Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Arc resource bridge is a prepackaged virtual appliance that runs as a Kubernetes-based management cluster deployed on your on-premises infrastructure (private cloud). It acts as a core component of the Azure Arc private cloud products and enables Azure-based management of on-premises resources. Azure Arc resource bridge provides a secure conduit between Azure and your on-premises infrastructure. It allows projection of on-premises resources into Azure as native Azure resources, enabling consistent governance, automation, and management with Azure tools. The resource bridge facilitates self-service provisioning and lifecycle management of on-premises Windows and Linux virtual machines directly from Azure.
Azure Arc resource bridge integrates with the following private cloud platforms:
Azure Local (via Azure Arc VM management)
VMware (via Azure Arc-enabled VMware vSphere)
System Center Virtual Machine Manager (via Azure Arc-enabled SCVMM)
Once deployed in your private cloud, the resource bridge is granted credentials to the local virtualization infrastructure, allowing it to project on-premises resources into Azure as Arc-enabled resources. This projection enables consistent management and automation using Azure tools, such as Azure Policy, and Azure CLI.
Arc resource bridge enables the following hybrid management capabilities:
Native Azure experience: Projects on-premises VMs as Azure resources, allowing you to view on-premises VMs in Azure and apply tags, policies, and extensions just like native Azure VMs.
VM self-service from Azure: Create, manage, and delete VMs on-premises through the Azure portal or CLI.
Native Azure integration: Extend Azure governance, monitoring, and automation capabilities to on-premises VMs.
Overview
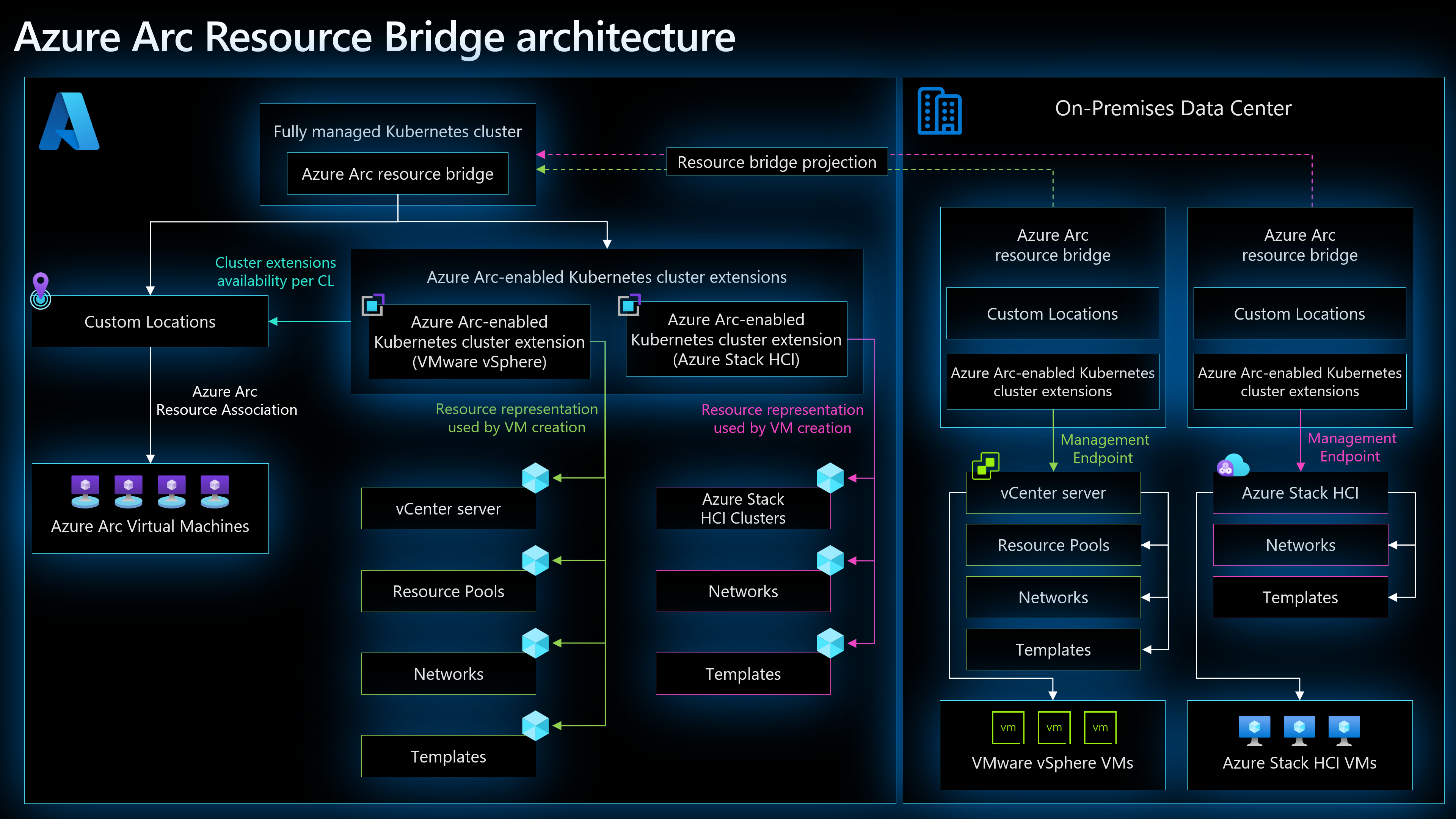
Azure Arc resource bridge is a key component that allows Azure to manage on-premises private cloud infrastructure. Supported private clouds are VMware vSphere, SCVMM, and Azure Local. It acts as a local appliance VM that connects your private cloud to Azure, enabling Azure to project and manage your on-premises resources as if they were native cloud assets.
To deliver this functionality, the resource bridge hosts additional Azure Arc components, including:
Custom location – These define the target infrastructure for deployments. The custom location maps to your private cloud infrastructure. When you create a VM from Azure, you choose a custom location. Azure knows where to route the request and what private cloud location it maps to based on the custom location. For example, for Arc-enabled VMware, the custom location maps to an instance of vCenter. For Azure Local, it maps to an Azure Local instance. For more information about custom location, refer to Create and manage custom locations.
Cluster extension – A cluster extension enables capabilities on the resource bridge. The supported extensions are Arc-enabled VMware (microsoft.vmware), Arc-enabled AVS (microsoft.avs), Arc-enabled SCVMM (microsoft.scvmm), Azure Local (microsoft.azstackhci.operator, microsoft.diagnosis.operator) and AKS Arc (microsoft.hybridaksoperator).
Azure Arc agents – Power the communication and control layer between Azure and your infrastructure.
To download architecture diagrams in high resolution, visit Jumpstart Gems.
Custom locations and cluster extensions are both Azure resources linked to the Azure Arc resource bridge resource in Azure Resource Manager. When you create a VM from Azure, you select the custom location. Azure uses the custom location to determine the mapping to your private cloud infrastructure and routes the create VM request to your private cloud. A VM is created in your private cloud and a corresponding Azure resource is created in Azure as a representation of your on-premises VM in Azure. Azure Arc resource bridge enables this hybrid management of your on-premises resources from Azure.
Some VM creation inputs vary based on the private cloud:
For VMware, you must specify the resource pool, network, and VM template.
For Azure Local, you provide the custom location, network, and template.
The custom location, infrastructure and VM resources in Azure are projections of your on-premises environment. If an underlying on-premises resource becomes unhealthy, this status may be reflected in its corresponding Azure resource.
Azure Arc resource bridge enables this projection and acts as the control plane that enables Azure to manage your private cloud infrastructure. If the resource bridge becomes unavailable or unhealthy, Azure may lose visibility or management capabilities of your on-premises resources. However, your on-premises resources, such as VMs running in vCenter, Azure Local or SCVMM, should not be affected and should continue to remain operational.
Azure Arc resource bridge requires ongoing operational maintenance. Maintenance tasks include updating the private cloud credentials, monitoring the appliance health and ensuring the appliance stays within the supported versions. Microsoft may offer cloud-managed upgrades to assist in maintenance, but this does not replace the need for regular manual upgrades every 6 months.
Benefits of Azure Arc resource bridge
Azure Arc resource bridge enables you to manage on-premises Windows and Linux virtual machines directly from Azure. Depending on the supported private cloud, you may be able to perform the following VM management operations:
Provision and delete VMs from Azure portal or CLI
Start, stop, and restart VMs
Control access using Azure RBAC and apply Azure tags
Add, remove or update networking, disks, and VM size (CPU cores and memory)
Enable guest management
Install supported Azure Arc VM extensions (Ex: Azure Monitor, Azure Policy)
Example scenarios
These examples show how Azure Arc resource bridge enables hybrid management of on-premises environments from Azure.
Apply Azure Policy and other Azure services to on-premises VMware VMs
A customer deploys the Arc resource bridge into their on-premises VMware vSphere environment. The resource bridge connects to their vCenter instance. Visibility and management of VMware virtual machines in Azure are scoped to specific resource pools, networks, and VM templates defined during deployment.
From Azure portal, the customer selects the VMware virtual machines and enables Azure Arc. The Arc-enabled virtual machines can now be managed alongside native Azure VMs. The customer can enable Azure services, such as Defender for Cloud and Azure Policy, to their on-premises VMware workloads. This enables consistent security and compliance enforcement across both cloud and on-premises environments, with centralized policy management through Azure.
Create physical Azure Local VMs on-premises from Azure
A customer has multiple datacenter locations in Canada and New York. They deploy Arc resource bridge in each datacenter and enable Azure Arc VM management of their Azure Local VMs in Azure. They can then sign into Azure portal and see all their Arc-enabled VMs from the two physical locations in one central view from Azure portal. From Azure portal, they can:
View and manage all Arc-enabled VMs across both datacenters
Centrally create new VMs in either datacenter from Azure portal
Each new VM is provisioned on-premises in the selected location but appears in Azure portal as an Arc-enabled VM. This setup enables centralized VM management across multiple physical sites all from within Azure.
Version and region support
Supported regions
To use an Azure Arc-enabled private cloud in a specific region, both Azure Arc resource bridge and the Arc-enabled private cloud must be supported in that region. For example, to use Azure-Arc enabled VMware in East US, both Arc resource bridge and Arc-enabled VMware must be available in East US. To confirm region availability for an Arc-enabled private cloud, review the corresponding onboarding documentation. There could be instances where Arc resource bridge is available in a region but the private cloud isn't yet available.
Arc resource bridge supports the following Azure regions:
East US
East US 2
West US 2
West US 3
Central US
North Central US
South Central US
US Gov Virginia
Canada Central
Australia East
Australia SouthEast
West Europe
North Europe
UK South
UK West
Sweden Central
Italy North
Japan East
Southeast Asia
East Asia
Central India
Regional resiliency
While Azure includes redundancy across all levels of its infrastructure, the Azure Arc resource bridge does not currently support cross-region failover or other resiliency capabilities. If a service-impacting event occurs and the resource bridge becomes unavailable, your on-premises VMs will continue to run without interruption. However, management capabilities from Azure will be temporarily unavailable until the service is restored.
Private cloud environments
The following private clouds and their versions are officially supported for Arc resource bridge:
- VMware vSphere version 7.0, 8.0
- Azure Local
- SCVMM
Supported versions
We generally recommend keeping your Arc resource bridge on a version released within the last 6 months or within the latest n-3 versions, whichever is more recent. This ensures your appliance benefits from the latest features, security updates, and refreshed internal components such as certificates. While the support policy includes the latest version and the three preceding versions (n-3), you must still upgrade at least once every 6 months, even if your current version is technically within the supported range. This is critical to maintain system health and compatibility. To estimate your last upgrade date, check your appliance version and its corresponding release date. For version release news, please refer to Arc resource bridge release notes
Private link support
Arc resource bridge currently doesn't support private link.
Next steps
- Learn how Azure Arc-enabled VMware vSphere extends Azure's governance and management capabilities to VMware vSphere infrastructure.
- Learn how Azure Arc-enabled SCVMM extends Azure's governance and management capabilities to System Center managed infrastructure.
- Learn about provisioning and managing on-premises Windows and Linux VMs running on Azure Local instances.
- Review the system requirements for deploying and managing Arc resource bridge.