@Geert Claes Welcome to Microsoft Q & A Community Forum.
There could be several reasons for the virtual machine to be unavailable. I have provided some of the reasons below.
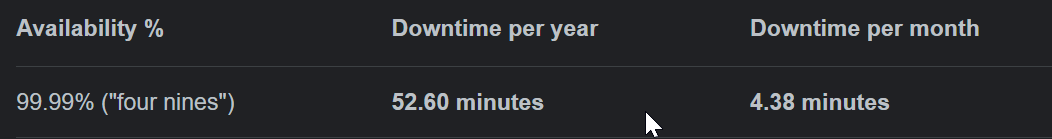
- All virtual machines adhere to the SLA's defined by Microsoft. Here are the SLA's for virtual machines. For instance, for all Virtual Machines that have two or more instances deployed across two or more Availability Zones in the same Azure region, Microsoft guarantees you will have Virtual Machine Connectivity to at least one instance at least 99.99% of the time. That means virtual machines will be unavailable for 52.60 minutes in a year due to maintenance updates, unplanned events etc.
- Host server faults : The VM is hosted on a physical server that is running inside an Azure datacenter. The physical server runs an agent called the Host Agent in addition to a few other Azure components. When these Azure software components on the physical server become unresponsive, the monitoring system triggers a reboot of the host server to attempt recovery. The VM is usually available again within five minutes and continues to live on the same host as previously.
- Auto-recovery : If the host server cannot reboot for any reason, the Azure platform initiates an auto-recovery action to take the faulty host server out of rotation for further investigation. All VMs on that host are automatically relocated to a different, healthy host server. This process is usually complete within 15 minutes To find the root cause of your issue , I would suggest you to traverse to Resource health and use Diagnose and solve problems and select the appropriate problem to troubleshoot the issue. If it doesn't help, I would suggest you to raise a Technical support ticket to investigate the case further where azure technical engineers connect one-on-one and provide you root cause of your issue.
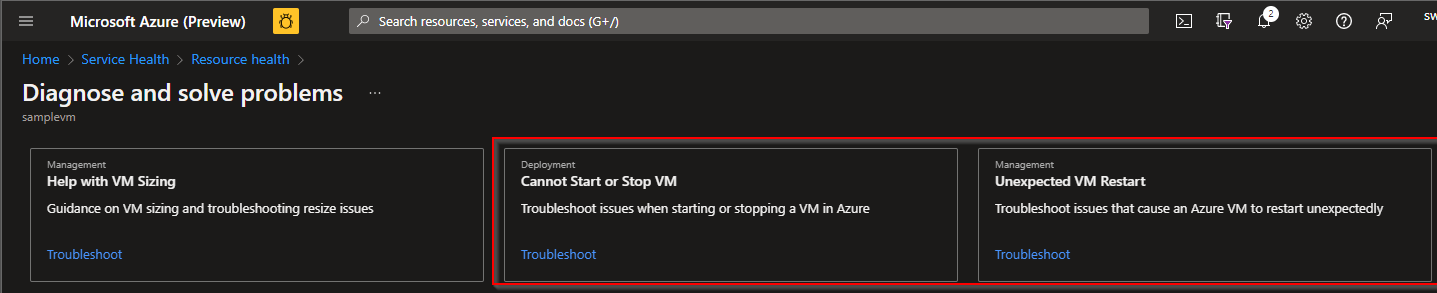
Some of the references for vm unavailability :