Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
Azure SQL Managed Instance
This article teaches you how to monitor backup activity for Azure SQL Managed Instance by either querying the msdb database or by configuring extended event (XEvent) sessions.
Overview
Azure SQL Managed Instance stores backup information in the msdb database and also emits events (also known as Extended Events or XEvents) during backup activity, which can be used for reporting. Configure an XEvent session to track information such as backup status, backup type, size, time, and location within the msdb database. This information can be integrated with backup monitoring software and also used for Enterprise Audit.
Enterprise Audits might require proof of successful backups, time of backup, and duration of the backup.
Query msdb database
To view backup activity, run the following query from user-defined database:
SELECT TOP (100)
DB_NAME(DB_ID(bs.database_name)) AS [Database Name],
CONVERT (BIGINT, bs.backup_size / 1048576) AS [Uncompressed Backup Size (MB)],
CONVERT (BIGINT, bs.compressed_backup_size / 1048576) AS [Compressed Backup Size (MB)],
CONVERT (NUMERIC (20, 2),
CASE
WHEN bs.compressed_backup_size > 0
THEN CONVERT (FLOAT, bs.backup_size) / CONVERT (FLOAT, bs.compressed_backup_size)
ELSE NULL
END
) AS [Compression Ratio],
bs.is_copy_only,
-- bs.user_name, -- Applicable only for user-initiated COPY ONLY backups.
bs.has_backup_checksums,
DATEDIFF(SECOND, bs.backup_start_date, bs.backup_finish_date) AS [Backup Elapsed Time (sec)],
bs.backup_finish_date AS [Backup Finish Date],
bmf.physical_block_size
FROM msdb.dbo.backupset AS bs WITH (NOLOCK)
INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.backupmediafamily AS bmf WITH (NOLOCK)
ON bs.media_set_id = bmf.media_set_id
WHERE bs.[type] = 'D'
-- AND bs.[is_copy_only] = 1 -- If you want to filter out for user initiated COPY ONLY backups.
ORDER BY bs.backup_finish_date DESC
OPTION (RECOMPILE); -- Optimize for ad hoc execution
Note
When querying msdb system tables such as dbo.backupmediaset or dbo.backupset, you see encryption-related fields indicating that backup files aren't encrypted. This status reflects only engine-level encryption. All automatic backups are encrypted at rest.
Configure XEvent session
Use the extended event backup_restore_progress_trace to record the progress of your SQL Managed Instance back up. Modify the XEvent sessions as needed to track the information you're interested in for your business. These T-SQL snippets store the XEvent sessions in the ring buffer, but it's also possible to write to Azure Blob Storage. XEvent sessions storing data in the ring buffer have a limit of about 1,000 messages so should only be used to track recent activity. Additionally, ring buffer data is lost upon failover. As such, for a historical record of backups, write to an event file instead.
Basic tracking
Configure a basic XEvent session to capture events about complete full backups. This script collects the name of the database, the total number of bytes processed, and the time the backup completed.
Use Transact-SQL (T-SQL) to configure the basic XEvent session:
CREATE EVENT SESSION [Basic backup trace] ON SERVER
ADD EVENT sqlserver.backup_restore_progress_trace
(
WHERE operation_type = 0
AND trace_message LIKE '%100 percent%'
)
ADD TARGET package0.ring_buffer WITH (STARTUP_STATE = ON);
GO
ALTER EVENT SESSION [Basic backup trace] ON SERVER
STATE = start;
Verbose tracking
Configure a verbose XEvent session to track greater details about your backup activity. This script captures start and finish of both full, differential and log backups. Since this script is more verbose, it fills up the ring buffer faster, so entries might recycle faster than with the basic script.
Use T-SQL to configure the verbose XEvent session:
CREATE EVENT SESSION [Verbose backup trace] ON SERVER
ADD EVENT sqlserver.backup_restore_progress_trace(
WHERE (
[operation_type]=(0) AND (
[trace_message] like '%100 percent%' OR
[trace_message] like '%BACKUP DATABASE%' OR [trace_message] like '%BACKUP LOG%'))
)
ADD TARGET package0.ring_buffer
WITH (MAX_MEMORY=4096 KB,EVENT_RETENTION_MODE=ALLOW_SINGLE_EVENT_LOSS,
MAX_DISPATCH_LATENCY=30 SECONDS,MAX_EVENT_SIZE=0 KB,MEMORY_PARTITION_MODE=NONE,
TRACK_CAUSALITY=OFF,STARTUP_STATE=ON)
ALTER EVENT SESSION [Verbose backup trace] ON SERVER
STATE = start;
Monitor backup progress
After the XEvent session is created, you can use T-SQL to query ring buffer results and monitor the progress of the backup. Once the XEvent starts, it collects all backup events so entries are added to the session roughly every 5-10 minutes.
Basic tracking
The following T-SQL code queries the basic XEvent session and returns the name of the database, the total number of bytes processed, and the time the backup completed:
WITH
a AS (SELECT CAST (xet.target_data AS XML) AS xed
FROM sys.dm_xe_session_targets AS xet
INNER JOIN sys.dm_xe_sessions AS xe
ON (xe.address = xet.event_session_address)
WHERE xe.name = 'Backup trace'),
b AS (SELECT d.n.value('(@timestamp)[1]', 'datetime2') AS [timestamp],
ISNULL(db.name, d.n.value('(data[@name="database_name"]/value)[1]', 'varchar(200)')) AS database_name,
d.n.value('(data[@name="trace_message"]/value)[1]', 'varchar(4000)') AS trace_message
FROM a
CROSS APPLY xed.nodes('/RingBufferTarget/event') AS d(n)
LEFT OUTER JOIN master.sys.databases AS db
ON db.physical_database_name = d.n.value('(data[@name="database_name"]/value)[1]', 'varchar(200)'))
SELECT * FROM b;
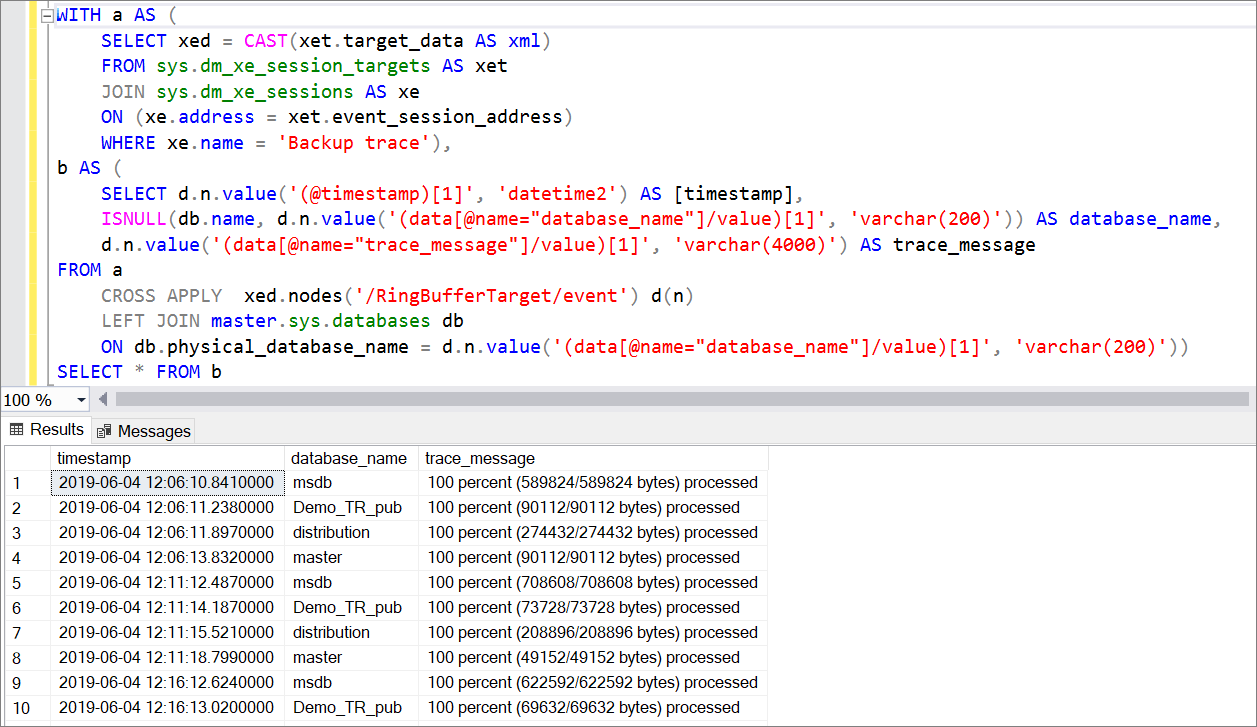
The following screenshot shows an example of the output of the previous query:
In this example, five databases were automatically backed up over the course of 2 hours and 30 minutes, and there are 130 entries in the XEvent session.
Verbose tracking
The following T-SQL code queries the verbose XEvent session and returns the name of the database, as well as the start and finish of both full, differential and log backups.
WITH
a AS (SELECT CAST (xet.target_data AS XML) AS xed
FROM sys.dm_xe_session_targets AS xet
INNER JOIN sys.dm_xe_sessions AS xe
ON (xe.address = xet.event_session_address)
WHERE xe.name = 'Verbose backup trace'),
b AS (SELECT d.n.value('(@timestamp)[1]', 'datetime2') AS [timestamp],
ISNULL(db.name, d.n.value('(data[@name="database_name"]/value)[1]', 'varchar(200)')) AS database_name,
d.n.value('(data[@name="trace_message"]/value)[1]', 'varchar(4000)') AS trace_message
FROM a
CROSS APPLY xed.nodes('/RingBufferTarget/event') AS d(n)
LEFT OUTER JOIN master.sys.databases AS db
ON db.physical_database_name = d.n.value('(data[@name="database_name"]/value)[1]', 'varchar(200)'))
SELECT * FROM b;
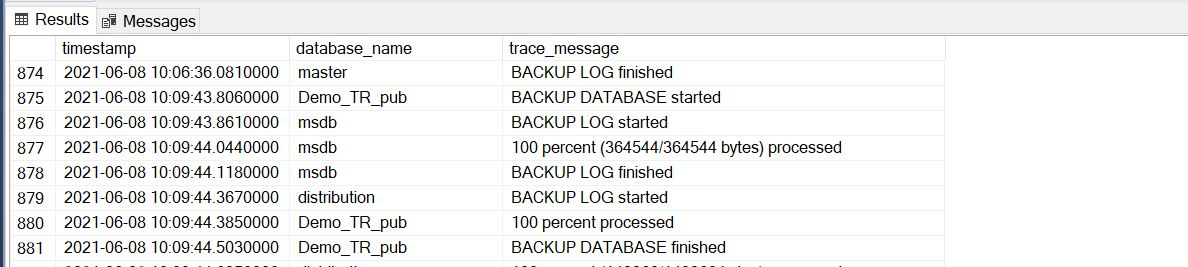
The following screenshot shows an example of a full backup in the XEvent session:
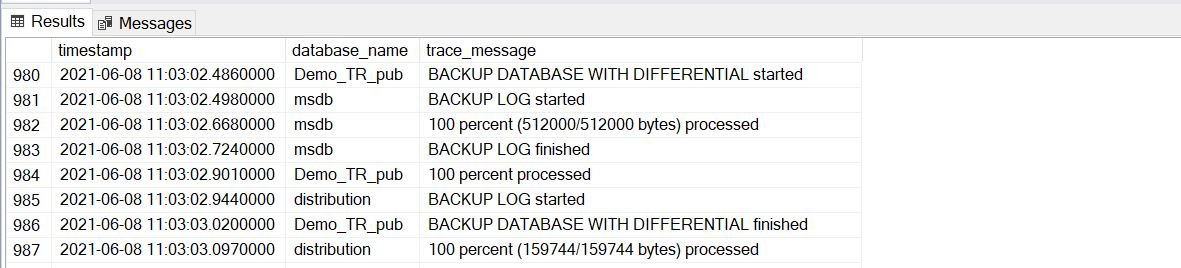
The following screenshot shows an example of an output of a differential backup in the XEvent session: