Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Note
This isn't the latest version of this article. For the current release, see the .NET 10 version of this article.
Warning
This version of ASP.NET Core is no longer supported. For more information, see the .NET and .NET Core Support Policy. For the current release, see the .NET 10 version of this article.
This article explains how to configure and manage SignalR connections in Blazor apps.
For general guidance on ASP.NET Core SignalR configuration, see the topics in the Overview of ASP.NET Core SignalR area of the documentation, especially ASP.NET Core SignalR configuration.
Server-side apps use ASP.NET Core SignalR to communicate with the browser. SignalR's hosting and scaling conditions apply to server-side apps.
Blazor works best when using WebSockets as the SignalR transport due to lower latency, reliability, and security. Long Polling is used by SignalR when WebSockets isn't available or when the app is explicitly configured to use Long Polling.
Azure SignalR Service with stateful reconnect
The Azure SignalR Service with SDK v1.26.1 or later supports SignalR stateful reconnect (WithStatefulReconnect).
WebSocket compression for Interactive Server components
By default, Interactive Server components:
Enable compression for WebSocket connections. DisableWebSocketCompression (default:
false) controls WebSocket compression.Adopt a
frame-ancestorsContent Security Policy (CSP) directive set to'self', which is the default and only permits embedding the app in an<iframe>of the origin from which the app is served when compression is enabled or when a configuration for the WebSocket context is provided.
The default frame-ancestors CSP can be changed by setting the value of ContentSecurityFrameAncestorsPolicy to null if you want to configure the CSP in a centralized way or 'none' for an even stricter policy. When the frame-ancestors CSP is managed in a centralized fashion, care must be taken to apply a policy whenever the first document is rendered. We don't recommend removing the policy completely, as it will make the app vulnerable to attack. For more information, see Enforce a Content Security Policy for ASP.NET Core Blazor and the MDN CSP Guide.
Use ConfigureWebSocketAcceptContext to configure the WebSocketAcceptContext for the WebSocket connections used by the server components. By default, a policy that enables compression and sets a CSP for the frame ancestors defined in ContentSecurityFrameAncestorsPolicy is applied.
Usage examples:
Disable compression by setting DisableWebSocketCompression to true, which reduces the vulnerability of the app to attack but may result in reduced performance:
builder.MapRazorComponents<App>()
.AddInteractiveServerRenderMode(o => o.DisableWebSocketCompression = true)
When compression is enabled, configure a stricter frame-ancestors CSP with a value of 'none' (single quotes required), which allows WebSocket compression but prevents browsers from embedding the app into an <iframe>:
builder.MapRazorComponents<App>()
.AddInteractiveServerRenderMode(o => o.ContentSecurityFrameAncestorsPolicy = "'none'")
When compression is enabled, remove the frame-ancestors CSP by setting ContentSecurityFrameAncestorsPolicy to null. This scenario is only recommended for apps that set the CSP in a centralized way:
builder.MapRazorComponents<App>()
.AddInteractiveServerRenderMode(o => o.ContentSecurityFrameAncestorsPolicy = null)
Important
Browsers apply CSP directives from multiple CSP headers using the strictest policy directive value. Therefore, a developer can't add a weaker frame-ancestors policy than 'self' on purpose or by mistake.
Single quotes are required on the string value passed to ContentSecurityFrameAncestorsPolicy:
Unsupported values: none, self
Supported values: 'none', 'self'
Additional options include specifying one or more host sources and scheme sources.
For security implications, see Threat mitigation guidance for ASP.NET Core Blazor interactive server-side rendering. For more information, see Enforce a Content Security Policy for ASP.NET Core Blazor and CSP: frame-ancestors (MDN documentation).
Disable response compression for Hot Reload
When using Hot Reload, disable Response Compression Middleware in the Development environment. Whether or not the default code from a project template is used, always call UseResponseCompression first in the request processing pipeline.
In the Program file:
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseResponseCompression();
}
Client-side SignalR cross-origin negotiation for authentication
This section explains how to configure SignalR's underlying client to send credentials, such as cookies or HTTP authentication headers.
Use SetBrowserRequestCredentials to set Include on cross-origin fetch requests.
IncludeRequestCredentialsMessageHandler.cs:
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebAssembly.Http;
public class IncludeRequestCredentialsMessageHandler : DelegatingHandler
{
protected override Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync(
HttpRequestMessage request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
request.SetBrowserRequestCredentials(BrowserRequestCredentials.Include);
return base.SendAsync(request, cancellationToken);
}
}
Where a hub connection is built, assign the HttpMessageHandler to the HttpMessageHandlerFactory option:
private HubConnectionBuilder? hubConnection;
...
hubConnection = new HubConnectionBuilder()
.WithUrl(new Uri(Navigation.ToAbsoluteUri("/chathub")), options =>
{
options.HttpMessageHandlerFactory = innerHandler =>
new IncludeRequestCredentialsMessageHandler { InnerHandler = innerHandler };
}).Build();
The preceding example configures the hub connection URL to the absolute URI address at /chathub. The URI can also be set via a string, for example https://signalr.example.com, or via configuration. Navigation is an injected NavigationManager.
For more information, see ASP.NET Core SignalR configuration.
Client-side rendering
If prerendering is configured, prerendering occurs before the client connection to the server is established. For more information, see ASP.NET Core Blazor prerendered state persistence.
If prerendering is configured, prerendering occurs before the client connection to the server is established. For more information, see the following articles:
Prerendered state size and SignalR message size limit
A large prerendered state size may exceed Blazor's SignalR circuit message size limit, which results in the following:
- The SignalR circuit fails to initialize with an error on the client: Circuit host not initialized.
- The reconnection UI on the client appears when the circuit fails. Recovery isn't possible.
To resolve the problem, use either of the following approaches:
- Reduce the amount of data that you are putting into the prerendered state.
- Increase the SignalR message size limit. WARNING: Increasing the limit may increase the risk of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks.
Additional client-side resources
- Secure a SignalR hub
- Overview of ASP.NET Core SignalR
- ASP.NET Core SignalR configuration
- Blazor samples GitHub repository (
dotnet/blazor-samples) (how to download)
Use session affinity (sticky sessions) for server-side web farm hosting
When more than one backend server is in use, the app must implement session affinity, also called sticky sessions. Session affinity ensures that a client's circuit reconnects to the same server if the connection is dropped, which is important because client state is only held in the memory of the server that first established the client's circuit.
The following error is thrown by an app that hasn't enabled session affinity in a web farm:
Uncaught (in promise) Error: Invocation canceled due to the underlying connection being closed.
For more information on session affinity with Azure App Service hosting, see Host and deploy ASP.NET Core server-side Blazor apps.
Azure SignalR Service
The optional Azure SignalR Service works in conjunction with the app's SignalR hub for scaling up a server-side app to a large number of concurrent connections. In addition, the service's global reach and high-performance data centers significantly aid in reducing latency due to geography.
The service isn't required for Blazor apps hosted in Azure App Service or Azure Container Apps but can be helpful in other hosting environments:
- To facilitate connection scale out.
- Handle global distribution.
For more information, see Host and deploy ASP.NET Core server-side Blazor apps.
Server-side circuit handler options
Configure the circuit with CircuitOptions. View default values in the reference source.
Note
Documentation links to .NET reference source usually load the repository's default branch, which represents the current development for the next release of .NET. To select a tag for a specific release, use the Switch branches or tags dropdown list. For more information, see How to select a version tag of ASP.NET Core source code (dotnet/AspNetCore.Docs #26205).
Read or set the options in the Program file with an options delegate to AddInteractiveServerComponents. The {OPTION} placeholder represents the option, and the {VALUE} placeholder is the value.
In the Program file:
builder.Services.AddRazorComponents().AddInteractiveServerComponents(options =>
{
options.{OPTION} = {VALUE};
});
Read or set the options in the Program file with an options delegate to AddServerSideBlazor. The {OPTION} placeholder represents the option, and the {VALUE} placeholder is the value.
In the Program file:
builder.Services.AddServerSideBlazor(options =>
{
options.{OPTION} = {VALUE};
});
Read or set the options in Startup.ConfigureServices with an options delegate to AddServerSideBlazor. The {OPTION} placeholder represents the option, and the {VALUE} placeholder is the value.
In Startup.ConfigureServices of Startup.cs:
services.AddServerSideBlazor(options =>
{
options.{OPTION} = {VALUE};
});
To configure the HubConnectionContext, use HubConnectionContextOptions with AddHubOptions. View the defaults for the hub connection context options in reference source. For option descriptions in the SignalR documentation, see ASP.NET Core SignalR configuration. The {OPTION} placeholder represents the option, and the {VALUE} placeholder is the value.
Note
Documentation links to .NET reference source usually load the repository's default branch, which represents the current development for the next release of .NET. To select a tag for a specific release, use the Switch branches or tags dropdown list. For more information, see How to select a version tag of ASP.NET Core source code (dotnet/AspNetCore.Docs #26205).
In the Program file:
builder.Services.AddRazorComponents().AddInteractiveServerComponents().AddHubOptions(options =>
{
options.{OPTION} = {VALUE};
});
In the Program file:
builder.Services.AddServerSideBlazor().AddHubOptions(options =>
{
options.{OPTION} = {VALUE};
});
In Startup.ConfigureServices of Startup.cs:
services.AddServerSideBlazor().AddHubOptions(options =>
{
options.{OPTION} = {VALUE};
});
Warning
The default value of MaximumReceiveMessageSize is 32 KB. Increasing the value may increase the risk of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks.
Blazor relies on MaximumParallelInvocationsPerClient set to 1, which is the default value. For more information, see MaximumParallelInvocationsPerClient > 1 breaks file upload in Blazor Server mode (dotnet/aspnetcore #53951).
For information on memory management, see Manage memory in deployed ASP.NET Core server-side Blazor apps.
Blazor hub options
Configure MapBlazorHub options to control HttpConnectionDispatcherOptions of the Blazor hub. View the defaults for the hub connection dispatcher options in reference source. The {OPTION} placeholder represents the option, and the {VALUE} placeholder is the value.
Note
Documentation links to .NET reference source usually load the repository's default branch, which represents the current development for the next release of .NET. To select a tag for a specific release, use the Switch branches or tags dropdown list. For more information, see How to select a version tag of ASP.NET Core source code (dotnet/AspNetCore.Docs #26205).
Place the call to app.MapBlazorHub after the call to app.MapRazorComponents in the app's Program file:
app.MapBlazorHub(options =>
{
options.{OPTION} = {VALUE};
});
Configuring the hub used by AddInteractiveServerRenderMode with MapBlazorHub fails with an AmbiguousMatchException:
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Routing.Matching.AmbiguousMatchException: The request matched multiple endpoints.
To workaround the problem for apps targeting .NET 8/9, take the following approach.
At the top of the Program file, add a using statement for Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Connections:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Connections;
Where MapRazorComponents is called, chain the following endpoint convention to the RazorComponentsEndpointConventionBuilder:
app.MapRazorComponents<App>()
.AddInteractiveServerRenderMode()
.Add(e =>
{
var metadata = e.Metadata;
var dispatcherOptions = metadata.OfType<HttpConnectionDispatcherOptions>().FirstOrDefault();
if (dispatcherOptions != null)
{
dispatcherOptions.CloseOnAuthenticationExpiration = true;
}
});
For more information, see the following resources:
- MapBlazorHub configuration in NET8 throws a The request matched multiple endpoints exception (
dotnet/aspnetcore#51698) - Attempts to map multiple blazor entry points with MapBlazorHub causes Ambiguous Route Error. This worked with net7 (
dotnet/aspnetcore#52156) - [Blazor] Provide access to the underlying SignalR HttpConnectionDispatcherOptions in AddInteractiveServerRenderMode (
dotnet/aspnetcore#63520)
Supply the options to app.MapBlazorHub in the app's Program file:
app.MapBlazorHub(options =>
{
options.{OPTION} = {VALUE};
});
Supply the options to app.MapBlazorHub in endpoint routing configuration:
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapBlazorHub(options =>
{
options.{OPTION} = {VALUE};
});
...
});
Maximum receive message size
This section only applies to projects that implement SignalR.
The maximum incoming SignalR message size permitted for hub methods is limited by the HubOptions.MaximumReceiveMessageSize (default: 32 KB). SignalR messages larger than MaximumReceiveMessageSize throw an error. The framework doesn't impose a limit on the size of a SignalR message from the hub to a client.
When SignalR logging isn't set to Debug or Trace, a message size error only appears in the browser's developer tools console:
Error: Connection disconnected with error 'Error: Server returned an error on close: Connection closed with an error.'.
When SignalR server-side logging is set to Debug or Trace, server-side logging surfaces an InvalidDataException for a message size error.
appsettings.Development.json:
{
"DetailedErrors": true,
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
...
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.SignalR": "Debug"
}
}
}
Error:
System.IO.InvalidDataException: The maximum message size of 32768B was exceeded. The message size can be configured in AddHubOptions.
One approach involves increasing the limit by setting MaximumReceiveMessageSize in the Program file. The following example sets the maximum receive message size to 64 KB:
builder.Services.AddRazorComponents().AddInteractiveServerComponents()
.AddHubOptions(options => options.MaximumReceiveMessageSize = 64 * 1024);
Increasing the SignalR incoming message size limit comes at the cost of requiring more server resources, and it increases the risk of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. Additionally, reading a large amount of content in to memory as strings or byte arrays can also result in allocations that work poorly with the garbage collector, resulting in additional performance penalties.
A better option for reading large payloads is to send the content in smaller chunks and process the payload as a Stream. This can be used when reading large JavaScript (JS) interop JSON payloads or if JS interop data is available as raw bytes. For an example that demonstrates sending large binary payloads in server-side apps that uses techniques similar to the InputFile component, see the Binary Submit sample app and the Blazor InputLargeTextArea Component Sample.
Note
Documentation links to .NET reference source usually load the repository's default branch, which represents the current development for the next release of .NET. To select a tag for a specific release, use the Switch branches or tags dropdown list. For more information, see How to select a version tag of ASP.NET Core source code (dotnet/AspNetCore.Docs #26205).
Forms that process large payloads over SignalR can also use streaming JS interop directly. For more information, see Call .NET methods from JavaScript functions in ASP.NET Core Blazor. For a forms example that streams <textarea> data to the server, see Troubleshoot ASP.NET Core Blazor forms.
One approach involves increasing the limit by setting MaximumReceiveMessageSize in the Program file. The following example sets the maximum receive message size to 64 KB:
builder.Services.AddServerSideBlazor()
.AddHubOptions(options => options.MaximumReceiveMessageSize = 64 * 1024);
Increasing the SignalR incoming message size limit comes at the cost of requiring more server resources, and it increases the risk of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. Additionally, reading a large amount of content in to memory as strings or byte arrays can also result in allocations that work poorly with the garbage collector, resulting in additional performance penalties.
A better option for reading large payloads is to send the content in smaller chunks and process the payload as a Stream. This can be used when reading large JavaScript (JS) interop JSON payloads or if JS interop data is available as raw bytes. For an example that demonstrates sending large binary payloads in Blazor Server that uses techniques similar to the InputFile component, see the Binary Submit sample app and the Blazor InputLargeTextArea Component Sample.
Note
Documentation links to .NET reference source usually load the repository's default branch, which represents the current development for the next release of .NET. To select a tag for a specific release, use the Switch branches or tags dropdown list. For more information, see How to select a version tag of ASP.NET Core source code (dotnet/AspNetCore.Docs #26205).
Forms that process large payloads over SignalR can also use streaming JS interop directly. For more information, see Call .NET methods from JavaScript functions in ASP.NET Core Blazor. For a forms example that streams <textarea> data in a Blazor Server app, see Troubleshoot ASP.NET Core Blazor forms.
Increase the limit by setting MaximumReceiveMessageSize in Startup.ConfigureServices:
services.AddServerSideBlazor()
.AddHubOptions(options => options.MaximumReceiveMessageSize = 64 * 1024);
Increasing the SignalR incoming message size limit comes at the cost of requiring more server resources, and it increases the risk of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. Additionally, reading a large amount of content in to memory as strings or byte arrays can also result in allocations that work poorly with the garbage collector, resulting in additional performance penalties.
Consider the following guidance when developing code that transfers a large amount of data:
- Leverage the native streaming JS interop support to transfer data larger than the SignalR incoming message size limit:
- General tips:
- Don't allocate large objects in JS and C# code.
- Free consumed memory when the process is completed or cancelled.
- Enforce the following additional requirements for security purposes:
- Declare the maximum file or data size that can be passed.
- Declare the minimum upload rate from the client to the server.
- After the data is received by the server, the data can be:
- Temporarily stored in a memory buffer until all of the segments are collected.
- Consumed immediately. For example, the data can be stored immediately in a database or written to disk as each segment is received.
- Slice the data into smaller pieces, and send the data segments sequentially until all of the data is received by the server.
- Don't allocate large objects in JS and C# code.
- Don't block the main UI thread for long periods when sending or receiving data.
- Free consumed memory when the process is completed or cancelled.
- Enforce the following additional requirements for security purposes:
- Declare the maximum file or data size that can be passed.
- Declare the minimum upload rate from the client to the server.
- After the data is received by the server, the data can be:
- Temporarily stored in a memory buffer until all of the segments are collected.
- Consumed immediately. For example, the data can be stored immediately in a database or written to disk as each segment is received.
Blazor server-side Hub endpoint route configuration
In the Program file, call MapBlazorHub to map the Blazor Hub to the app's default path. The Blazor script (blazor.*.js) automatically points to the endpoint created by MapBlazorHub.
Reflect the server-side connection state in the UI
If the client detects a lost connection to the server, a default UI is displayed to the user while the client attempts to reconnect:

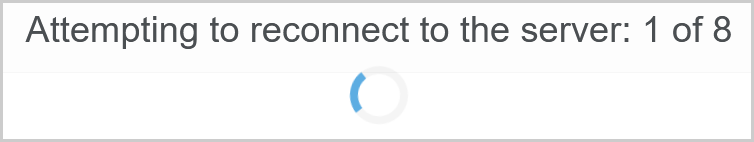
If reconnection fails, the user is instructed to retry or reload the page:


If reconnection succeeds, user state is often lost. Custom code can be added to any component to save and reload user state across connection failures. For more information, see ASP.NET Core Blazor state management overview and ASP.NET Core Blazor server-side state management.
To create UI elements that track reconnection state, the following table describes:
- A set of
components-reconnect-*CSS classes (Css class column) that are set or unset by Blazor on an element with anidofcomponents-reconnect-modal. - A
components-reconnect-state-changedevent (Event column) that indicates a reconnection status change.
| CSS class | Event | Indicates… |
|---|---|---|
components-reconnect-show |
show |
A lost connection. The client is attempting to reconnect. The reconnection modal is shown. |
components-reconnect-hide |
hide |
An active connection is re-established to the server. The reconnection model is closed. |
components-reconnect-retrying |
retrying |
The client is attempting to reconnect. |
components-reconnect-failed |
failed |
Reconnection failed, probably due to a network failure. |
components-reconnect-rejected |
rejected |
Reconnection rejected. |
When the reconnection state change in components-reconnect-state-changed is failed, call Blazor.reconnect() in JavaScript to attempt reconnection.
When the reconnection state change is rejected, the server was reached but refused the connection, and the user's state on the server is lost. To reload the app, call location.reload() in JavaScript. This connection state may result when:
- A crash in the server-side circuit occurs.
- The client is disconnected long enough for the server to drop the user's state. Instances of the user's components are disposed.
- The server is restarted, or the app's worker process is recycled.
The developer adds an event listener on the reconnect modal element to monitor and react to reconnection state changes, as seen in the following example:
const reconnectModal = document.getElementById("components-reconnect-modal");
reconnectModal.addEventListener("components-reconnect-state-changed",
handleReconnectStateChanged);
function handleReconnectStateChanged(event) {
if (event.detail.state === "show") {
reconnectModal.showModal();
} else if (event.detail.state === "hide") {
reconnectModal.close();
} else if (event.detail.state === "failed") {
Blazor.reconnect();
} else if (event.detail.state === "rejected") {
location.reload();
}
}
An element with an id of components-reconnect-max-retries displays the maximum number of reconnect retries:
<span id="components-reconnect-max-retries"></span>
An element with an id of components-reconnect-current-attempt displays the current reconnect attempt:
<span id="components-reconnect-current-attempt"></span>
An element with an id of components-seconds-to-next-attempt displays the number of seconds to the next reconnection attempt:
<span id="components-seconds-to-next-attempt"></span>
The Blazor Web App project template includes a ReconnectModal component (Components/Layout/ReconnectModal.razor) with collocated stylesheet and JavaScript files (ReconnectModal.razor.css, ReconnectModal.razor.js) that can be customized as needed. These files can be examined in the ASP.NET Core reference source or by inspecting an app created from the Blazor Web App project template. The component is added to the project when the project is created in Visual Studio with Interactive render mode set to Server or Auto or created with the .NET CLI with the option --interactivity server (default) or --interactivity auto.
Note
Documentation links to .NET reference source usually load the repository's default branch, which represents the current development for the next release of .NET. To select a tag for a specific release, use the Switch branches or tags dropdown list. For more information, see How to select a version tag of ASP.NET Core source code (dotnet/AspNetCore.Docs #26205).
To customize the UI, define a single element with an id of components-reconnect-modal in the <body> element content. The following example places the element in the App component.
App.razor:
To customize the UI, define a single element with an id of components-reconnect-modal in the <body> element content. The following example places the element in the host page.
Pages/_Host.cshtml:
To customize the UI, define a single element with an id of components-reconnect-modal in the <body> element content. The following example places the element in the layout page.
Pages/_Layout.cshtml:
To customize the UI, define a single element with an id of components-reconnect-modal in the <body> element content. The following example places the element in the host page.
Pages/_Host.cshtml:
<div id="components-reconnect-modal">
Connection lost.<br>Attempting to reconnect...
</div>
Note
If more than one element with an id of components-reconnect-modal are rendered by the app, only the first rendered element receives CSS class changes to display or hide the element.
Add the following CSS styles to the site's stylesheet.
wwwroot/app.css:
wwwroot/css/site.css:
#components-reconnect-modal {
display: none;
}
#components-reconnect-modal.components-reconnect-show,
#components-reconnect-modal.components-reconnect-failed,
#components-reconnect-modal.components-reconnect-rejected {
display: block;
background-color: white;
padding: 2rem;
border-radius: 0.5rem;
text-align: center;
box-shadow: 0 3px 6px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
margin: 50px 50px;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
z-index: 10001;
}
The following table describes the CSS classes applied to the components-reconnect-modal element by the Blazor framework.
| CSS class | Indicates… |
|---|---|
components-reconnect-show |
A lost connection. The client is attempting to reconnect. Show the modal. |
components-reconnect-hide |
An active connection is re-established to the server. Hide the modal. |
components-reconnect-failed |
Reconnection failed, probably due to a network failure. To attempt reconnection, call window.Blazor.reconnect() in JavaScript. |
components-reconnect-rejected |
Reconnection rejected. The server was reached but refused the connection, and the user's state on the server is lost. To reload the app, call location.reload() in JavaScript. This connection state may result when:
|
Customize the delay before the reconnection UI appears by setting the transition-delay property in the site's CSS for the modal element. The following example sets the transition delay from 500 ms (default) to 1,000 ms (1 second).
wwwroot/app.css:
wwwroot/css/site.css:
#components-reconnect-modal {
transition: visibility 0s linear 1000ms;
}
To display the current reconnect attempt, define an element with an id of components-reconnect-current-attempt. To display the maximum number of reconnect retries, define an element with an id of components-reconnect-max-retries. The following example places these elements inside a reconnect attempt modal element following the previous example.
<div id="components-reconnect-modal">
There was a problem with the connection!
(Current reconnect attempt:
<span id="components-reconnect-current-attempt"></span> /
<span id="components-reconnect-max-retries"></span>)
</div>
When the custom reconnect modal appears, it renders the following content with a reconnection attempt counter:
There was a problem with the connection! (Current reconnect attempt: 1 / 8)
Server-side rendering
By default, components are prerendered on the server before the client connection to the server is established. For more information, see ASP.NET Core Blazor prerendered state persistence.
By default, components are prerendered on the server before the client connection to the server is established. For more information, see Component Tag Helper in ASP.NET Core.
Monitor server-side circuit activity
Monitor inbound circuit activity using the CreateInboundActivityHandler method on CircuitHandler. Inbound circuit activity is any activity sent from the browser to the server, such as UI events or JavaScript-to-.NET interop calls.
For example, you can use a circuit activity handler to detect if the client is idle and log its circuit ID (Circuit.Id):
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Server.Circuits;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using Timer = System.Timers.Timer;
public sealed class IdleCircuitHandler : CircuitHandler, IDisposable
{
private Circuit? currentCircuit;
private readonly ILogger logger;
private readonly Timer timer;
public IdleCircuitHandler(ILogger<IdleCircuitHandler> logger,
IOptions<IdleCircuitOptions> options)
{
timer = new Timer
{
Interval = options.Value.IdleTimeout.TotalMilliseconds,
AutoReset = false
};
timer.Elapsed += CircuitIdle;
this.logger = logger;
}
private void CircuitIdle(object? sender, System.Timers.ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
logger.LogInformation("{CircuitId} is idle", currentCircuit?.Id);
}
public override Task OnCircuitOpenedAsync(Circuit circuit,
CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
currentCircuit = circuit;
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
public override Func<CircuitInboundActivityContext, Task> CreateInboundActivityHandler(
Func<CircuitInboundActivityContext, Task> next)
{
return context =>
{
timer.Stop();
timer.Start();
return next(context);
};
}
public void Dispose() => timer.Dispose();
}
public class IdleCircuitOptions
{
public TimeSpan IdleTimeout { get; set; } = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5);
}
public static class IdleCircuitHandlerServiceCollectionExtensions
{
public static IServiceCollection AddIdleCircuitHandler(
this IServiceCollection services,
Action<IdleCircuitOptions> configureOptions)
{
services.Configure(configureOptions);
services.AddIdleCircuitHandler();
return services;
}
public static IServiceCollection AddIdleCircuitHandler(
this IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddScoped<CircuitHandler, IdleCircuitHandler>();
return services;
}
}
Register the service in the Program file. The following example configures the default idle timeout of five minutes to five seconds in order to test the preceding IdleCircuitHandler implementation:
builder.Services.AddIdleCircuitHandler(options =>
options.IdleTimeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5));
Circuit activity handlers also provide an approach for accessing scoped Blazor services from other non-Blazor dependency injection (DI) scopes. For more information and examples, see:
Blazor startup
Configure the manual start of Blazor's SignalR circuit in the App.razor file of a Blazor Web App:
Configure the manual start of Blazor's SignalR circuit in the Pages/_Host.cshtml file (Blazor Server):
Configure the manual start of Blazor's SignalR circuit in the Pages/_Layout.cshtml file (Blazor Server):
Configure the manual start of Blazor's SignalR circuit in the Pages/_Host.cshtml file (Blazor Server):
- Add an
autostart="false"attribute to the<script>tag for theblazor.*.jsscript. - Place a script that calls
Blazor.start()after the Blazor script is loaded and inside the closing</body>tag.
When autostart is disabled, any aspect of the app that doesn't depend on the circuit works normally. For example, client-side routing is operational. However, any aspect that depends on the circuit isn't operational until Blazor.start() is called. App behavior is unpredictable without an established circuit. For example, component methods fail to execute while the circuit is disconnected.
For more information, including how to initialize Blazor when the document is ready and how to chain to a JS Promise, see ASP.NET Core Blazor startup.
Configure SignalR timeouts and Keep-Alive on the client
Configure the following values for the client:
withServerTimeout: Configures the server timeout in milliseconds. If this timeout elapses without receiving any messages from the server, the connection is terminated with an error. The default timeout value is 30 seconds. The server timeout should be at least double the value assigned to the Keep-Alive interval (withKeepAliveInterval).withKeepAliveInterval: Configures the Keep-Alive interval in milliseconds (default interval at which to ping the server). This setting allows the server to detect hard disconnects, such as when a client unplugs their computer from the network. The ping occurs at most as often as the server pings. If the server pings every five seconds, assigning a value lower than5000(5 seconds) pings every five seconds. The default value is 15 seconds. The Keep-Alive interval should be less than or equal to half the value assigned to the server timeout (withServerTimeout).
The following example for the App.razor file (Blazor Web App) shows the assignment of default values.
Blazor Web App:
<script src="{BLAZOR SCRIPT}" autostart="false"></script>
<script>
Blazor.start({
circuit: {
configureSignalR: function (builder) {
builder.withServerTimeout(30000).withKeepAliveInterval(15000);
}
}
});
</script>
The following example for the Pages/_Host.cshtml file (Blazor Server, all versions except ASP.NET Core in .NET 6) or Pages/_Layout.cshtml file (Blazor Server, ASP.NET Core in .NET 6).
Blazor Server:
<script src="{BLAZOR SCRIPT}" autostart="false"></script>
<script>
Blazor.start({
configureSignalR: function (builder) {
builder.withServerTimeout(30000).withKeepAliveInterval(15000);
}
});
</script>
In the preceding example, the {BLAZOR SCRIPT} placeholder is the Blazor script path and file name. For the location of the script and the path to use, see ASP.NET Core Blazor project structure.
When creating a hub connection in a component, set the ServerTimeout (default: 30 seconds) and KeepAliveInterval (default: 15 seconds) on the HubConnectionBuilder. Set the HandshakeTimeout (default: 15 seconds) on the built HubConnection. The following example shows the assignment of default values:
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
hubConnection = new HubConnectionBuilder()
.WithUrl(Navigation.ToAbsoluteUri("/chathub"))
.WithServerTimeout(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30))
.WithKeepAliveInterval(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(15))
.Build();
hubConnection.HandshakeTimeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(15);
hubConnection.On<string, string>("ReceiveMessage", (user, message) => ...
await hubConnection.StartAsync();
}
Configure the following values for the client:
serverTimeoutInMilliseconds: The server timeout in milliseconds. If this timeout elapses without receiving any messages from the server, the connection is terminated with an error. The default timeout value is 30 seconds. The server timeout should be at least double the value assigned to the Keep-Alive interval (keepAliveIntervalInMilliseconds).keepAliveIntervalInMilliseconds: Default interval at which to ping the server. This setting allows the server to detect hard disconnects, such as when a client unplugs their computer from the network. The ping occurs at most as often as the server pings. If the server pings every five seconds, assigning a value lower than5000(5 seconds) pings every five seconds. The default value is 15 seconds. The Keep-Alive interval should be less than or equal to half the value assigned to the server timeout (serverTimeoutInMilliseconds).
The following example for the Pages/_Host.cshtml file (Blazor Server, all versions except ASP.NET Core in .NET 6) or Pages/_Layout.cshtml file (Blazor Server, ASP.NET Core in .NET 6):
<script src="{BLAZOR SCRIPT}" autostart="false"></script>
<script>
Blazor.start({
configureSignalR: function (builder) {
let c = builder.build();
c.serverTimeoutInMilliseconds = 30000;
c.keepAliveIntervalInMilliseconds = 15000;
builder.build = () => {
return c;
};
}
});
</script>
In the preceding example, the {BLAZOR SCRIPT} placeholder is the Blazor script path and file name. For the location of the script and the path to use, see ASP.NET Core Blazor project structure.
When creating a hub connection in a component, set the ServerTimeout (default: 30 seconds), HandshakeTimeout (default: 15 seconds), and KeepAliveInterval (default: 15 seconds) on the built HubConnection. The following example shows the assignment of default values:
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
hubConnection = new HubConnectionBuilder()
.WithUrl(Navigation.ToAbsoluteUri("/chathub"))
.Build();
hubConnection.ServerTimeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30);
hubConnection.HandshakeTimeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(15);
hubConnection.KeepAliveInterval = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(15);
hubConnection.On<string, string>("ReceiveMessage", (user, message) => ...
await hubConnection.StartAsync();
}
When changing the values of the server timeout (ServerTimeout) or the Keep-Alive interval (KeepAliveInterval):
- The server timeout should be at least double the value assigned to the Keep-Alive interval.
- The Keep-Alive interval should be less than or equal to half the value assigned to the server timeout.
For more information, see the Global deployment and connection failures sections of the following articles:
- Host and deploy ASP.NET Core server-side Blazor apps
- Host and deploy ASP.NET Core Blazor WebAssembly
Adjust the server-side reconnection retry count and interval
To adjust the reconnection retry count and interval, set the number of retries (maxRetries) and period in milliseconds permitted for each retry attempt (retryIntervalMilliseconds).
Blazor Web App:
<script src="{BLAZOR SCRIPT}" autostart="false"></script>
<script>
Blazor.start({
circuit: {
reconnectionOptions: {
maxRetries: 3,
retryIntervalMilliseconds: 2000
}
}
});
</script>
Blazor Server:
<script src="{BLAZOR SCRIPT}" autostart="false"></script>
<script>
Blazor.start({
reconnectionOptions: {
maxRetries: 3,
retryIntervalMilliseconds: 2000
}
});
</script>
In the preceding example, the {BLAZOR SCRIPT} placeholder is the Blazor script path and file name. For the location of the script and the path to use, see ASP.NET Core Blazor project structure.
When the user navigates back to an app with a disconnected circuit, reconnection is attempted immediately rather than waiting for the duration of the next reconnect interval. This behavior seeks to resume the connection as quickly as possible for the user.
The default reconnect timing uses a computed backoff strategy. The first several reconnection attempts occur in rapid succession before computed delays are introduced between attempts. The default logic for computing the retry interval is an implementation detail subject to change without notice, but you can find the default logic that the Blazor framework uses in the computeDefaultRetryInterval function (reference source).
Note
Documentation links to .NET reference source usually load the repository's default branch, which represents the current development for the next release of .NET. To select a tag for a specific release, use the Switch branches or tags dropdown list. For more information, see How to select a version tag of ASP.NET Core source code (dotnet/AspNetCore.Docs #26205).
Customize the retry interval behavior by specifying a function to compute the retry interval. In the following exponential backoff example, the number of previous reconnection attempts is multiplied by 1,000 ms to calculate the retry interval. When the count of previous attempts to reconnect (previousAttempts) is greater than the maximum retry limit (maxRetries), null is assigned to the retry interval (retryIntervalMilliseconds) to cease further reconnection attempts:
Blazor.start({
circuit: {
reconnectionOptions: {
retryIntervalMilliseconds: (previousAttempts, maxRetries) =>
previousAttempts >= maxRetries ? null : previousAttempts * 1000
},
},
});
An alternative is to specify the exact sequence of retry intervals. After the last specified retry interval, retries stop because the retryIntervalMilliseconds function returns undefined:
Blazor.start({
circuit: {
reconnectionOptions: {
retryIntervalMilliseconds:
Array.prototype.at.bind([0, 1000, 2000, 5000, 10000, 15000, 30000]),
},
},
});
For more information on Blazor startup, see ASP.NET Core Blazor startup.
Control when the reconnection UI appears
Controlling when the reconnection UI appears can be useful in the following situations:
- A deployed app frequently displays the reconnection UI due to ping timeouts caused by internal network or Internet latency, and you would like to increase the delay.
- An app should report to users that the connection has dropped sooner, and you would like to shorten the delay.
The timing of the appearance of the reconnection UI is influenced by adjusting the Keep-Alive interval and timeouts on the client. The reconnection UI appears when the server timeout is reached on the client (withServerTimeout, Client configuration section). However, changing the value of withServerTimeout requires changes to other Keep-Alive, timeout, and handshake settings described in the following guidance.
As general recommendations for the guidance that follows:
- The Keep-Alive interval should match between client and server configurations.
- Timeouts should be at least double the value assigned to the Keep-Alive interval.
Server configuration
Set the following:
- ClientTimeoutInterval (default: 30 seconds): The time window clients have to send a message before the server closes the connection.
- HandshakeTimeout (default: 15 seconds): The interval used by the server to timeout incoming handshake requests by clients.
- KeepAliveInterval (default: 15 seconds): The interval used by the server to send keep alive pings to connected clients. Note that there is also a Keep-Alive interval setting on the client, which should match the server's value.
The ClientTimeoutInterval and HandshakeTimeout can be increased, and the KeepAliveInterval can remain the same. The important consideration is that if you change the values, make sure that the timeouts are at least double the value of the Keep-Alive interval and that the Keep-Alive interval matches between server and client. For more information, see the Configure SignalR timeouts and Keep-Alive on the client section.
In the following example:
- The ClientTimeoutInterval is increased to 60 seconds (default value: 30 seconds).
- The HandshakeTimeout is increased to 30 seconds (default value: 15 seconds).
- The KeepAliveInterval isn't set in developer code and uses its default value of 15 seconds. Decreasing the value of the Keep-Alive interval increases the frequency of communication pings, which increases the load on the app, server, and network. Care must be taken to avoid introducing poor performance when lowering the Keep-Alive interval.
Blazor Web App (.NET 8 or later) in the server project's Program file:
builder.Services.AddRazorComponents().AddInteractiveServerComponents()
.AddHubOptions(options =>
{
options.ClientTimeoutInterval = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(60);
options.HandshakeTimeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30);
});
Blazor Server in the Program file:
builder.Services.AddServerSideBlazor()
.AddHubOptions(options =>
{
options.ClientTimeoutInterval = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(60);
options.HandshakeTimeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30);
});
For more information, see the Server-side circuit handler options section.
Client configuration
Set the following:
withServerTimeout(default: 30 seconds): Configures the server timeout, specified in milliseconds, for the circuit's hub connection.withKeepAliveInterval(default: 15 seconds): The interval, specified in milliseconds, at which the connection sends Keep-Alive messages.
The server timeout can be increased, and the Keep-Alive interval can remain the same. The important consideration is that if you change the values, make sure that the server timeout is at least double the value of the Keep-Alive interval and that the Keep-Alive interval values match between server and client. For more information, see the Configure SignalR timeouts and Keep-Alive on the client section.
In the following startup configuration example (location of the Blazor script), a custom value of 60 seconds is used for the server timeout. The Keep-Alive interval (withKeepAliveInterval) isn't set and uses its default value of 15 seconds.
Blazor Web App:
<script src="{BLAZOR SCRIPT}" autostart="false"></script>
<script>
Blazor.start({
circuit: {
configureSignalR: function (builder) {
builder.withServerTimeout(60000);
}
}
});
</script>
Blazor Server:
<script src="{BLAZOR SCRIPT}" autostart="false"></script>
<script>
Blazor.start({
configureSignalR: function (builder) {
builder.withServerTimeout(60000);
}
});
</script>
When creating a hub connection in a component, set the server timeout (WithServerTimeout, default: 30 seconds) on the HubConnectionBuilder. Set the HandshakeTimeout (default: 15 seconds) on the built HubConnection. Confirm that the timeouts are at least double the Keep-Alive interval (WithKeepAliveInterval/KeepAliveInterval) and that the Keep-Alive value matches between server and client.
The following example is based on the Index component in the SignalR with Blazor tutorial. The server timeout is increased to 60 seconds, and the handshake timeout is increased to 30 seconds. The Keep-Alive interval isn't set and uses its default value of 15 seconds.
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
hubConnection = new HubConnectionBuilder()
.WithUrl(Navigation.ToAbsoluteUri("/chathub"))
.WithServerTimeout(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(60))
.Build();
hubConnection.HandshakeTimeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30);
hubConnection.On<string, string>("ReceiveMessage", (user, message) => ...
await hubConnection.StartAsync();
}
Set the following:
serverTimeoutInMilliseconds(default: 30 seconds): Configures the server timeout, specified in milliseconds, for the circuit's hub connection.keepAliveIntervalInMilliseconds(default: 15 seconds): The interval, specified in milliseconds, at which the connection sends Keep-Alive messages.
The server timeout can be increased, and the Keep-Alive interval can remain the same. The important consideration is that if you change the values, make sure that the server timeout is at least double the value of the Keep-Alive interval and that the Keep-Alive interval values match between server and client. For more information, see the Configure SignalR timeouts and Keep-Alive on the client section.
In the following startup configuration example (location of the Blazor script), a custom value of 60 seconds is used for the server timeout. The Keep-Alive interval (keepAliveIntervalInMilliseconds) isn't set and uses its default value of 15 seconds.
In Pages/_Host.cshtml:
<script src="_framework/blazor.server.js" autostart="false"></script>
<script>
Blazor.start({
configureSignalR: function (builder) {
let c = builder.build();
c.serverTimeoutInMilliseconds = 60000;
builder.build = () => {
return c;
};
}
});
</script>
When creating a hub connection in a component, set the ServerTimeout (default: 30 seconds) and HandshakeTimeout (default: 15 seconds) on the built HubConnection. Confirm that the timeouts are at least double the Keep-Alive interval. Confirm that the Keep-Alive interval matches between server and client.
The following example is based on the Index component in the SignalR with Blazor tutorial. The ServerTimeout is increased to 60 seconds, and the HandshakeTimeout is increased to 30 seconds. The Keep-Alive interval (KeepAliveInterval) isn't set and uses its default value of 15 seconds.
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
hubConnection = new HubConnectionBuilder()
.WithUrl(Navigation.ToAbsoluteUri("/chathub"))
.Build();
hubConnection.ServerTimeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(60);
hubConnection.HandshakeTimeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30);
hubConnection.On<string, string>("ReceiveMessage", (user, message) => ...
await hubConnection.StartAsync();
}
Modify the server-side reconnection handler
The reconnection handler's circuit connection events can be modified for custom behaviors, such as:
- To notify the user if the connection is dropped.
- To perform logging (from the client) when a circuit is connected.
To modify the connection events, register callbacks for the following connection changes:
- Dropped connections use
onConnectionDown. - Established/re-established connections use
onConnectionUp.
Both onConnectionDown and onConnectionUp must be specified.
Blazor Web App:
<script src="{BLAZOR SCRIPT}" autostart="false"></script>
<script>
Blazor.start({
circuit: {
reconnectionHandler: {
onConnectionDown: (options, error) => console.error(error),
onConnectionUp: () => console.log("Up, up, and away!")
}
}
});
</script>
Blazor Server:
<script src="{BLAZOR SCRIPT}" autostart="false"></script>
<script>
Blazor.start({
reconnectionHandler: {
onConnectionDown: (options, error) => console.error(error),
onConnectionUp: () => console.log("Up, up, and away!")
}
});
</script>
In the preceding example, the {BLAZOR SCRIPT} placeholder is the Blazor script path and file name. For the location of the script and the path to use, see ASP.NET Core Blazor project structure.
Programmatic control of reconnection and reload behavior
Blazor automatically attempts reconnection and refreshes the browser when reconnection fails. For more information, see the Adjust the server-side reconnection retry count and interval section. However, developer code can implement a custom reconnection handler to take full control of reconnection behavior.
The default reconnection behavior requires the user to take manual action to refresh the page after reconnection fails. However, developer code can implement a custom reconnection handler to take full control of reconnection behavior, including implementing automatic page refresh after reconnection attempts fail.
App.razor:
Pages/_Host.cshtml:
<div id="reconnect-modal" style="display: none;"></div>
<script src="{BLAZOR SCRIPT}" autostart="false"></script>
<script src="boot.js"></script>
In the preceding example, the {BLAZOR SCRIPT} placeholder is the Blazor script path and file name. For the location of the script and the path to use, see ASP.NET Core Blazor project structure.
Create the following wwwroot/boot.js file.
Blazor Web App:
(() => {
const maximumRetryCount = 3;
const retryIntervalMilliseconds = 5000;
const reconnectModal = document.getElementById('reconnect-modal');
const startReconnectionProcess = () => {
reconnectModal.style.display = 'block';
let isCanceled = false;
(async () => {
for (let i = 0; i < maximumRetryCount; i++) {
reconnectModal.innerText = `Attempting to reconnect: ${i + 1} of ${maximumRetryCount}`;
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, retryIntervalMilliseconds));
if (isCanceled) {
return;
}
try {
const result = await Blazor.reconnect();
if (!result) {
// The server was reached, but the connection was rejected; reload the page.
location.reload();
return;
}
// Successfully reconnected to the server.
return;
} catch {
// Didn't reach the server; try again.
}
}
// Retried too many times; reload the page.
location.reload();
})();
return {
cancel: () => {
isCanceled = true;
reconnectModal.style.display = 'none';
},
};
};
let currentReconnectionProcess = null;
Blazor.start({
circuit: {
reconnectionHandler: {
onConnectionDown: () => currentReconnectionProcess ??= startReconnectionProcess(),
onConnectionUp: () => {
currentReconnectionProcess?.cancel();
currentReconnectionProcess = null;
}
}
}
});
})();
Blazor Server:
(() => {
const maximumRetryCount = 3;
const retryIntervalMilliseconds = 5000;
const reconnectModal = document.getElementById('reconnect-modal');
const startReconnectionProcess = () => {
reconnectModal.style.display = 'block';
let isCanceled = false;
(async () => {
for (let i = 0; i < maximumRetryCount; i++) {
reconnectModal.innerText = `Attempting to reconnect: ${i + 1} of ${maximumRetryCount}`;
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, retryIntervalMilliseconds));
if (isCanceled) {
return;
}
try {
const result = await Blazor.reconnect();
if (!result) {
// The server was reached, but the connection was rejected; reload the page.
location.reload();
return;
}
// Successfully reconnected to the server.
return;
} catch {
// Didn't reach the server; try again.
}
}
// Retried too many times; reload the page.
location.reload();
})();
return {
cancel: () => {
isCanceled = true;
reconnectModal.style.display = 'none';
},
};
};
let currentReconnectionProcess = null;
Blazor.start({
reconnectionHandler: {
onConnectionDown: () => currentReconnectionProcess ??= startReconnectionProcess(),
onConnectionUp: () => {
currentReconnectionProcess?.cancel();
currentReconnectionProcess = null;
}
}
});
})();
For more information on Blazor startup, see ASP.NET Core Blazor startup.
Disconnect Blazor's SignalR circuit from the client
Blazor's SignalR circuit is disconnected when the unload page event is triggered. To disconnect the circuit for other scenarios on the client, invoke Blazor.disconnect in the appropriate event handler. In the following example, the circuit is disconnected when the page is hidden (pagehide event):
window.addEventListener('pagehide', () => {
Blazor.disconnect();
});
For more information on Blazor startup, see ASP.NET Core Blazor startup.
Server-side circuit handler
You can define a circuit handler, which allows running code on changes to the state of a user's circuit. A circuit handler is implemented by deriving from CircuitHandler and registering the class in the app's service container. The following example of a circuit handler tracks open SignalR connections.
TrackingCircuitHandler.cs:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Server.Circuits;
public class TrackingCircuitHandler : CircuitHandler
{
private HashSet<Circuit> circuits = new();
public override Task OnConnectionUpAsync(Circuit circuit,
CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
circuits.Add(circuit);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
public override Task OnConnectionDownAsync(Circuit circuit,
CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
circuits.Remove(circuit);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
public int ConnectedCircuits => circuits.Count;
}
Circuit handlers are registered using DI. Scoped instances are created per instance of a circuit. Using the TrackingCircuitHandler in the preceding example, a singleton service is created because the state of all circuits must be tracked.
In the Program file:
builder.Services.AddSingleton<CircuitHandler, TrackingCircuitHandler>();
In Startup.ConfigureServices of Startup.cs:
services.AddSingleton<CircuitHandler, TrackingCircuitHandler>();
If a custom circuit handler's methods throw an unhandled exception, the exception is fatal to the circuit. To tolerate exceptions in a handler's code or called methods, wrap the code in one or more try-catch statements with error handling and logging.
When a circuit ends because a user has disconnected and the framework is cleaning up the circuit state, the framework disposes of the circuit's DI scope. Disposing the scope disposes any circuit-scoped DI services that implement System.IDisposable. If any DI service throws an unhandled exception during disposal, the framework logs the exception. For more information, see ASP.NET Core Blazor dependency injection.
Server-side circuit handler to capture users for custom services
Use a CircuitHandler to capture a user from the AuthenticationStateProvider and set that user in a service. For more information and example code, see ASP.NET Core server-side and Blazor Web App additional security scenarios.
Closure of circuits when there are no remaining Interactive Server components
Interactive Server components handle web UI events using a real-time connection with the browser called a circuit. A circuit and its associated state are created when a root Interactive Server component is rendered. The circuit is closed when there are no remaining Interactive Server components on the page, which frees up server resources.
Start the SignalR circuit at a different URL
Prevent automatically starting the app by adding autostart="false" to the Blazor <script> tag (location of the Blazor start script). Manually establish the circuit URL using Blazor.start. The following examples use the path /signalr.
Blazor Web Apps:
- <script src="_framework/blazor.web.js"></script>
+ <script src="_framework/blazor.web.js" autostart="false"></script>
+ <script>
+ Blazor.start({
+ circuit: {
+ configureSignalR: builder => builder.withUrl("/signalr")
+ },
+ });
+ </script>
Blazor Server:
- <script src="_framework/blazor.server.js"></script>
+ <script src="_framework/blazor.server.js" autostart="false"></script>
+ <script>
+ Blazor.start({
+ configureSignalR: builder => builder.withUrl("/signalr")
+ });
+ </script>
Add the following MapBlazorHub call with the hub path to the middleware processing pipeline in the server app's Program file.
Blazor Web Apps:
app.MapBlazorHub("/signalr");
Blazor Server:
Leave the existing call to MapBlazorHub in the file and add a new call to MapBlazorHub with the path:
app.MapBlazorHub();
+ app.MapBlazorHub("/signalr");
Impersonation for Windows Authentication
Authenticated hub connections (HubConnection) are created with UseDefaultCredentials to indicate the use of default credentials for HTTP requests. For more information, see Authentication and authorization in ASP.NET Core SignalR.
When the app is running in IIS Express as the signed-in user under Windows Authentication, which is likely the user's personal or work account, the default credentials are those of the signed-in user.
When the app is published to IIS, the app runs under the Application Pool Identity. The HubConnection connects as the IIS "user" account hosting the app, not the user accessing the page.
Implement impersonation with the HubConnection to use the identity of the browsing user.
In the following example:
- The user from the authentication state provider is cast to a WindowsIdentity.
- The identity's access token is passed to WindowsIdentity.RunImpersonatedAsync with the code that builds and starts the HubConnection.
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
var authState = await AuthenticationStateProvider.GetAuthenticationStateAsync();
if (authState?.User.Identity is not null)
{
var user = authState.User.Identity as WindowsIdentity;
if (user is not null)
{
await WindowsIdentity.RunImpersonatedAsync(user.AccessToken,
async () =>
{
hubConnection = new HubConnectionBuilder()
.WithUrl(NavManager.ToAbsoluteUri("/hub"), config =>
{
config.UseDefaultCredentials = true;
})
.WithAutomaticReconnect()
.Build();
hubConnection.On<string>("name", userName =>
{
name = userName;
InvokeAsync(StateHasChanged);
});
await hubConnection.StartAsync();
});
}
}
}
In the preceding code, NavManager is a NavigationManager, and AuthenticationStateProvider is an AuthenticationStateProvider service instance (AuthenticationStateProvider documentation).
Additional server-side resources
- Server-side host and deployment guidance: SignalR configuration
- Overview of ASP.NET Core SignalR
- ASP.NET Core SignalR configuration
- Server-side security documentation
- IHttpContextAccessor/HttpContext in ASP.NET Core Blazor apps
- Server-side reconnection events and component lifecycle events
- What is Azure SignalR Service?
- Performance guide for Azure SignalR Service
- Publish an ASP.NET Core SignalR app to Azure App Service
- Blazor samples GitHub repository (
dotnet/blazor-samples) (how to download)
ASP.NET Core
