Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
After you complete labeling your utterances, you can start training a model. Training is the process where the model learns from your labeled utterances.
To train a model, start a training job. Only successfully completed jobs create a model. Training jobs expire after seven days, then you can no longer retrieve the job details. If your training job completed successfully and a model was created, the job doesn't expire. You can only have one training job running at a time, and you can't start other jobs in the same fine tuning task.
Note
When using the Quick Deploy option, Conversational Language Understanding (CLU) automatically creates an instant training job to set up your CLU intent router using your selected LLM deployment.
The training times can be anywhere from a few seconds for simple projects, up to several hours when you reach the maximum limit of utterances.
Model evaluation is triggered automatically after training is completed successfully. The evaluation process starts by using the trained model to run predictions on the utterances in the testing set, and compares the predicted results with the provided labels (which establishes a baseline of truth).
Prerequisites
- An active Azure subscription. If you don't have one, you can create one for free.
- Requisite permissions. Make sure the person establishing the account and project is assigned as the Azure AI Account Owner role at the subscription level. Alternatively, having either the Contributor or Cognitive Services Contributor role at the subscription scope also meets this requirement. For more information, see Role based access control (RBAC)
- A project created in the Azure AI Foundry. For more information, see Create an AI Foundry project
- Your labeled utterances tagged for your fine tuning task.
Balance training data
When it comes to training data, try to keep your schema well-balanced. Including large quantities of one intent and few of another results in a model with bias towards particular intents.
To address this scenario, you might need to down sample your training set. Or you might need to add to it. To down sample, you can:
- Get rid of a certain percentage of the training data randomly.
- Analyze the dataset and remove overrepresented duplicate entries, which is a more systematic manner.
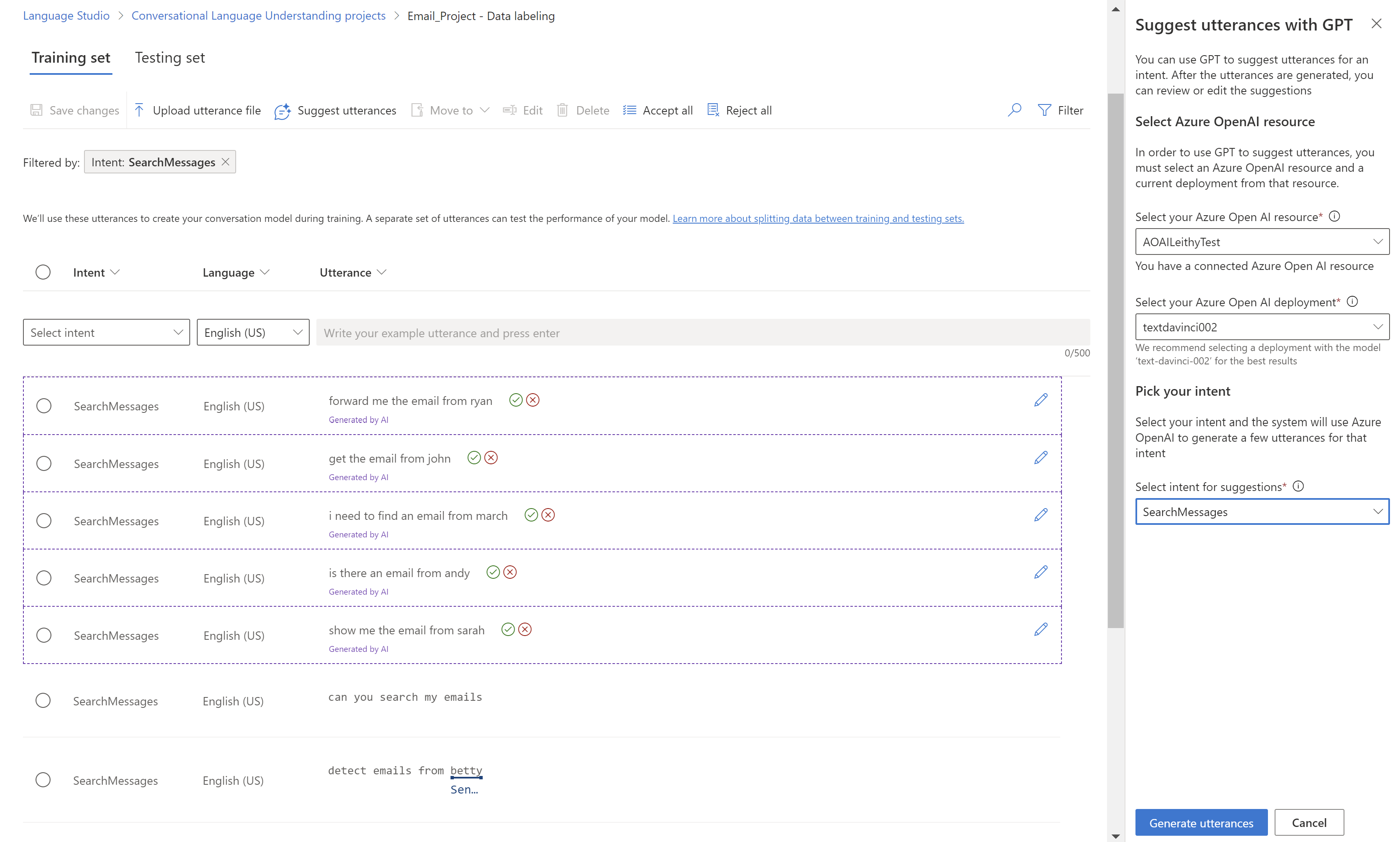
To add to the training set, in Language Studio, on the Data labeling tab, select Suggest utterances. Conversational Language Understanding sends a call to Azure OpenAI to generate similar utterances.
You should also look for unintentional patterns in the training set. For example, look to see if the training set for a particular intent is all lowercase or starts with a particular phrase. In such cases, the model you train might learn these unintended biases in the training set instead of being able to generalize.
We recommend that you introduce casing and punctuation diversity in the training set. If your model is expected to handle variations, be sure to have a training set that also reflects that diversity. For example, include some utterances in proper casing and some in all lowercase.
Data splitting
Before you start the training process, labeled utterances in your project are divided into a training set and a testing set. Each one of them serves a different function. The training set is used in training the model, the set from which the model learns the labeled utterances. The testing set is a blind set that isn't introduced to the model during training but only during evaluation.
After the model is trained successfully, the model can be used to make predictions from the utterances in the testing set. These predictions are used to calculate evaluation metrics. We recommend that you make sure that all your intents and entities are adequately represented in both the training and testing set.
Conversational language understanding supports two methods for data splitting:
- Automatically splitting the testing set from training data: The system splits your tagged data between the training and testing sets, according to the percentages you choose. The recommended percentage split is 80% for training and 20% for testing.
Note
If you choose the Automatically splitting the testing set from training data option, only the data assigned to a training set is split according to the percentages provided.
- Use a manual split of training and testing data: This method enables users to define which utterances should belong to which set. This step is only enabled if you added utterances to your testing set during labeling.
Training modes
Conversational Language Understanding (CLU) supports two modes for training your models
Standard training uses fast machine learning algorithms to quickly train your models. This training level is currently only available for English and is disabled for any project that doesn't use English (US), or English (UK) as its primary language. This training option is free of charge. Standard training allows you to add utterances and test them quickly free of charge. The evaluation scores shown should guide you on where to make changes in your project and add more utterances. While standard training is best for testing and updating your model quickly, you should see better model quality when using advanced training. While standard training is best for testing and updating your model quickly, you should see better model quality when using advanced training. Once you iterate a few times and made incremental improvements, you can consider using advanced training to train another version of your model.
Advanced training uses the latest in machine learning technology to customize models with your data. This training level is expected to show better performance scores for your models and enables you to use the multilingual capabilities of CLU as well. Advanced training is priced differently. See the pricing information for details.
Use the evaluation scores to guide your decisions. There may be times where a specific example is predicted incorrectly in advanced training as opposed to when you used standard training mode. However, if the overall evaluation results are better using advanced training, then we recommend that you use that model as your final model. If that isn't the case and you aren't looking to use any multilingual capabilities, you can continue to use model trained with standard mode.
Note
You should expect to see a difference in behaviors in intent confidence scores between the training modes as each algorithm calibrates their scores differently.
Train your model
Navigate to the Azure AI Foundry.
If you aren't already signed in, the portal prompts you to do so with your Azure credentials.
Once signed in, you can create or access your existing projects within Azure AI Foundry.
If you're not already at your project for this task, select it.
Select Fine-tuning from the left navigation panel.

Select the AI Service fine-tuning tab and then + Fine-tune button.

From Create service fine-tuning window, choose the Conversational language understanding tab then select Next.

In Create CLU fine tuning task window, complete the Name and Language fields. If you're using the free Standard Training mode, select English for the language field.
Note
- Standard training enables faster training times and quicker iterations; however it's only available for English.
- Advanced training includes longer training durations and is supported for English, other languages, and multilingual projects.
- For more information, see Training modes.
From the immediate left navigation panel, choose Train model.

Next, select the + Train model button from the main window.
In the Train a new model window, select one of the following:
- Create a new training model. Enter a new Model name
- Overwrite an existing model name. Replace an existing model trained on the new data.
Select Your current training version. The training version is the algorithm that determines how your model learns from your data. The machine learning used to train models is regularly updated. We recommend using the latest version for training, as it underwent thorough testing and provides the most balanced model predictions from your data.

Select Next.
Select one of the Data splitting methods presented in the Train a new model window:
Automatically split the testing set from training data enables the system to split your utterances between the training and testing sets, according to the specified percentages.
Use a manual split of training and testing data enables the system to use the training and testing sets that you assigned and labeled to create your custom model. *This option is only available if you have added utterances to your testing set when you labeled your utterances.

Select Next and then select Create.
Choose the training job ID from the list. A panel appears that details the training progress, job status, and other details for this job.
Note
- Only successfully completed training jobs generate models.
- Training can take from a few minutes to a few hours based on the count of utterances.
- You can only have one training job running at a time. You can't start other training jobs within the same project until the running job is completed.
Cancel training job
When you're done with your custom model, you can delete the deployment and model. You can also delete the training and validation files you uploaded to the service, if needed:
To delete your custom model, on the left navigation pane select My assets → Models + endpoints. Choose the custom model to delete from the Model deployments tab, and then select Delete.
To delete your training and validation files uploaded for training, on the left navigation pane select Data + indexes. Choose the file to delete, and then select Delete.

Next steps
Review your model's performance with model evaluation metrics.