The Team Data Science Process (TDSP) is an agile, iterative data science methodology that you can use to deliver predictive analytics solutions and AI applications efficiently. The TDSP helps improve team collaboration and learning by suggesting how team roles work best together. The TDSP includes best practices and structures from Microsoft and other industry leaders to help your team successfully implement data science initiatives and fully realize the benefits of your analytics program.
This article provides an overview of TDSP and its main components. It presents guidance about how to implement the TDSP by using Microsoft tools and infrastructure. You can find more detailed resources throughout the article.
Key components of the TDSP
The TDSP has the following key components:
- A data science lifecycle definition
- A standardized project structure
- Infrastructure and resources recommended for data science projects
- Tools and utilities recommended for project execution
Data science lifecycle
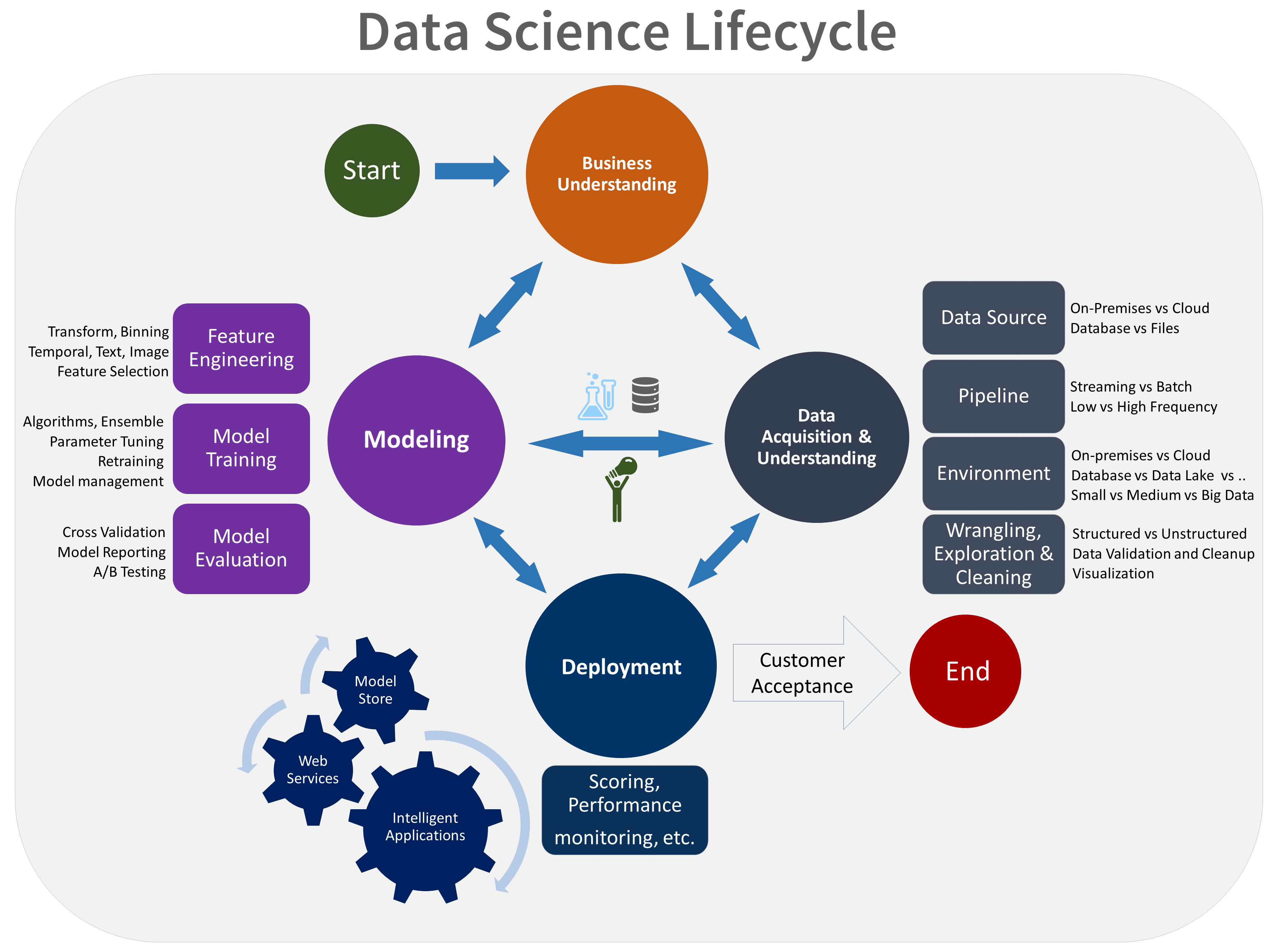
The TDSP provides a lifecycle that you can use to structure the development of your data science projects. The lifecycle outlines the full steps that successful projects follow.
You can combine the task-based TDSP with other data science lifecycles, such as cross-industry standard process for data mining (CRISP-DM), the knowledge discovery in databases (KDD) process, or another custom process. At a high level, these different methodologies have much in common.
You should use this lifecycle if you have a data science project that's part of an intelligent application. Intelligent applications deploy machine learning or AI models for predictive analytics. You can also use this process for exploratory data science projects and improvised analytics projects.
The TDSP lifecycle is composed of five major stages that your team performs iteratively. These stages include:
Here's a visual representation of the TDSP lifecycle:
For information about the goals, tasks, and documentation artifacts for each stage, see The Team Data Science Process lifecycle.
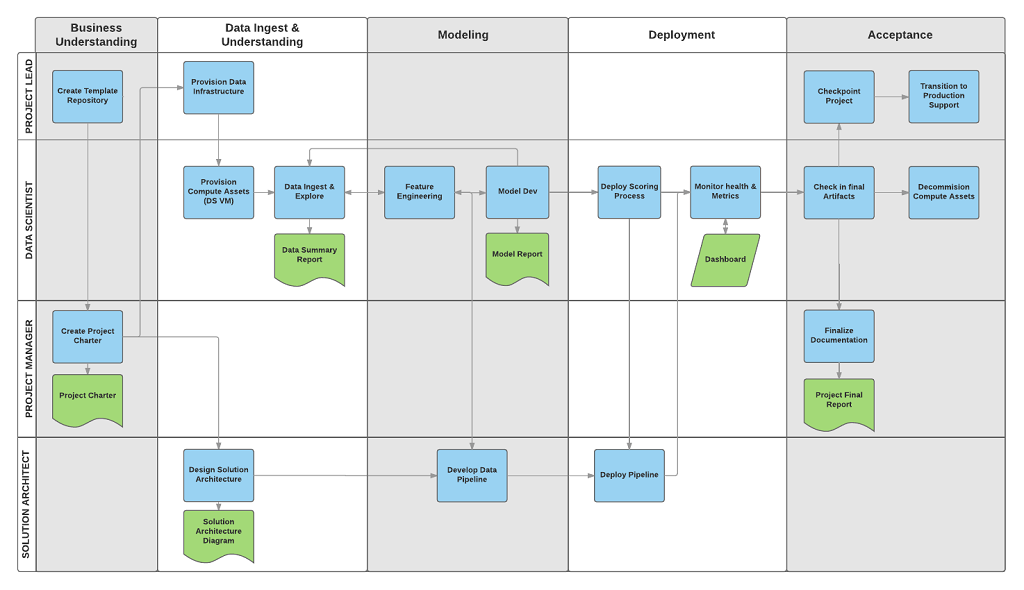
These tasks and artifacts are associated with project roles, for example:
- Solution architect.
- Project manager.
- Data engineer.
- Data scientist.
- Application developer.
- Project lead.
The following diagram shows the tasks (in blue) and artifacts (in green) associated with each stage of the lifecycle (on the horizontal axis) for these roles (on the vertical axis).
Standardized project structure
Your team can use the Azure infrastructure to organize your data science assets.
Azure Machine Learning supports the open-source MLflow. We recommend using MLflow for data science and AI project management. MLflow is designed to manage the complete machine learning lifecycle. It trains and serves models on different platforms, so you can use a consistent set of tools regardless of where your experiments run. You can use MLflow locally on your computer, on a remote compute target, on a virtual machine, or on a Machine Learning compute instance.
MLflow consists of several key functionalities:
Track experiments: With MLflow, you can keep track of experiments, including parameters, code versions, metrics, and output files. This feature helps you compare different runs and manage the experimentation process efficiently.
Package code: It offers a standardized format for packaging machine learning code, which includes dependencies and configurations. This packaging makes it easier to reproduce runs and share code with others.
Manage models: MLflow provides functionalities for managing and versioning models. It supports various machine learning frameworks, so you can store, version, and serve models.
Serve and deploy models: MLflow integrates model serving and deployment capabilities, so you can easily deploy models in diverse environments.
Register models: You can manage the lifecycle of a model, including versioning, stage transitions, and annotations. MLflow is useful for maintaining a centralized model store in a collaborative environment.
Use an API and UI: Inside Azure, MLflow is bundled within the Machine Learning API version 2, so you can interact with the system programmatically. You can use the Azure portal to interact with a UI.
MLflow aims to simplify and standardize the process of machine learning development, from experimentation to deployment.
Machine Learning integrates with Git repositories, so you can use Git-compatible services: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps, or another Git-compatible service. In addition to the assets already tracked in Machine Learning, your team can develop their own taxonomy within their Git-compatible service to store other project information, such as:
- Documentation
- Project, for example the final project report
- Data report, for example the data dictionary or data quality reports
- Model, for example model reports
- Code
- Data preparation
- Model development
- Operationalization, including security and compliance
Infrastructure and resources
The TDSP provides recommendations for managing shared analytics and storage infrastructure such as:
- Cloud file systems for storing datasets
- Databases
- Big data clusters, for example SQL or Spark
- Machine learning services
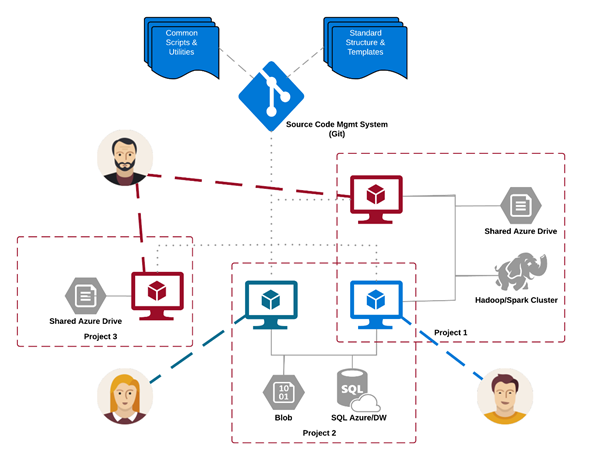
You can place the analytics and storage infrastructure, where raw and processed datasets are stored, in the cloud or on-premises. This infrastructure enables reproducible analysis. It also prevents duplication, which can lead to inconsistencies and unnecessary infrastructure costs. The infrastructure has tools to provision the shared resources, track them, and allow each team member to connect to those resources securely. It's also a good practice to have project members create a consistent compute environment. Various team members can then replicate and validate experiments.
Here's an example of a team working on multiple projects and sharing various cloud analytics infrastructure components:
Tools and utilities
In most organizations, it's challenging to introduce processes. The infrastructure provides tools to implement the TDSP and lifecycle help lower the barriers to and increase the consistency of their adoption.
With Machine Learning, data scientists can apply open-source tooling as part of the data science pipeline or workflow. Within Machine Learning, Microsoft promotes responsible AI tools, which helps achieve Microsoft's Responsible AI Standard.
Peer-reviewed citations
TDSP is a well-established methodology used across Microsoft engagements, and therefore has been documented and studied in peer-reviewed literature. These citations provide an opportunity to investigate TDSP features and applications. See the lifecycle overview page for a list of citations.