernetes service address range: This parameter is the set of virtual IPs that Kubernetes assigns to internal services in your cluster. You can use any private address range that satisfies the following requirements:
- Must not be within the virtual network IP address range of your cluster
- Must not overlap with any other virtual networks with which the cluster virtual network peers
- Must not overlap with any on-premises IPs
- Must not be within the ranges
169.254.0.0/16,172.30.0.0/16,172.31.0.0/16, or192.0.2.0/24
Although it's technically possible to specify a service address range within the same virtual network as your cluster, doing so is not recommended. Unpredictable behavior can result if overlapping IP ranges are used. For more information, see the FAQ section of this article. For more information on Kubernetes services, see Services in the Kubernetes documentation.
Service address CIDR must be smaller than /12. You can reuse this range across different AKS clusters.
For example:
az aks show -g $RG -n akstest --query networkProfile.serviceCidr -o tsv
10.0.0.0/16
az aks show -g $RG -n akstest --query networkProfile.podCidr -o tsv
10.244.0.0/16
The Kubernetes Service Address Range for this cluster is 10.0.0.0/16 and the Pod CIDR is 10.244.0.0/16
Thus, from
az aks get-credentials -g $RG -n akstest
Merged "akstest" as current context in $HOME/.kube/config
kubectl get all -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod/nginx 1/1 Running 0 20s 10.244.2.20 aks-agentpool-xxxxxxxx-vmss000001 <none> <none>
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.0.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 359d <none>
we can see that the Cluster IP of Service resources (here service/kubernetes, CLuster IP: 10.0.0.1) in Kubernetes are allocated from the Kubernetes Service Address Range (here 10.0.0.0/16)
Pods (here pod/nginx, IP: 10.244.2.20) get their IP addresses from the Pod CIDR (here 10.244.0.0/16). With Azure CNI network plugin, the Pod CIDR is the address range of the Azure Virtual Network subnet with which the AKS cluster is deployed.
Docker Bridge address: The Docker bridge network address represents the default docker0 bridge network address present in all Docker installations. While docker0 bridge is not used by AKS clusters or the pods themselves, you must set this address to continue to support scenarios such as docker build within the AKS cluster. It is required to select a CIDR for the Docker bridge network address because otherwise Docker will pick a subnet automatically which could conflict with other CIDRs. You must pick an address space that does not collide with the rest of the CIDRs on your networks, including the cluster's service CIDR and pod CIDR. Default is 172.17.0.1/16. You can reuse this range across different AKS clusters.
For example:
az aks show -g $RG -n akstest --query networkProfile.dockerBridgeCidr -o tsv
172.17.0.1/16
This cluster has a Docker Bridge Address Range of 172.17.0.1/16
On SSH into a node on the AKS Cluster
root@aks-agentpool-xxxxxxxx-vmss000000:/# docker network ls
NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE
b9d678e05482 bridge bridge local
3a646177172f host host local
df1b33cceea6 none null local
root@aks-agentpool-xxxxxxxx-vmss000000:/# docker inspect b9d678e05482
[
{
"Name": "bridge",
"Id": "b9d678e05482xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
...
"Driver": "bridge",
"EnableIPv6": false,
"IPAM": {
"Driver": "default",
"Options": null,
"Config": [
{
"Subnet": "172.17.0.0/16",
"Gateway": "172.17.0.1"
}
]
},
...
}
]
For more information please check this document
Lets say if I specify 10.0.4.0/24 to the Kubernetes Service Address Range, will it mean that all the services that I create it will be from that range ?
The ClusterIP of the services in the cluster will be allocated from the Kubernetes Service Address Range.
If so, will I then be able to route/connect directly from any machine connected within the same VNET (example a VM that in same vnet but different subnet) to a service of type cluster IP on its cluster-IP within the k8s cluster ? I would not need an ingress for that or I will still need an ingress ?
With Azure Container Networking Interface (CNI), every pod gets an IP address from the subnet and can be accessed directly from any device within the network or a connected network. Reference
ClusterIP of Services, on the other will be allocated from the Kubernetes Service Address Range, discussed above. Although, it's technically possible to specify a service address range within the same virtual network as your cluster, doing so is not recommended. Unpredictable behavior can result if overlapping IP ranges are used. For more information, see the FAQ section of this article.
Instead, we recommend you to use an internal load balancer with Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS). An internal load balancer makes a Kubernetes service accessible only to applications running in the same virtual network (and connected networks) as the Kubernetes cluster.
Ingress exposes HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster. Traffic routing is controlled by rules defined on the Ingress resource.
Here is a simple example where an Ingress sends all its traffic to one Service:
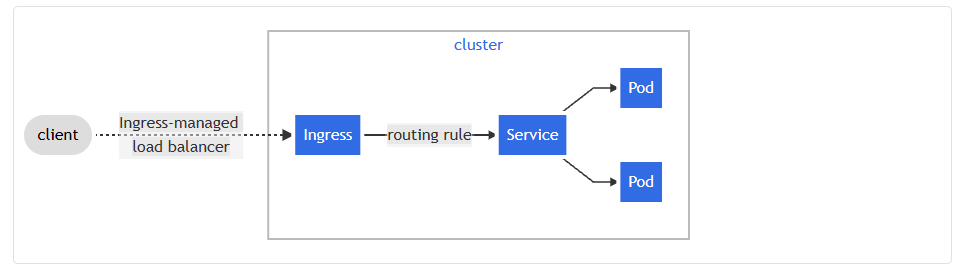
For more information please check this document.
To summarize, unless your use-case involves specific in-cluster routing rules for the Services on AKS, Ingress is not necessary. For Kubernetes Services to connect both ways with your on-premise network which is connected to the AKS cluster, services of type Azure internal load balancer should be sufficient.
If I have to use ingress for (3) above, what is the difference between using a CNI vs Kubenet. I understand Kubenet services also need Ingress as they can't be directly connected to. Our use-case is that we have a Site-To-Site VPN between Azure and On-Premise and we want kubernetes services to connect to on-site services both-ways. I understand I have to use the CNI for that. If i use kubenet, I can only have one-way (pod initiated) connection to the on-site services but not vice-versa.
Both kubenet and Azure CNI provide network connectivity for your AKS clusters. However, there are advantages and disadvantages to each. At a high level, the following considerations apply:
kubenet
- Conserves IP address space.
- Uses Kubernetes internal or external load balancer to reach pods from outside of the cluster.
- You manually manage and maintain user-defined routes (UDRs).
- Maximum of 400 nodes per cluster.
Azure CNI
- Pods get full virtual network connectivity and can be directly reached via their private IP address from connected networks.
- Requires more IP address space.
The following behavior differences exist between kubenet and Azure CNI:
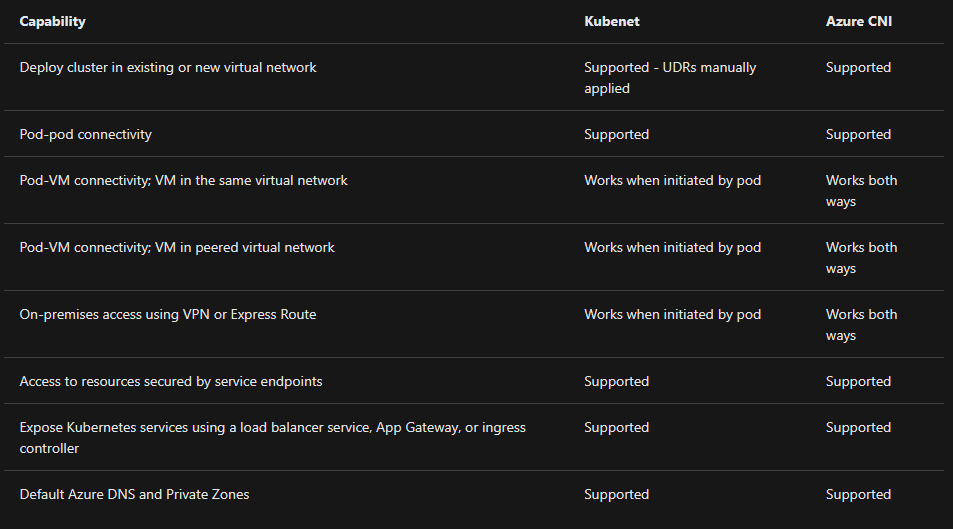
Regarding DNS, with both kubenet and Azure CNI plugins DNS are offered by CoreDNS, a deployment running in AKS with its own autoscaler. For more information on CoreDNS on Kubernetes, see Customizing DNS Service. CoreDNS by default is configured to forward unknown domains to the DNS functionality of the Azure Virtual Network where the AKS cluster is deployed. Hence, Azure DNS and Private Zones will work for pods running in AKS.
Summing up, if you need AKS pod connectivity to and from your on-premise network then Azure CNI is the only option for network plugin. However, if you want outbound traffic from the AKS pod(s) to your on-premise network directly and inbound traffic to the AKS pod(s) via Kubernetes Service resources (internal load balancer) then you can use either kubenet or Azure CNI as network plugin.
----------
Hope this helps.
Please "Accept as Answer" if it helped, so that it can help others in the community looking for help on similar topics.
