Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Azure App Service Hybrid Connections feature enables access to resources in other networks. You can learn more about this capability in the Hybrid Connections documentation. This article describes how to use this capability to run PowerShell functions that target an on-premises server. This server can then be used to manage all resources in the on-premises environment from an Azure PowerShell function.
Configure an on-premises server for PowerShell remoting
The following script enables PowerShell remoting, and it creates a new firewall rule and a WinRM https listener. For testing purposes, a self-signed certificate is used. In a production environment, we recommend that you use a signed certificate.
# For configuration of WinRM, see
# https://learn.microsoft.com/windows/win32/winrm/installation-and-configuration-for-windows-remote-management.
# Enable PowerShell remoting.
Enable-PSRemoting -Force
# Create firewall rule for WinRM. The default HTTPS port is 5986.
New-NetFirewallRule -Name "WinRM HTTPS" `
-DisplayName "WinRM HTTPS" `
-Enabled True `
-Profile "Any" `
-Action "Allow" `
-Direction "Inbound" `
-LocalPort 5986 `
-Protocol "TCP"
# Create new self-signed-certificate to be used by WinRM.
$Thumbprint = (New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName $env:COMPUTERNAME -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\My).Thumbprint
# Create WinRM HTTPS listener.
$Cmd = "winrm create winrm/config/Listener?Address=*+Transport=HTTPS @{Hostname=""$env:COMPUTERNAME ""; CertificateThumbprint=""$Thumbprint""}"
cmd.exe /C $Cmd
Create a PowerShell function app in the portal
The App Service Hybrid Connections feature is available only in Basic, Standard, and Isolated pricing plans. When you create the function app with PowerShell, create or select one of these plans.
From the Azure portal menu or the Home page, select Create a resource.
In the New page, select Compute > Function App.
On the Basics page, use the function app settings as specified in the following table.
Setting Suggested value Description Subscription Your subscription The subscription under which this new function app is created. Resource Group myResourceGroup Name for the new resource group in which to create your function app. Function App name Globally unique name Name that identifies your new function app. Valid characters are a-z(case insensitive),0-9, and-.Publish Code Option to publish code files or a Docker container. Runtime stack Preferred language Choose PowerShell Core. Version Version number Choose the version of your installed runtime. Region Preferred region Choose a region near you or near other services your functions access. 
Select Next : Hosting. On the Hosting page, enter the following settings.
Setting Suggested value Description Storage account Globally unique name Create a storage account used by your function app. Storage account names must be between 3 and 24 characters in length and can contain numbers and lowercase letters only. You can also use an existing account, which must meet the storage account requirements. Operating system Preferred operating system An operating system is pre-selected for you based on your runtime stack selection, but you can change the setting if necessary. Plan type App service plan Choose App service plan. When you run in an App Service plan, you must manage the scaling of your function app. 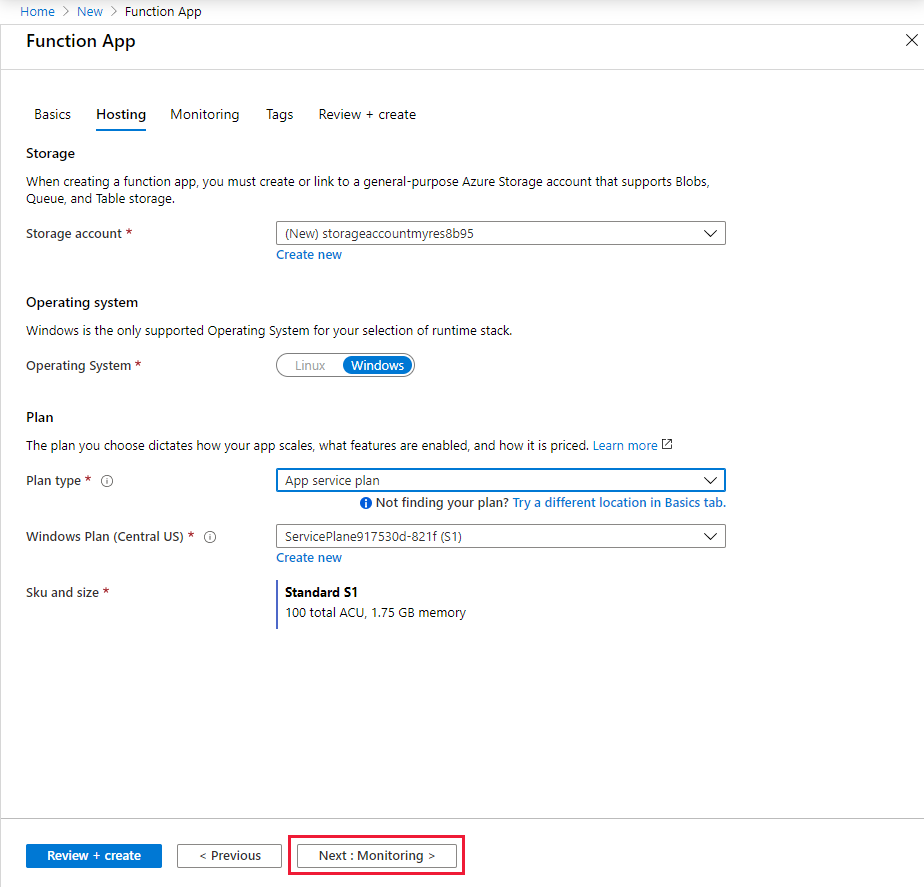
Select Next : Monitoring. On the Monitoring page, enter the following settings.
Setting Suggested value Description Application Insights Default Creates an Application Insights resource of the same App name in the nearest supported region. By expanding this setting or selecting Create new, you can change the Application Insights name or choose a different region in an Azure geography where you want to store your data. 
Select Review + create to review the app configuration selections.
On the Review + create page, review your settings, and then select Create to provision and deploy the function app.
Select the Notifications icon in the upper-right corner of the portal and watch for the Deployment succeeded message.
Select Go to resource to view your new function app. You can also select Pin to dashboard. Pinning makes it easier to return to this function app resource from your dashboard.
Create a hybrid connection for the function app
Hybrid connections are configured from the networking section of the function app:
Under Settings in the function app you just created, select Networking.
Select Configure your hybrid connections endpoints.

Select Add hybrid connection.
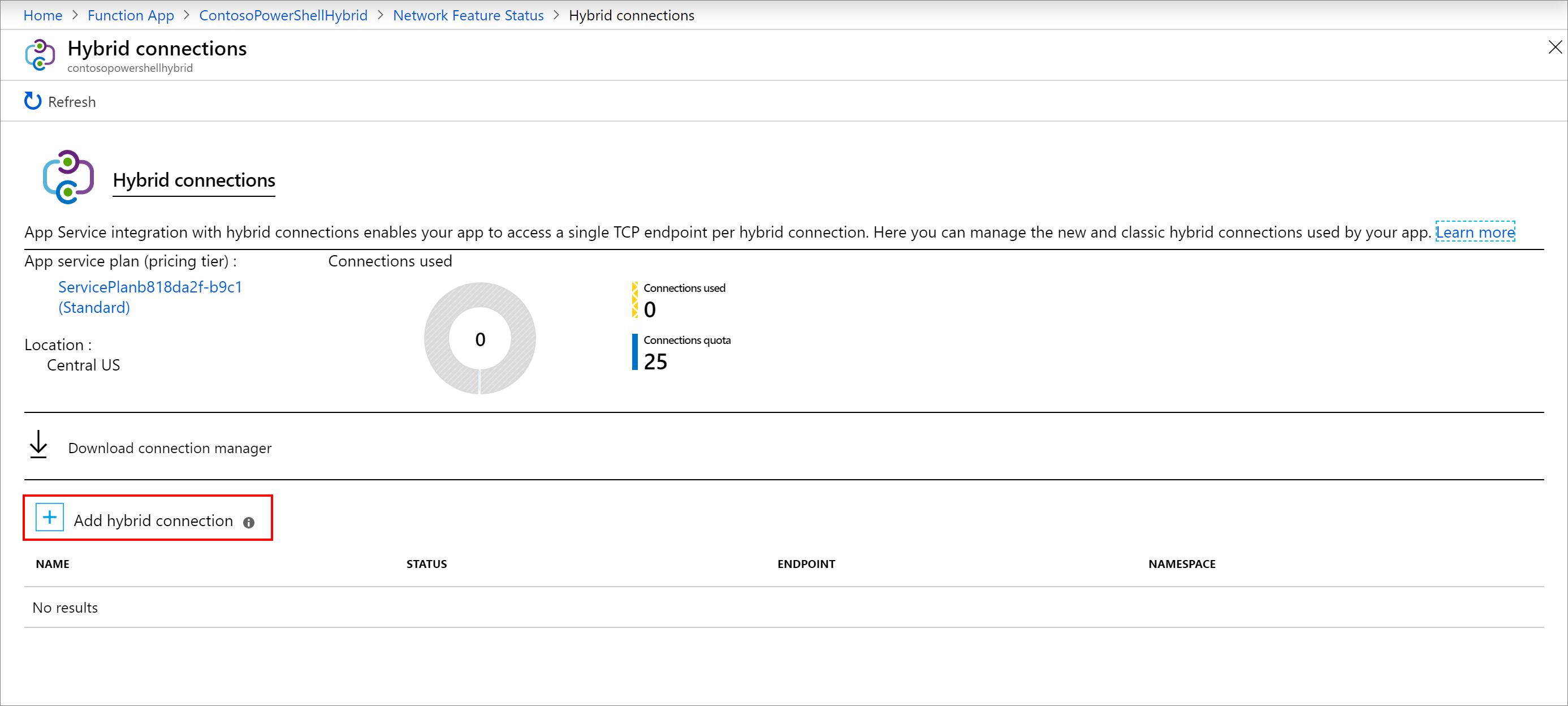
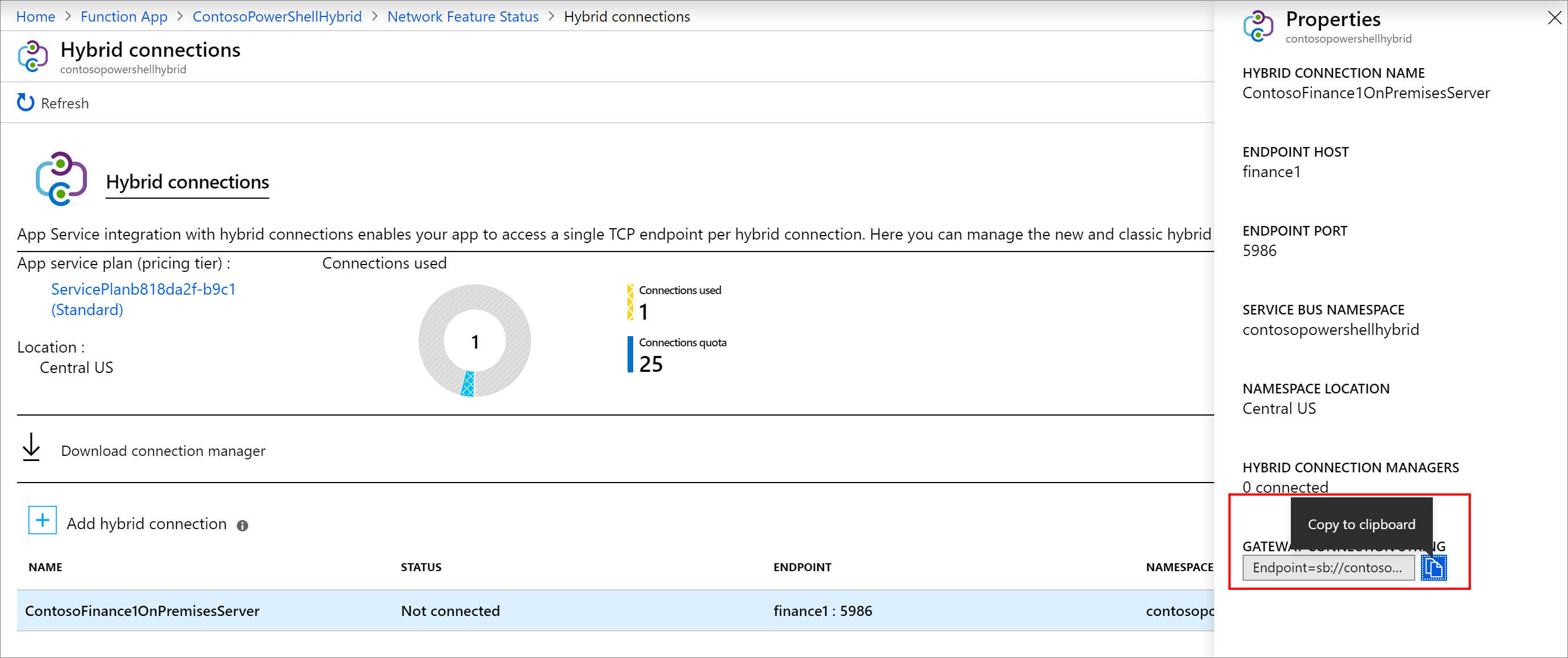
Enter information about the hybrid connection as shown after the following screenshot. For Endpoint Host, use the host name of the on-premises server for which you created the self-signed certificate. You'll have connection issues when the certificate name and the host name of the on-premise server don't match. The port matches the default Windows remote management service port that was defined on the server earlier.
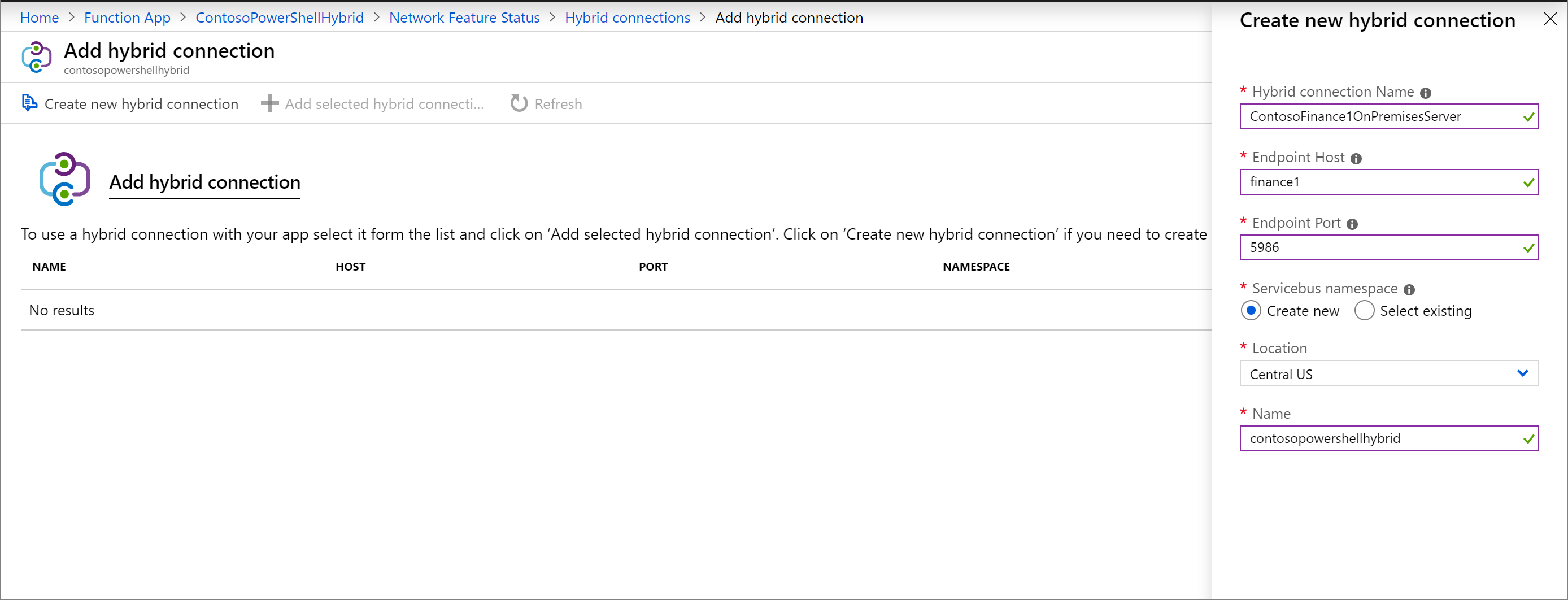
Setting Suggested value Hybrid connection name ContosoHybridOnPremisesServer Endpoint Host finance1 Endpoint Port 5986 Servicebus namespace Create New Location Pick an available location Name contosopowershellhybrid Select OK to create the hybrid connection.
Download and install the hybrid connection
Select Download connection manager to save the .msi file locally on your computer.

Copy the .msi file from your local computer to the on-premises server.
Run the Hybrid Connection Manager installer to install the service on the on-premises server.
From the portal, open the hybrid connection and then copy the gateway connection string to the clipboard.
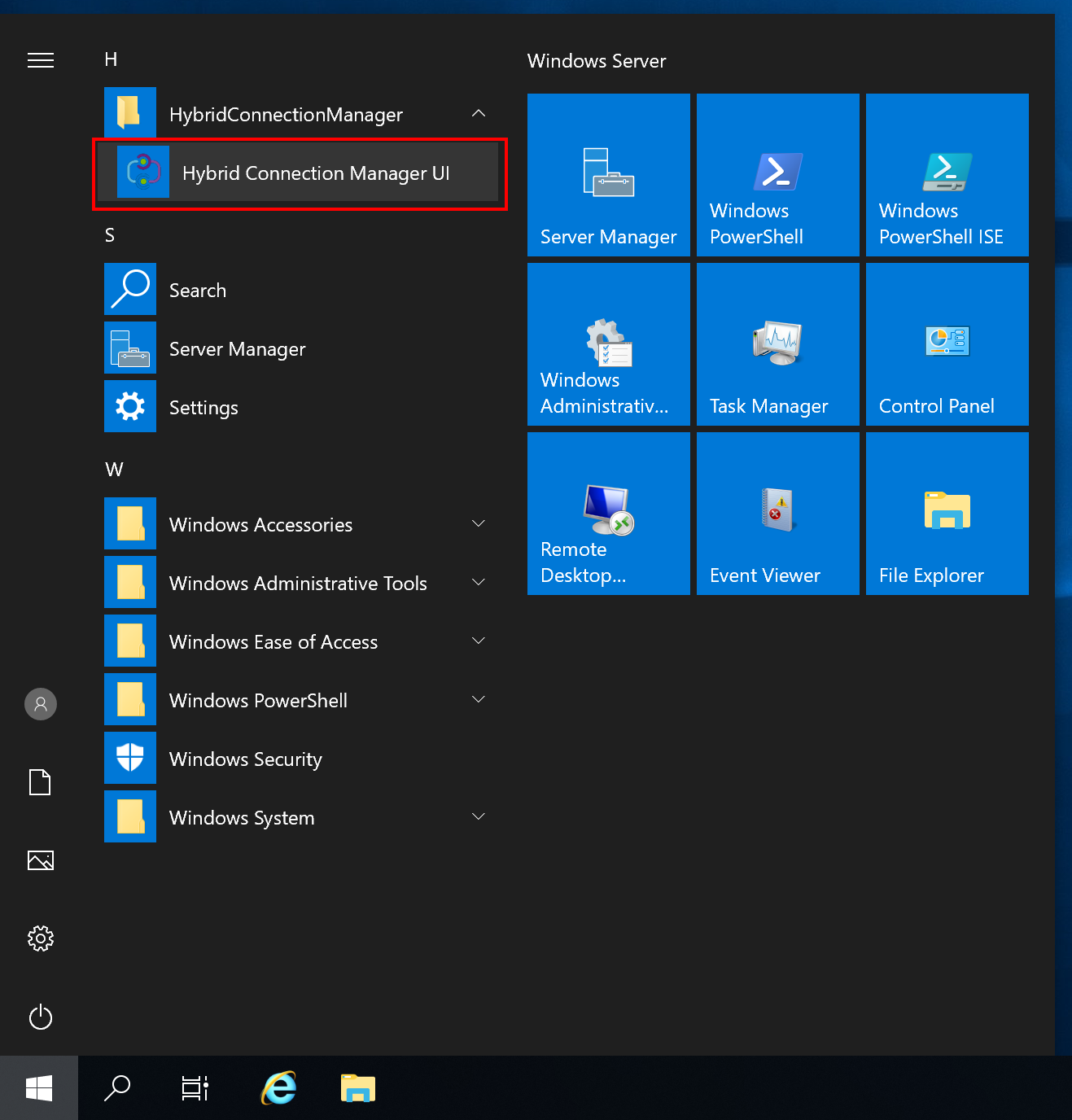
Open the Hybrid Connection Manager UI on the on-premises server.
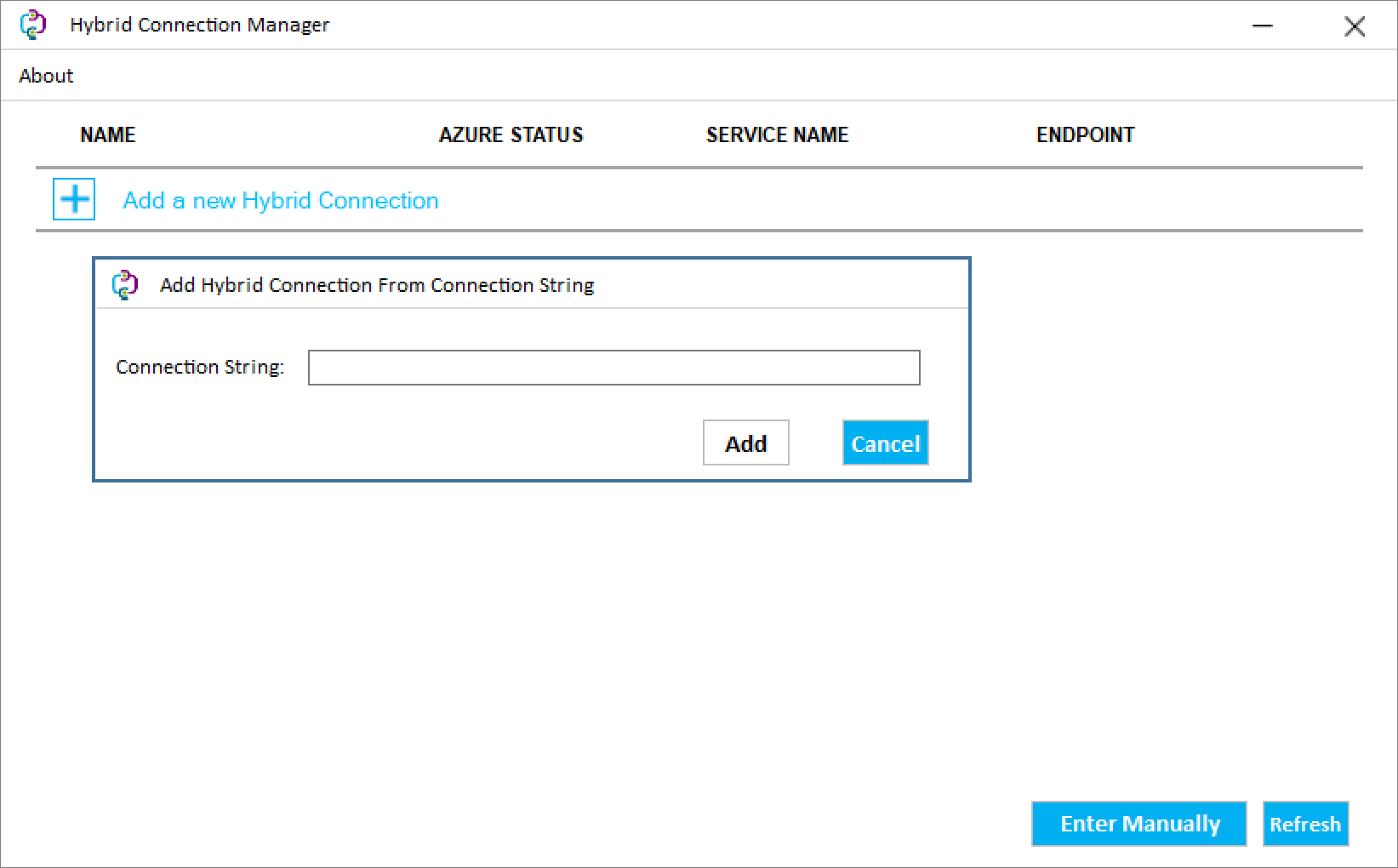
Select Enter Manually and paste the connection string from the clipboard.
Restart the Hybrid Connection Manager from PowerShell if it doesn't show as connected.
Restart-Service HybridConnectionManager
Create an app setting for the password of an administrator account
Under Settings for your function app, select Configuration.
Select + New application setting.
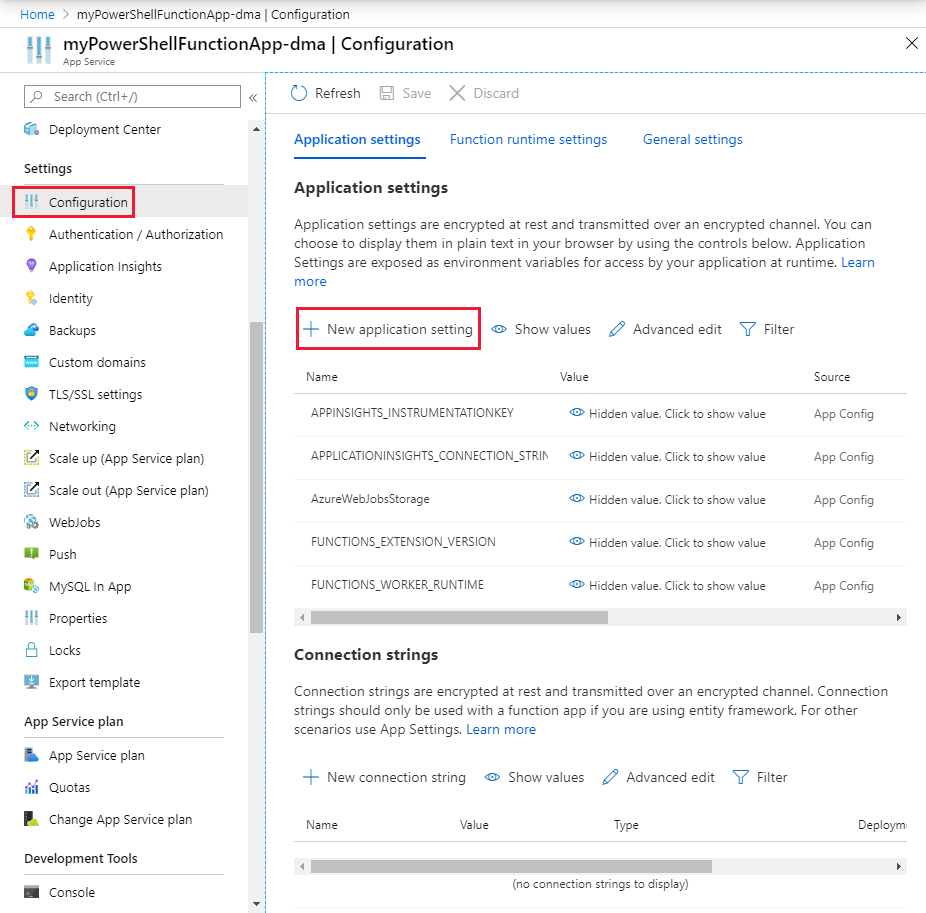
Name the setting ContosoUserPassword, and enter the password. Select OK.
Select Save to store the password in the function application.
Create a function HTTP trigger
In your function app, select Functions, and then select + Add.
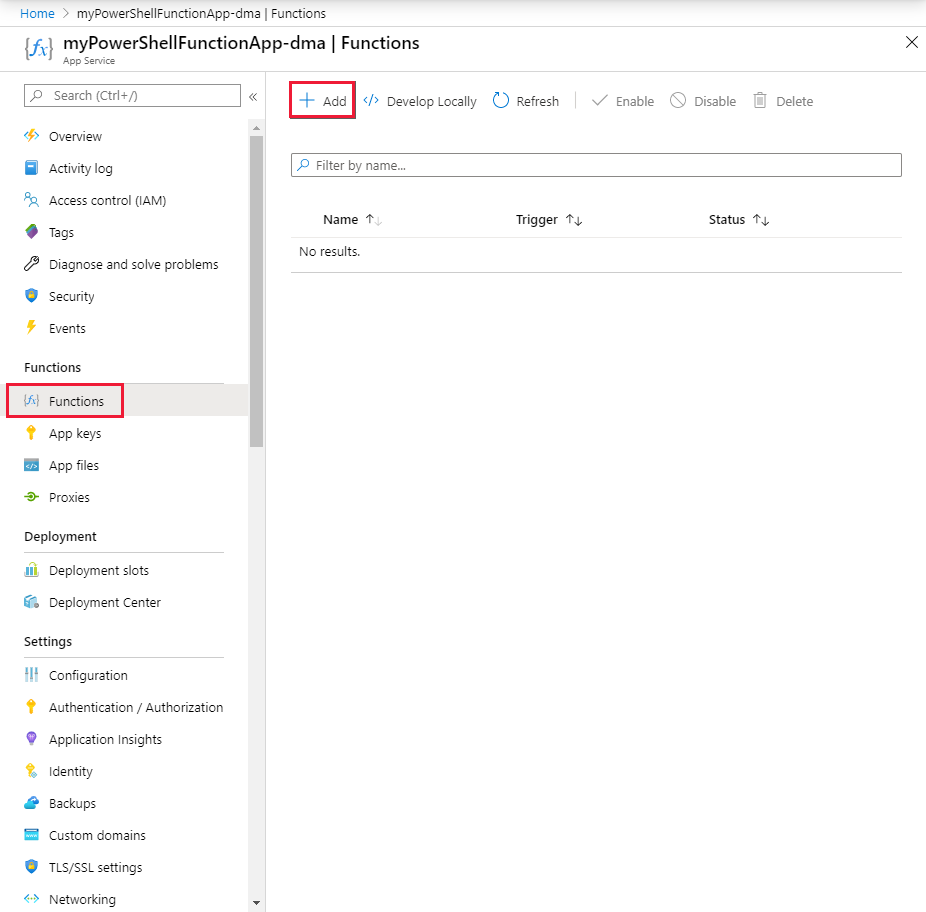
Select the HTTP trigger template, name the new function, and select Create Function.

Test the function
In the new function, select Code + Test. Replace the PowerShell code from the template with the following code:
# Input bindings are passed in via param block. param($Request, $TriggerMetadata) # Write to the Azure Functions log stream. Write-Output "PowerShell HTTP trigger function processed a request." # Note that ContosoUserPassword is a function app setting, so I can access it as $env:ContosoUserPassword. $UserName = "ContosoUser" $securedPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString $Env:ContosoUserPassword -AsPlainText -Force $Credential = [System.management.automation.pscredential]::new($UserName, $SecuredPassword) # This is the name of the hybrid connection Endpoint. $HybridEndpoint = "finance1" $Script = { Param( [Parameter(Mandatory=$True)] [String] $Service ) Get-Service $Service } Write-Output "Scenario 1: Running command via Invoke-Command" Invoke-Command -ComputerName $HybridEndpoint ` -Credential $Credential ` -Port 5986 ` -UseSSL ` -ScriptBlock $Script ` -ArgumentList "*" ` -SessionOption (New-PSSessionOption -SkipCACheck)Select Save to save your changes, then select Test > Run to test the function.
Select Logs to review the logs and verify that the test was successful.
Managing other systems on-premises
You can use the connected on-premises server to connect to other servers and management systems in the local environment. This lets you manage your datacenter operations from Azure by using your PowerShell functions. The following script registers a PowerShell configuration session that runs under the provided credentials. These credentials must be for an administrator on the remote servers. You can then use this configuration to access other endpoints on the local server or datacenter.
# Input bindings are passed in via param block.
param($Request, $TriggerMetadata)
# Write to the Azure Functions log stream.
Write-Host "PowerShell HTTP trigger function processed a request."
# Note that ContosoUserPassword is a function app setting, so I can access it as $env:ContosoUserPassword.
$UserName = "ContosoUser"
$SecuredPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString $Env:ContosoUserPassword -AsPlainText -Force
$Credential = [System.management.automation.pscredential]::new($UserName, $SecuredPassword)
# This is the name of the hybrid connection Endpoint.
$HybridEndpoint = "finance1"
# The remote server that will be connected to run remote PowerShell commands on
$RemoteServer = "finance2".
Write-Output "Use hybrid connection server as a jump box to connect to a remote machine"
# We are registering an endpoint that runs under credentials ($Credential) that has access to the remote server.
$SessionName = "HybridSession"
$ScriptCommand = {
param (
[Parameter(Mandatory=$True)]
$SessionName)
if (-not (Get-PSSessionConfiguration -Name $SessionName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue))
{
Register-PSSessionConfiguration -Name $SessionName -RunAsCredential $Using:Credential
}
}
Write-Output "Registering session on hybrid connection jumpbox"
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $HybridEndpoint `
-Credential $Credential `
-Port 5986 `
-UseSSL `
-ScriptBlock $ScriptCommand `
-ArgumentList $SessionName `
-SessionOption (New-PSSessionOption -SkipCACheck)
# Script to run on the jump box to run against the second machine.
$RemoteScriptCommand = {
param (
[Parameter(Mandatory=$True)]
$ComputerName)
# Write out the hostname of the hybrid connection server.
hostname
# Write out the hostname of the remote server.
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $ComputerName -Credential $Using:Credential -ScriptBlock {hostname} `
-UseSSL -Port 5986 -SessionOption (New-PSSessionOption -SkipCACheck)
}
Write-Output "Running command against remote machine via jumpbox by connecting to the PowerShell configuration session"
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $HybridEndpoint `
-Credential $Credential `
-Port 5986 `
-UseSSL `
-ScriptBlock $RemoteScriptCommand `
-ArgumentList $RemoteServer `
-SessionOption (New-PSSessionOption -SkipCACheck) `
-ConfigurationName $SessionName
Replace the following variables in this script with the applicable values from your environment:
- $HybridEndpoint
- $RemoteServer
In the two preceding scenarios, you can connect and manage your on-premises environments by using PowerShell in Azure Functions and Hybrid Connections. We encourage you to learn more about Hybrid Connections and PowerShell in functions.
You can also use Azure virtual networks to connect to your on-premises environment through Azure Functions.