Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
This article provides an overview of the active geo-replication feature for Azure SQL Database, which lets you continuously replicate data from a primary database to a readable secondary database. The readable secondary database might be in the same Azure region as the primary, or, more commonly, in a different region. This kind of readable secondary database is also known as a geo-secondary or geo-replica.
Active geo-replication is configured per database. To fail over a group of databases, or if your application requires a stable connection endpoint, consider Failover groups instead.
You can also migrate a SQL database with active geo-replication.
Overview
Active geo-replication is designed as a business continuity solution. Active geo-replication lets you perform quick disaster recovery of individual databases if there's a regional disaster or a large scale outage. Once geo-replication is set up, you can initiate a geo-failover to a geo-secondary in a different Azure region. The geo-failover is initiated programmatically by the application or manually by the user.
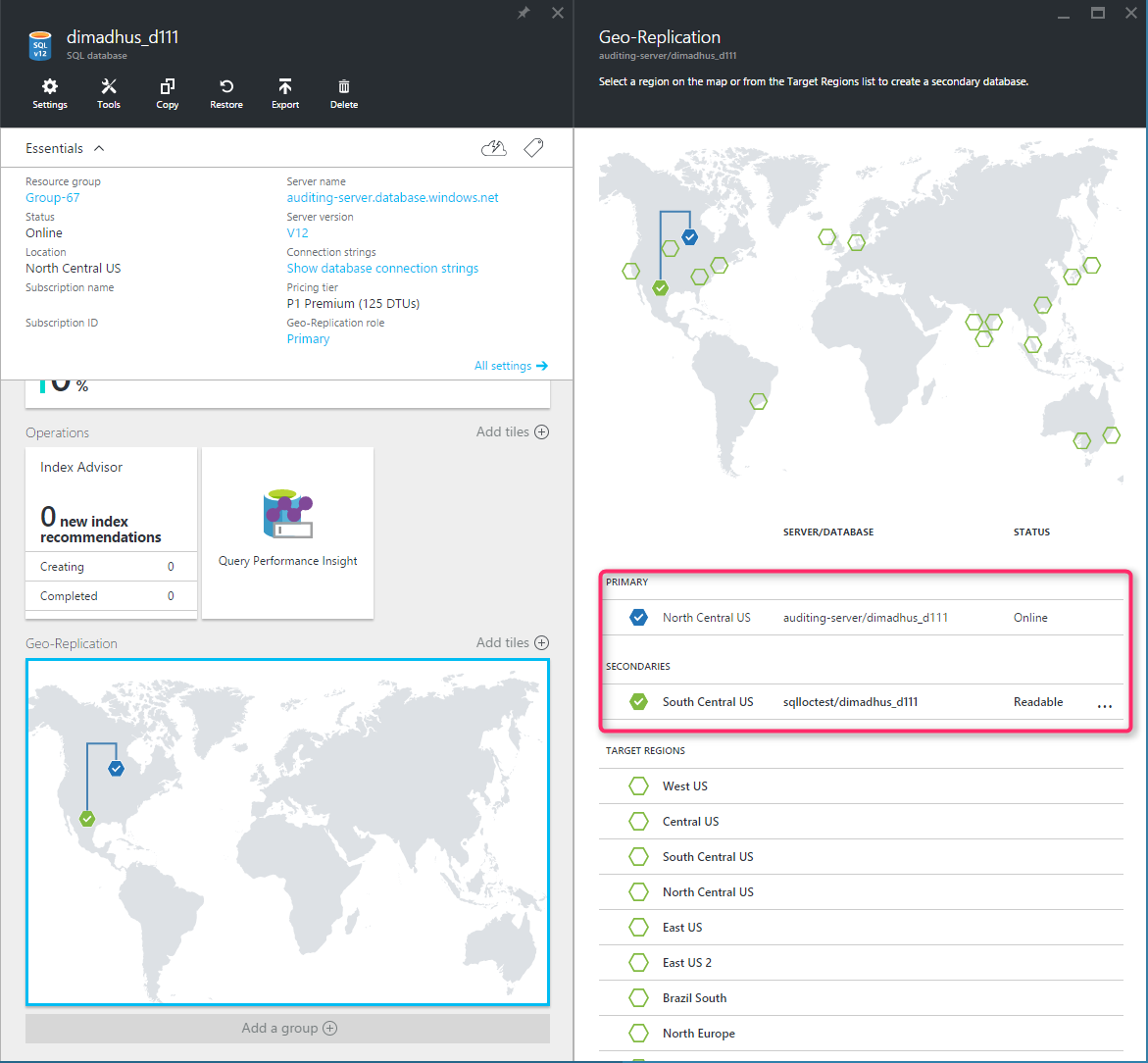
The following diagram illustrates a typical configuration of a geo-redundant cloud application using Active geo-replication.
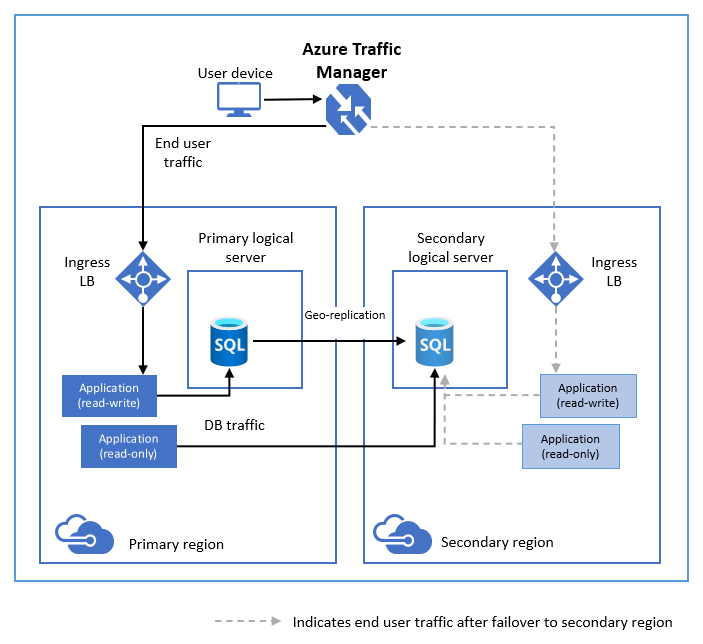
If for any reason your primary database fails, you can initiate a geo-failover to any of your secondary databases. When a secondary is promoted to the primary role, all other secondaries are automatically linked to the new primary.
You can manage geo-replication and initiate a geo-failover using any of the following methods:
- The Azure portal
- PowerShell: Single database
- PowerShell: Elastic pool
- Transact-SQL: Single database or elastic pool
- REST API: Single database
Active geo-replication uses the Always On availability group technology to asynchronously replicate the transaction log generated on the primary replica to all geo-replicas. While at any given point, a secondary database might be slightly behind the primary database, the data on a secondary is guaranteed to be transactionally consistent. In other words, changes made by uncommitted transactions aren't visible.
Note
Active geo-replication replicates changes by streaming database transaction log from the primary replica to secondary replicas. It is unrelated to transactional replication, which replicates changes by executing DML (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) commands on subscribers.
Geo-replication provides regional redundancy. Regional redundancy enables applications to quickly recover from a permanent loss of an entire Azure region or parts of a region, caused by natural disasters, catastrophic human errors, or malicious acts. Geo-replication RPO can be found in Business continuity in Azure SQL Database.
The following figure shows an example of active geo-replication configured with a primary in the West US 2 region and a geo-secondary in the East US region.
In addition to disaster recovery, active geo-replication can be used in the following scenarios:
- Database migration: You can use active geo-replication to migrate a database from one server to another with minimum downtime.
- Application upgrades: You can create an extra secondary as a fail back copy during application upgrades.
To achieve full business continuity, adding database regional redundancy is only a part of the solution. Recovering an application (service) end-to-end after a catastrophic failure requires recovery of all components that constitute the service and any dependent services. Examples of these components include the client software (for example, a browser with a custom JavaScript), web front ends, storage, and DNS. It's critical that all components are resilient to the same failures and become available within the recovery time objective (RTO) of your application. Therefore, you need to identify all dependent services and understand the guarantees and capabilities they provide. Then, you must take adequate steps to ensure that your service functions during the failover of the services on which it depends. For more information about designing solutions for disaster recovery, see Designing globally available services using Azure SQL Database.
Terminology and capabilities
Automatic asynchronous replication: You can only create a geo-secondary for an existing database. The geo-secondary can be created on any logical server, other than the server with the primary database. Once created, the geo-secondary replica is populated with the data of the primary database. This process is known as seeding. After a geo-secondary has been created and seeded, updates to the primary database are automatically and asynchronously replicated to the geo-secondary replica. Asynchronous replication means that transactions are committed on the primary database before they're replicated.
Readable geo-secondary replicas: An application can access a geo-secondary replica to execute read-only queries using the same or different security principals used for accessing the primary database. For more information, see Use read-only replicas to offload read-only query workloads.
Important
You can use geo-replication to create secondary replicas in the same region as the primary. You can use these secondaries to satisfy read scale-out scenarios in the same region. However, a secondary replica in the same region does not provide additional resilience to catastrophic failures or large scale outages, and therefore is not a suitable failover target for disaster recovery purposes. It also does not guarantee availability zone isolation. Use Business Critical or Premium service tiers zone redundant configuration or General Purpose service tier zone redundant configuration to achieve availability zone isolation.
Failover (no data loss): When a Failover (no data loss) is initiated, a full data synchronization step is completed before switching the roles of the primary and geo-secondary databases. This ensures there is no data loss. Duration of the failover depends on the size of the transaction log on the primary that needs to be synchronized to the geo-secondary. Failover is designed for the following scenarios:
- Perform DR drills in production when the data loss isn't acceptable
- Relocate the database to a different region
- Return the database to the primary region after the outage has been mitigated (known as failback).
Forced failover (potential data loss): Forced failover immediately switches the geo-secondary to the primary role without waiting for synchronization with the primary. Any transactions committed on the primary but not yet replicated to the secondary are lost. This operation is designed as a recovery method during outages when the primary isn't accessible, but database availability must be quickly restored. When the original primary is back online, it's automatically reconnected, reseeded using current data from the primary, and become the new geo-secondary.
Important
After either failover or forced failover, the connection endpoint for the new primary changes because the new primary is now located on a different logical server.
- Multiple readable geo-secondaries: Up to four geo-secondaries can be created for a primary. If there's only one secondary, and it fails, the application is exposed to higher risk until a new secondary is created. If multiple secondaries exist, the application remains protected even if one of the secondaries fails. Additional secondaries can also be used to scale out read-only workloads.
Tip
If you are using active geo-replication to build a globally distributed application and need to provide read-only access to data in more than four regions, you can create a secondary of a secondary (a process known as chaining) to create additional geo-replicas. Replication lag on chained geo-replicas might be higher than on geo-replicas connected directly to the primary. Setting up chained geo-replication topologies is only supported programmatically, and not from Azure portal.
Geo-replication of databases in an elastic pool: Each geo-secondary can be a single database or a database in an elastic pool. The elastic pool choice for each geo-secondary database is separate and doesn't depend on the configuration of any other replica in the topology (either primary or secondary). Each elastic pool is contained within a single logical server. Because database names on a logical server must be unique, multiple geo-secondaries of the same primary can never share an elastic pool.
User-controlled geo-failover and failback: A geo-secondary that has finished initial seeding can be explicitly switched to the primary role (failed over) at any time by the application or the user. During an outage where the primary is inaccessible, only forced failover can be used, which immediately promotes a geo-secondary to be the new primary. When the outage is mitigated, the system automatically makes the recovered primary a geo-secondary, and brings it up-to-date with the new primary. Due to the asynchronous nature of geo-replication, recent transactions might be lost during forced failovers if the primary fails before these transactions are replicated to a geo-secondary. When a primary with multiple geo-secondaries fails over, the system automatically reconfigures replication relationships and links the remaining geo-secondaries to the newly promoted primary, without requiring any user intervention. After the outage that caused the geo-failover is mitigated, it might be desirable to return the primary to its original region. To do that, perform a manual failover.
Standby replica: If your secondary replica is used only for disaster recovery (DR) and doesn't have any read or write workloads, you can designate the replica as standby to save on licensing costs.
Prepare for geo-failover
To ensure that your application can immediately access the new primary after geo-failover, validate that authentication and network access for your secondary server are properly configured. For details, see Configure and manage Azure SQL Database security for geo-restore or failover. Also validate that backup retention policy on the secondary database matches that of the primary. This setting isn't a part of the database and isn't replicated from the primary. By default, the geo-secondary is configured with a default PITR retention period of seven days. For more information, see Automated backups in Azure SQL Database.
Important
If your database is a member of a failover group, you cannot initiate its failover using the geo-replication failover command. Use the failover command for the group. If you need to failover an individual database, you must remove it from the failover group first. See Failover groups overview & best practices (Azure SQL Database) for details.
Configure geo-secondary
Both the primary and geo-secondary are required to have the same service tier. It's also strongly recommended that the geo-secondary is configured with the same backup storage redundancy, compute tier (provisioned or serverless) and compute size (DTUs or vCores) as the primary. If the primary is experiencing a heavy write workload, a geo-secondary with a lower compute size might not be able to keep up. That causes replication lag on the geo-secondary, and might eventually cause unavailability of the geo-secondary. To mitigate these risks, active geo-replication reduces (throttles) the primary's transaction log rate if necessary to allow its secondaries to catch up.
Another consequence of an imbalanced geo-secondary configuration is that after failover, application performance can suffer due to insufficient compute capacity of the new primary. In that case, it's necessary to scale up the database to have sufficient resources, which might take significant time, and requires a high availability failover at the end of the scale up process, which can interrupt application workloads.
If you decide to create the geo-secondary with a different configuration, you should monitor log I/O rate on the primary over time. This lets you estimate the minimal compute size of the geo-secondary required to sustain the replication load. For example, if your primary database is P6 (1000 DTU) and its log I/O is sustained at 50%, the geo-secondary needs to be at least P4 (500 DTU). To retrieve historical log I/O data, use the sys.resource_stats view. To retrieve recent log I/O data with higher granularity that better reflects short-term spikes, use the sys.dm_db_resource_stats view.
Tip
Transaction log I/O throttling can occur in the following scenarios:
- If the geo-secondary is at a lower compute size than the primary. Look for the
HADR_THROTTLE_LOG_RATE_MISMATCHED_SLOwait type in sys.dm_exec_requests and sys.dm_os_wait_stats database views. - Throttling can also occur for reasons unrelated to compute size, for example in heavy workloads for bulk insert,
SELECT INTO, and index builds. For more information on wait types for different kinds of log I/O throttling, see Transaction log rate governance.
By default, backup storage redundancy of the geo-secondary is same as for the primary database. You can choose to configure a geo-secondary with a different backup storage redundancy. Backups are always taken on the primary database. If the secondary is configured with a different backup storage redundancy, then after a geo-failover, when the geo-secondary is promoted to the primary, new backups will be stored and billed according to the type of storage (RA-GRS, ZRS, LRS) selected on the new primary (previous secondary).
Save on costs with the standby replica
If your secondary replica is used only for disaster recovery (DR) and doesn't have any read or write workloads, you can save on licensing costs by designating the database for standby when you configure a new active geo-replication relationship.
Review license-free standby replica to learn more.
Cross-subscription geo-replication
You can use the Azure portal to set up Active geo replication across subscriptions as long as both the subscriptions are in the same Microsoft Entra tenant.
- To create a geo-secondary replica in a subscription different from the subscription of the primary in a different Microsoft Entra tenant, use SQL authentication and T-SQL. Microsoft Entra authentication for Azure SQL for cross-subscription geo-replication is not supported when a logical server is in a different Azure tenant
- Cross-subscription geo-replication operations including setup and geo-failover are also supported using Databases Create or Update REST API.
Creating a cross-subscription geo-secondary on a logical server in the same or different Microsoft Entra tenant is not supported when Microsoft Entra-only authentication with Azure SQL is enabled on either primary or secondary logical server and the creation is attempted using a Microsoft Entra ID user.
For methods and step-by-step instructions, see Tutorial: Configure active geo-replication and failover (Azure SQL Database).
Private endpoints
Adding a geo-secondary using T-SQL is not supported when connecting to the primary server over a private endpoint.
If a private endpoint is configured but public network access is allowed, adding a geo-secondary is supported when connected to the primary server from a public IP address.
Once a geo-secondary is added, public network access can be denied.
Keep credentials and firewall rules in sync
When using public network access for connecting to the database, we recommend using database-level IP firewall rules for geo-replicated databases. These rules are replicated with the database, which ensures that all geo-secondaries have the same IP firewall rules as the primary. This approach eliminates the need for customers to manually configure and maintain firewall rules on servers hosting the primary and secondary databases. Similarly, using contained database users for data access ensures both primary and secondary databases always have the same authentication credentials. This way, after a geo-failover, there are no disruptions due to authentication credential mismatches. If you're using logins and users (rather than contained users), you must take extra steps to ensure that the same logins exist for your secondary database. For configuration details, see Configure and manage Azure SQL Database security for geo-restore or failover.
Scale primary database
You can scale up or scale down the primary database to a different compute size (within the same service tier) without disconnecting any geo-secondaries. When scaling up, we recommend that you scale up the geo-secondary first, and then scale up the primary. When scaling down, reverse the order: scale down the primary first, and then scale down the secondary.
For information about failover groups, review scale a replica in a failover group.
Prevent loss of critical data
Due to the high latency of wide area networks, geo-replication uses an asynchronous replication mechanism. Asynchronous replication makes the possibility of data loss unavoidable if the primary fails. To protect critical transactions from data loss, an application developer can call the sp_wait_for_database_copy_sync stored procedure immediately after committing the transaction. Calling sp_wait_for_database_copy_sync blocks the calling thread until the last committed transaction has been transmitted and hardened in the transaction log of the secondary database. It also waits for the transmitted transactions to be replayed (redone) on the secondary. The sp_wait_for_database_copy_sync system stored procedure is scoped to a specific geo-replication link. Any user with the connection rights to the primary database can call this procedure.
Note
sp_wait_for_database_copy_sync prevents data loss after geo-failover for specific transactions, but does not guarantee full synchronization for read access. The delay caused by a sp_wait_for_database_copy_sync procedure call can be significant and depends on the size of the not yet transmitted transaction log on the primary at the time of the call.
Monitor geo-replication lag
To monitor lag with respect to RPO, use the replication_lag_sec column of sys.dm_geo_replication_link_status on the primary database. It shows lag in seconds between the transactions committed on the primary, and hardened to the transaction log on the secondary. For example, if the lag is one second, it means that if the primary is affected by an outage at this moment and a geo-failover is initiated, transactions committed in the last second will be lost.
To measure lag with respect to changes on the primary database that have been hardened on the geo-secondary, compare last_commit time on the geo-secondary with the same value on the primary.
Tip
If replication_lag_sec on the primary is NULL, it means that the primary does not currently know how far behind a geo-secondary is. This typically happens after process restarts and should be a transient condition. Consider sending an alert if replication_lag_sec returns NULL for an extended period of time. It might indicate that the geo-secondary cannot communicate with the primary due to a connectivity failure.
There are also conditions that could cause the difference between last_commit time on the geo-secondary and on the primary to become large. For example, if a commit is made on the primary after a long period of no changes, the difference will jump up to a large value before quickly returning to zero. Consider sending an alert if the difference between these two values remains large for a long time.
Programmatically manage active geo-replication
Active geo-replication can also be managed programmatically using T-SQL, Azure PowerShell, and REST API. The following tables describe the set of commands available. Active geo-replication includes a set of Azure Resource Manager APIs for management, including the Azure SQL Database REST API and Azure PowerShell cmdlets. These APIs support Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC). For more information on how to implement access roles, see Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC).
Important
These T-SQL commands only apply to active geo-replication and do not apply to failover groups.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| ALTER DATABASE | Use ADD SECONDARY ON SERVER argument to create a secondary database for an existing database and starts data replication |
| ALTER DATABASE | Use FAILOVER or FORCE_FAILOVER_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS to switch a secondary database to be primary to initiate failover |
| ALTER DATABASE | Use REMOVE SECONDARY ON SERVER to terminate a data replication between a SQL Database and the specified secondary database. |
| sys.geo_replication_links | Returns information about all existing replication links for each database on a server. |
| sys.dm_geo_replication_link_status | Gets the last replication time, last replication lag, and other information about the replication link for a given database. |
| sys.dm_operation_status | Shows the status for all database operations including changes to replication links. |
| sys.sp_wait_for_database_copy_sync | Causes the application to wait until all committed transactions are hardened to the transaction log of a geo-secondary. |
Related content
Configure active geo-replication:
Other business continuity content: