Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
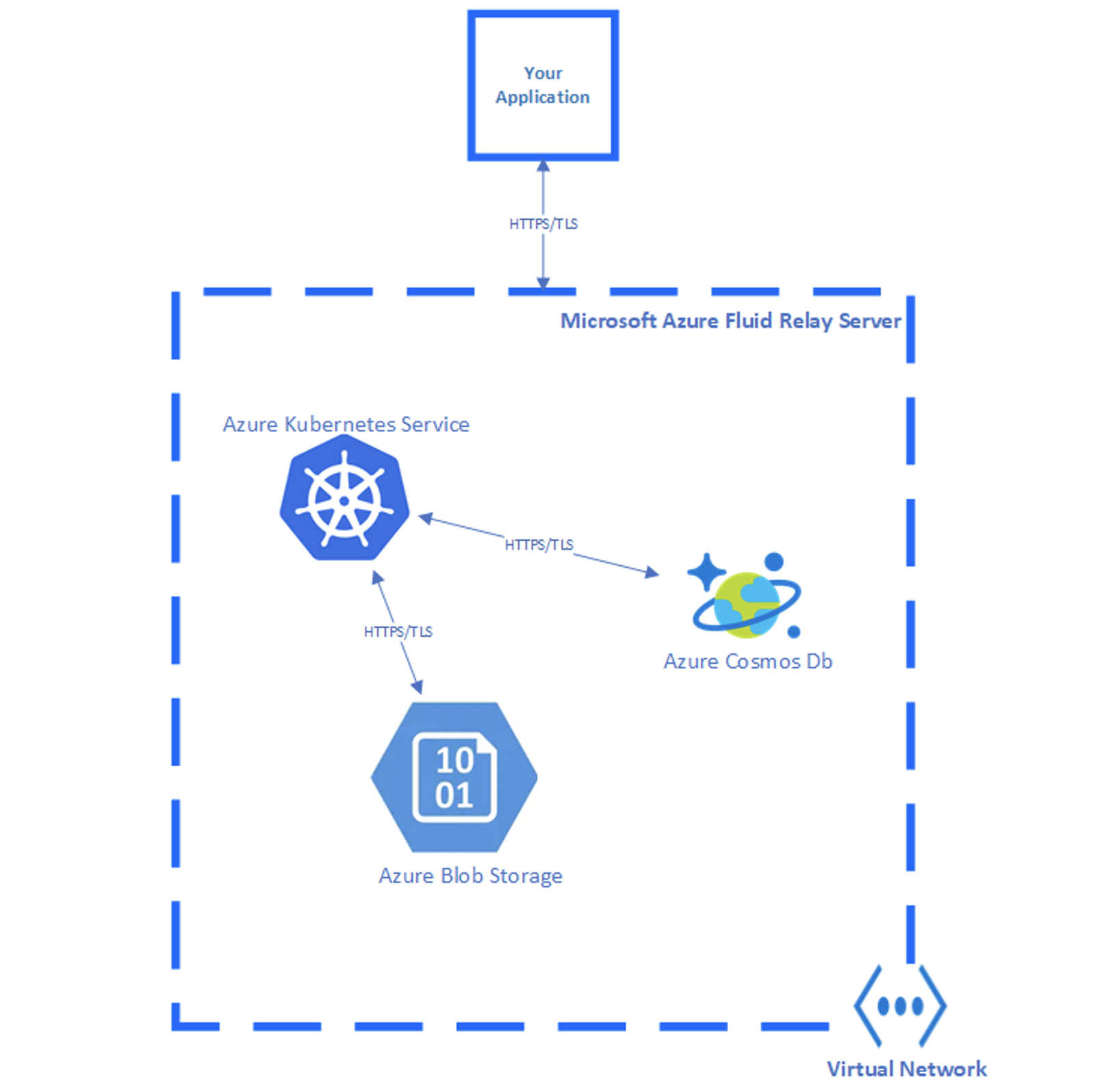
Azure Fluid Relay leverages the encryption-at-rest capability of Azure Kubernetes Service, Azure Cosmos DB and Azure Blob Storage. The service-to-service communication between Azure Fluid Relay and these resources is TLS encrypted and is enclosed in with the Azure Virtual Network boundary, protected from external interference by Network Security Rules.
The diagram below shows at a high level how Azure Fluid Relay is implemented and how it handles data storage.
Frequently asked questions
How much more does Azure Fluid Relay cost if encryption is enabled?
Encryption-at-rest is enabled by default. There's no additional cost.
Who manages the encryption keys?
The keys are managed by Microsoft.
How often are encryption keys rotated?
Microsoft has a set of internal guidelines for encryption key rotation which Azure Fluid Relay follows. The specific guidelines aren't published. Microsoft does publish the Security Development Lifecycle (SDL), which is seen as a subset of internal guidance and has useful best practices for developers.
Can I use my own encryption keys?
Yes. For more information, see Customer-managed keys for Azure Fluid Relay encryption.
What regions have encryption turned on?
All Azure Fluid Relay regions have encryption turned on for all user data.
Does encryption affect the performance latency and throughput?
A: There's no impact or changes to performance with encryption at rest enabled.