Solution ideas
This article describes a solution idea. Your cloud architect can use this guidance to help visualize the major components for a typical implementation of this architecture. Use this article as a starting point to design a well-architected solution that aligns with your workload's specific requirements.
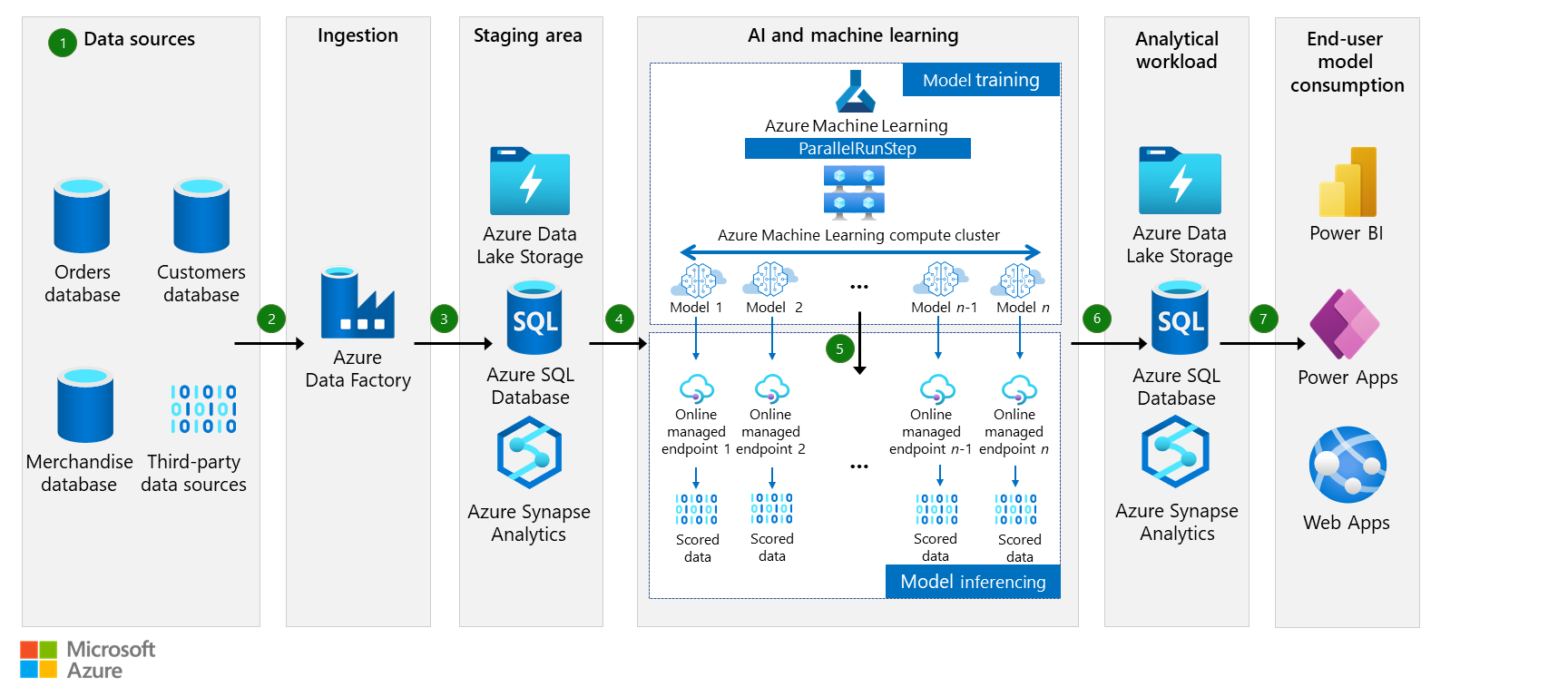
This article describes how merchandise distributors can use AI and machine learning to predict a customer's future order quantity for a specific SKU (stock-keeping unit). By using Next Order Forecasting (NOF), distributors can provide customers with product recommendations and suggest optimal quantities. This article builds on the concepts described in the many models machine learning architecture.
Architecture
Download a PowerPoint file of this architecture.
Dataflow
Data sources
To forecast future orders, you need comprehensive data about your customers' buying history for various SKUs at specific stores, including information about preferences and purchasing behavior. This kind of information is typically obtained from orders, merchandise, and customer databases. You also need to consider external factors like weather, holidays, and events. This data is usually obtained from third-party sources.
To create order forecasting models, you use data in a schema that includes several key variables:
- Date and time
- Customer store location
- Merchandise SKU
- Quantity ordered
- Price per unit
- Weather-related features, holidays, events, and other external factors
By analyzing this data, you can gain insights into customer behavior and make informed SKU and quantity recommendations for the customer's next order.
Ingestion
Data ingestion is the process of transferring data from various sources to a designated destination. This process involves using specific connectors for each data source and target destination.
Azure Data Factory provides connectors that you can use to extract data from various sources, including databases, file systems, and cloud services. These connectors are created by Microsoft or third-party vendors and are designed to function effectively with multiple data sources. For example, you can use SAP connectors for various SAP data ingestion scenarios. You can use the Snowflake connector to copy data from Snowflake.
Staging area
The staging area serves as a temporary storage location between the source and the destination. The main purpose of this staging area is to maintain data in a uniform and structured format while it undergoes transformations or quality checks, before it's loaded into its destination.
A consistent data format is critical for accurate analysis and modeling. If you consolidate and prepare the data in a staging area, Azure Machine Learning can process it more efficiently.
Machine learning model training
Model training is a machine learning process that involves using an algorithm to learn patterns from data and, in this case, selecting a model that can accurately predict a customer's next order.
In this solution, Azure Machine Learning is used to manage the entire machine learning project lifecycle, including training models, deploying models, and managing Machine Learning Operations (MLOps).
ParallelRunStep is used to process large amounts of data in parallel and create models that can forecast the next order for every customer store and merchandise SKU combination. You can reduce processing time by dividing the dataset into smaller parts and processing them simultaneously on multiple virtual machines. You can use Azure Machine Learning compute clusters to accomplish this distribution of workloads across multiple nodes.
After the data is prepared, Azure Machine Learning can start the parallel model training process by using ParallelRunStep with a range of forecasting models, including exponential smoothing, elastic net, and Prophet. Each node or compute instance starts building the model, so the process is more efficient and faster.
Machine learning model Inferencing
Model inferencing is a process that uses a trained machine learning model to generate predictions for previously unseen data points. In this solution, it forecasts the quantity of the merchandise SKU that a customer is likely to purchase.
Azure Machine Learning provides model registries for storing and versioning trained models. Model registries can help you organize and track trained models, ensuring that they're readily available for deployment.
Deploying a trained machine learning model enables the model to process new data for inferencing. We recommend that you use Azure managed endpoints for the deployment target. Endpoints enable easy scalability, performance tuning, and high availability.
In this use case, there are two ways to deploy models on the managed endpoints. The first option is to deploy each model on its own managed endpoint, as shown in the diagram. The second option is to bundle multiple models into a single model and deploy it on a single managed endpoint. The latter approach is more efficient, providing an easier way to deploy and manage multiple models simultaneously.
Analytical workload
The output of the model is stored in analytics systems like Azure Synapse Analytics, Azure Data Lake, or Azure SQL Database, where the input data is also collected and stored. This stage facilitates the availability of the prediction results for customer consumption, model monitoring, and retraining of models with new data to improve their accuracy.
End-user consumption
To present the scored model visually to customers, you can use the Web Apps feature of Azure App Service, a Power BI dashboard, or Power Apps. These tools can present the recommendations for the SKU and predicted quantities graphically in an intuitive and engaging way.
Customers are alerted to recommended SKUs and predicted quantities, so they can place orders proactively. The recommendations can help streamline the ordering process, reduce the likelihood of stockouts, and enhance customer satisfaction. If you use a Power BI dashboard or Power Apps, you can provide your customers with a seamless and efficient ordering experience.
Components
- Azure Synapse is an enterprise analytics service that speeds up time to insight across data warehouses and big data systems. Azure Synapse connects SQL technologies with other Azure services, like Power BI, Azure Cosmos DB, and Azure Machine Learning.
- Data Factory is a cloud-based data integration service that automates data movement and transformation.
- Data Lake is a limitless data storage service for housing data in various shapes and formats. It provides easy integration with the analytics tools in Azure. This solution uses a local data store for machine learning data and a premium data cache for training the machine learning model.
- Azure Machine Learning is an enterprise-grade machine learning service that provides easier model development and deployment to a wide range of machine learning compute targets. It provides users at all skill levels with a low-code designer, automated machine learning, and a hosted Jupyter Notebook environment that supports various integrated development environments.
- Azure Machine Learning compute clusters are managed compute structures that you can use to easily create single-node or multi-node compute resources.
- Azure Machine Learning endpoints are HTTPS endpoints that clients can call to receive the inferencing (scoring) output of a trained model. An endpoint provides a stable scoring URI that's authenticated via key-and-token authentication.
- Azure Machine Learning pipelines are independently executable workflows of complete machine learning tasks. Pipelines can help you standardize the best practices of producing a machine learning model and improve model building efficiency.
- SQL Database is an always-up-to-date, fully managed relational database service that's built for the cloud.
- Power BI provides business analytics and visually immersive and interactive insights. It provides a rich set of connectors to various data sources, easy transformation capabilities, and sophisticated visualization.
- Power Apps is a suite of apps, services, and connectors, together with a data platform, that provides a rapid development environment for building custom apps. You can use Power Apps to quickly build business apps that connect to your data. Data can be stored in the underlying data platform (Microsoft Dataverse) or in various online and on-premises data sources, like SharePoint, Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365, and SQL Server.
- Web applications built with ASP.NET Core, hosted in Azure, offer competitive advantages over traditional alternatives. ASP.NET Core is optimized for modern web application development practices and cloud hosting scenarios.
Alternatives
Azure Machine Learning provides data modeling and deployment in this solution. Alternatively, you can use Azure Databricks to build the solution with a code-first approach. To choose best the technology for your scenario, consider your team's preferences and expertise. Azure Machine Learning is a good choice if you prefer a user-friendly graphical interface. Azure Databricks is suited well for developers who want the flexibility of a code-first approach that enables more customization.
You can also use Azure Databricks instead of Azure Synapse to explore and manipulate data in this solution. Both options provide powerful data exploration and manipulation tools. Azure Synapse provides a unified workspace that includes features that make it easier to connect to and integrate data from various sources (Azure and third-party). Azure Databricks mainly provides data processing and analysis.
Azure Synapse includes a SQL engine that you can use to query and manipulate data with SQL syntax. Azure Databricks uses a notebook-based interface that supports the use of Python, R, Scala, and SQL.
Power BI is a popular tool for visualization. Grafana is another viable option. The main difference is that Grafana is open source, whereas Power BI is a SaaS product offered by Microsoft. If you prioritize customization and the use of open-source tools, Grafana is a better choice. If you prioritize a more seamless integration with other Microsoft products, and product support, Power BI is a better choice.
Rather than using an endpoint for each model, you can bundle multiple models into a single model for deployment to a single managed endpoint. Bundling models for deployment is known as model orchestration. Potential drawbacks of using this approach include increased complexity, potential conflicts between models, and increased risk of downtime if the single endpoint fails.
Scenario details
The merchandise distribution industry has historically struggled to gain insights into customer behavior and purchasing patterns, which makes it difficult to provide personalized product recommendations, improve customer satisfaction, and drive sales. By using AI and machine learning, merchandise distributors are transforming the industry.
They're adopting Next Order Forecasting (NOF), a methodology that they use to recommend products and quantities based on customer purchasing patterns. This methodology benefits customers by consolidating orders and reducing transportation and logistics costs. It also allows distributors to establish smart contracts with regular customers. These contracts enable distributors to proactively recommend products and quantities at a regular cadence, manage inventory, influence manufacturing efficiencies, save money, and promote sustainability. For example, by implementing accurate forecasting, distributors of perishable items can manage optimum levels of inventory and therefore avoid dumping excess stock into landfills.
NOF uses AI and machine learning algorithms to analyze customer orders and make recommendations for future orders. The architecture described in this article takes NOF to another level by enabling forecasting at the individual SKU and store level by using parallel processing. This combination enables businesses to forecast demand for specific products at specific stores. By using this methodology, you can provide your customers with personalized recommendations that meet their needs and exceed their expectations.
Potential use cases
NOF can be used by organizations that need to predict customer demand and optimize inventory management. Here are some specific use cases:
- E-commerce. Online retailers can forecast customer demand and recommend products based on customer purchase history, browsing behavior, and preferences. These predictions can improve the customer experience, increase sales, and reduce the cost of logistics and warehousing.
- Hospitality. Hotels and restaurants can predict customer demand for menu items, beverages, and other products. Doing so can help them optimize inventory, reduce food waste, and improve profitability.
- Healthcare. Hospitals and clinics can forecast patient demand for medical supplies, equipment, and medications. These forecasts can help them reduce inventory stockouts, avoid overstocking, and optimize procurement processes.
- Manufacturing. Manufacturers can forecast demand for products and raw materials, optimize inventory levels, and improve supply chain resilience.
- Energy. Energy companies can predict demand and optimize energy generation, transmission, and distribution. NOF can help them reduce their carbon footprint and improve sustainability.
Considerations
These considerations implement the pillars of the Azure Well-Architected Framework, a set of guiding tenets that you can use to improve the quality of a workload. For more information, see Microsoft Azure Well-Architected Framework.
The technologies in this solution were chosen for scalability, availability, and cost optimization.
Security
Security provides assurances against deliberate attacks and the abuse of your valuable data and systems. For more information, see Overview of the security pillar.
Improved security is built in to the components of this scenario. You can use Microsoft Entra authentication or role-based access control to manage permissions. Consider implementing Azure Machine Learning best practices for enterprise security to establish appropriate security levels.
Azure Synapse offers enterprise-grade security features that provide component isolation to help protect data, improve network security, and improve threat protection. Component isolation can minimize exposure in the case of a security vulnerability. Azure Synapse also enables data obfuscation to help protect sensitive personal data.
Data Lake provides improved data protection, data masking, and improved threat protection. For more information, see Data Lake security.
For more information about security for this architecture, see these resources:
- Deploy dedicated Azure services into virtual networks
- Enterprise security and governance for Azure Machine Learning
Operational excellence
Operational excellence covers the operations processes that deploy an application and keep it running in production. Observability, monitoring, and diagnostic settings are three important considerations to highlight under this pillar.
Observability refers to the ability to understand how the data flow of a system is functioning. Monitoring is the ongoing process of tracking the performance of a system over time. You can monitor metrics like CPU usage, network traffic, and response times. Diagnostic settings are configuration options that you can use to capture diagnostic information.
For more information, see Overview of the operational excellence pillar.
Follow MLOps guidelines to manage an end-to-end machine learning lifecycle that's scalable across multiple workspaces. Before you deploy your solution to production, make sure that it supports ongoing inference with retraining cycles and automated redeployment of models.
Here are some resources to consider:
Performance efficiency
Performance efficiency is the ability of your workload to scale to meet the demands placed on it by users in an efficient manner. For more information, see Performance efficiency pillar overview.
Most components in this architecture can be scaled up and down based on the analysis activity levels. Azure Synapse provides scalability and high performance and can be reduced or paused during low levels of activity.
You can scale Azure Machine Learning based on the amount of data and the compute resources needed for model training. You can scale the deployment and compute resources based on the expected load and scoring service.
Load testing is an important step for ensuring the performance efficiency of the machine learning model. This testing involves the simulation of a high volume of requests to the model to measure metrics like throughput, response time, and resource utilization. Load testing can help you identify bottlenecks and problems that can affect the model's performance in a production environment.
For more information about designing scalable solutions, see Performance efficiency checklist.
Contributors
This article is maintained by Microsoft. It was originally written by the following contributors.
Principal author:
- Manasa Ramalinga | Principal Cloud Solution Architect – US Customer Success
Other contributors:
- Mick Alberts | Technical Writer
- Oscar Shimabukuro Kiyan | Senior Cloud Solution Architect – US Customer Success
To see non-public LinkedIn profiles, sign in to LinkedIn.
Next steps
- Many Models Solution Accelerator
- What is Azure Machine Learning?
- Track machine learning models with MLflow and Azure Machine Learning
- Azure Data Factory documentation
- What is Azure Synapse Analytics?
- What is Azure SQL Database?
- What is Power BI?
- Welcome to Azure Stream Analytics
Related resources
- Many models machine learning at scale with Azure Machine Learning
- Solutions for the energy and environment industries
- Oil and gas tank level forecasting
- Demand forecasting for shipping and distribution
- Forecast energy and power demand with machine learning
- Interactive price analytics using transaction history data
- MLOps for Python models using Azure Machine Learning