Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) backup is a simple, cloud-native process that you can use to back up and restore containerized applications and data that run in your AKS cluster. You can configure scheduled backups for cluster state and application data stored on Kubernetes Persistent Volumes in Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver-based Azure Disk Storage.
The solution gives you granular control. You can back up or restore a specific namespace or an entire cluster by storing backups locally in a blob container and as disk snapshots. You can use AKS backup for end-to-end scenarios, including operational recovery, cloning developer or test environments, and cluster upgrade scenarios.
AKS backup integrates with Backup center in Azure, to provide a single view that can help you govern, monitor, operate, and analyze backups at scale. Your backups are also available in the Azure portal under Settings on the service menu for an AKS instance.
How does AKS backup work?
You can use AKS backup to back up your AKS workloads and Persistent Volumes that are deployed in AKS clusters. The solution requires the Backup extension to be installed inside the AKS cluster. The Backup vault communicates to the extension to complete backup and restore operations. Using the Backup extension is mandatory. The extension must be installed inside the AKS cluster to enable backup and restore for the cluster. When you configure AKS backup, you add values for a storage account and a blob container where backups are stored.
Along with the Backup extension, a user identity (called an extension identity) is created in the AKS cluster's managed resource group. The extension identity is assigned the Storage Account Contributor role on the storage account in which backups are stored in a blob container.
To support public, private, and authorized IP-based clusters, AKS backup requires that you enable the Trusted Access feature between the AKS cluster and the Backup vault. Trusted Access allows the Backup vault to access the AKS cluster because specific permissions are assigned to it for backup operations. For more information on AKS Trusted Access, see Enable Azure resources to access AKS clusters by using Trusted Access.
AKS backup allows you to store backups in both the Operational Tier and the Vault Tier. The Operational Tier is a local datastore (backups are stored in your tenant as snapshots). You can now move one recovery point per day and store it in the Vault Tier as a blob (outside your tenant) by using AKS backup. Backups stored in the Vault Tier can also be used to restore data in a secondary region (Azure-paired region).
After you install the Backup extension and enable Trusted Access, you can configure scheduled backups for the clusters according to your backup policy. You can also restore the backups to the original cluster or to a different cluster in the same subscription and region. As you set up the specific operation, you can choose a specific namespace or an entire cluster as a backup and restore configuration.
AKS backup enables backup operations for your AKS data sources that are deployed in the cluster. It also enables backup operations for the data stored in the Persistent Volume for the cluster. It then stores the backups in a blob container. The disk-based Persistent Volumes are backed up as disk snapshots in a snapshot resource group. The snapshots and cluster state in a blob combine to form a recovery point called the Operational Tier stored in your tenant. You can also convert backups (the first successful backup in a day, week, month, or year) in the Operational Tier to blobs, and then move them to a vault (outside your tenant) one time per day.
Note
Currently, Azure Backup supports only Persistent Volumes in CSI driver-based Azure Disk Storage. During backups, the solution skips other Persistent Volume types, such as Azure Files share and blobs. Also, if you set defined retention rules for the Vault Tier, backups are only eligible to be moved to the vault if the Persistent Volumes are less than or equal to 1 TB.
Configure backup
To configure backups for AKS clusters, first create a Backup vault. The vault gives you a consolidated view of the backups that are configured across different data sources. AKS backup supports backups for both the Operational Tier and the Vault Tier.
The Backup vault storage redundancy setting (locally redundant storage or geo-redundant storage) only applies to backups that are stored in the Vault Tier. If you want to use backups for disaster recovery, set the storage redundancy as GRS with Cross Region Restore enabled.
Note
The Backup vault and the AKS cluster that you want to back up or restore must be in the same region and subscription.
AKS backup automatically triggers a scheduled backup job. The job copies the cluster resources to a blob container and creates an incremental snapshot of the disk-based Persistent Volumes according to the backup frequency. The backups are retained in the Operational Tier and the Vault Tier according to the retention duration defined in the backup policy. The backups are deleted when the duration is over.
You can use AKS backup to create multiple backup instances for a single AKS cluster by using different backup configurations per backup instance. However, we recommend that you create each backup instance of an AKS cluster in one of the following two ways:
- In a different Backup vault
- By using a separate backup policy in the same Backup vault
Manage backup
When the backup configuration for an AKS cluster is finished, a backup instance is created in the Backup vault. You can view the backup instance for the cluster in the Backup section for an AKS instance in the Azure portal. You can perform any backup-related operations for the instance, such as initiating restores, monitoring, stopping protection, and so on, through its corresponding backup instance.
AKS backup also integrates directly with Backup center to help you centrally manage protection for all your AKS clusters and other backup-supported workloads. Backup center provides a single view for all your backup requirements, such as monitoring jobs and the state of backups and restores. Backup center helps you ensure compliance and governance, analyze backup usage, and perform critical operations to back up and restore data.
AKS backup uses managed identity to access other Azure resources. To configure the backup of an AKS cluster and to restore from an earlier backup, the Backup vault's managed identity requires a set of permissions on the AKS cluster. It also requires a set of permissions on the snapshot resource group where snapshots are created and managed. Currently, the AKS cluster requires a set of permissions on the snapshot resource group.
Also, the Backup extension creates a user identity and assigns a set of permissions to access the storage account where backups are stored in a blob. You can grant permissions to the managed identity by using Azure role-based access control. A managed identity is a special type of service principle that can be used only with Azure resources. Learn more about managed identities.
Restore from a backup
You can restore data from any point in time for which a recovery point exists. A recovery point is created when a backup instance is in a protected state. It can be used to restore data until the backup policy retains the data.
Azure Backup gives you the option to restore all the items that are backed up or to use granular controls to select specific items from the backups by using namespaces and other filter options. Also, you can do the restore on the original AKS cluster (the backed-up cluster) or on an alternate AKS cluster. You can restore backups that are stored in the Operational Tier and the Vault Tier to a cluster in the same or a different subscription. Only backups stored in the Vault Tier can be used to do a restore to a cluster in a different region (Azure-paired region).
To restore a backup stored in the Vault Tier, you must provide a staging location where the backup data is hydrated. This staging location includes a resource group and a storage account within the same region and subscription as the target cluster for restore. During restore, specific resources (blob container, disk, and disk snapshots) are created as part of hydration. They're cleared after the restore operation is complete.
Azure Backup for AKS currently supports the following two options for a scenario in which a resource clash happens. A resource clash occurs when a backed-up resource has the same name as the resource in the target AKS cluster. You can choose one of these options when defining the restore configuration.
Skip: This option is selected by default. For example, if you back up a Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) named
pvc-azurediskand you restore it in a target cluster that has a PVC with the same name, the backup extension skips the restore of the backed-up PVC. In such scenarios, we recommend that you delete the resource from the cluster. Then, do the restore operation so that the backed-up items are only available in the cluster and aren't skipped.Patch: This option allows the patching mutable variable in the backed-up resource on the resource in the target cluster. If you want to update the number of replicas in the target cluster, you can opt for patching as an operation.
Note
AKS backup doesn't currently delete and re-create resources in the target cluster if they already exist. If you attempt to restore Persistent Volumes in the original location, delete the existing Persistent Volumes, and then do the restore operation.
Use custom hooks for backup and restore
You can use custom hooks to take application-consistent snapshots of volumes that are used for databases deployed as containerized workloads.
What are custom hooks?
You can use AKS backup to execute custom hooks as part of a backup and restore operation. Hooks are configured to run one or more commands to execute in a pod under a container during a backup operation or after restore.
You define these hooks as a custom resource and deploy them in the AKS cluster that you want to back up or restore. When the custom resource is deployed in the AKS cluster in the required namespace, you provide the details as input for the flow to configure backup and restore. The Backup extension runs the hooks as defined in a YAML file.
Note
Hooks aren't executed in a shell on the containers.
Backup in AKS has two types of hooks:
- Backup hooks
- Restore hooks
Backup hooks
When you use a backup hook, you can configure the commands to run the hook before any custom action processing (PreHooks). You can also run the hook after all custom actions are finished and any additional items specified by custom actions are backed up (PostHooks).
For example, here's the YAML template for a custom resource to be deployed by using backup hooks:
apiVersion: clusterbackup.dataprotection.microsoft.com/v1alpha1
kind: BackupHook
metadata:
# BackupHook CR Name and Namespace
name: bkphookname0
namespace: default
spec:
# BackupHook is a list of hooks to execute before and after backing up a resource.
backupHook:
# BackupHook Name. This is the name of the hook that will be executed during backup.
# compulsory
- name: hook1
# Namespaces where this hook will be executed.
includedNamespaces:
- hrweb
excludedNamespaces:
labelSelector:
# PreHooks is a list of BackupResourceHooks to execute prior to backing up an item.
preHooks:
- exec:
# Container is the container in the pod where the command should be executed.
container: webcontainer
# Command is the command and arguments to execute.
command:
- /bin/uname
- -a
# OnError specifies how Velero should behave if it encounters an error executing this hook
onError: Continue
# Timeout is the amount of time to wait for the hook to complete before considering it failed.
timeout: 10s
- exec:
command:
- /bin/bash
- -c
- echo hello > hello.txt && echo goodbye > goodbye.txt
container: webcontainer
onError: Continue
# PostHooks is a list of BackupResourceHooks to execute after backing up an item.
postHooks:
- exec:
container: webcontainer
command:
- /bin/uname
- -a
onError: Continue
timeout: 10s
Restore hooks
In the restore hook script, custom commands or scripts are written to be executed in the containers of a restored AKS pod.
Here's the YAML template for a custom resource that's deployed via restore hooks:
apiVersion: clusterbackup.dataprotection.microsoft.com/v1alpha1
kind: RestoreHook
metadata:
name: restorehookname0
namespace: default
spec:
# RestoreHook is a list of hooks to execute after restoring a resource.
restoreHook:
# Name is the name of this hook.
- name: myhook-1
# Restored Namespaces where this hook will be executed.
includedNamespaces:
excludedNamespaces:
labelSelector:
# PostHooks is a list of RestoreResourceHooks to execute during and after restoring a resource.
postHooks:
- exec:
# Container is the container in the pod where the command should be executed.
container: webcontainer
# Command is the command and arguments to execute from within a container after a pod has been restored.
command:
- /bin/bash
- -c
- echo hello > hello.txt && echo goodbye > goodbye.txt
# OnError specifies how Velero should behave if it encounters an error executing this hook
# default value is Continue
onError: Continue
# Timeout is the amount of time to wait for the hook to complete before considering it failed.
execTimeout: 30s
# WaitTimeout defines the maximum amount of time Velero should wait for the container to be ready before attempting to run the command.
waitTimeout: 5m
Learn how to use hooks during AKS backup.
During restore, the backup extension waits for the container to come up and then executes exec commands on them, defined in the restore hooks.
If you're performing restore to the same namespace that was backed up, the restore hook isn't executed. It only looks for a newly spawned container. This result occurs regardless of whether you use the skip or patch policy.
Modify resource while restoring backups to AKS cluster
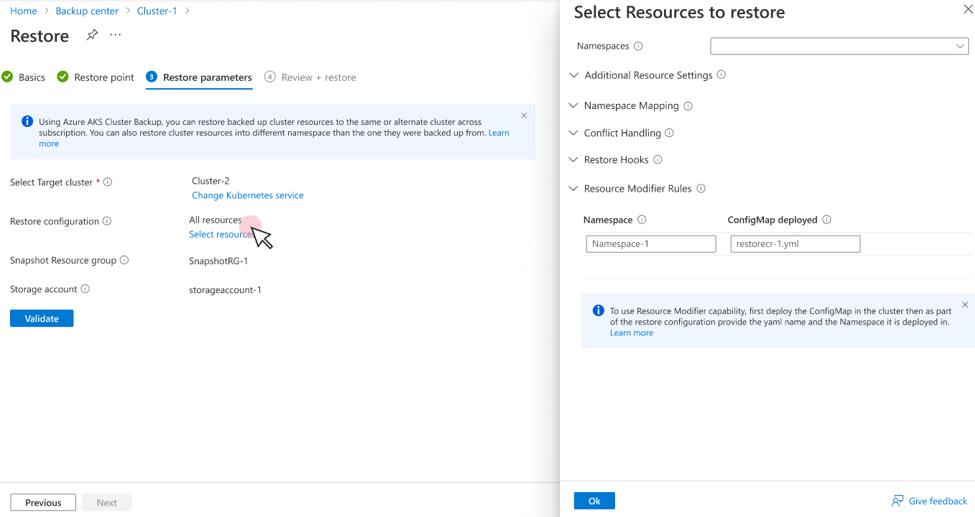
You can use the Resource Modification feature to modify backed-up Kubernetes resources during restore by specifying JSON patches as configmap deployed in the AKS cluster.
Create and apply a resource modifier configmap during restore
To create and apply resource modification, follow these steps:
Create a resource modifier
configmap.You need to create one
configmapin your preferred namespace from a YAML file that defined resource modifiers.Example for creating a command:
version: v1 resourceModifierRules: - conditions: groupResource: persistentvolumeclaims resourceNameRegex: "^mysql.*$" namespaces: - bar - foo labelSelector: matchLabels: foo: bar patches: - operation: replace path: "/spec/storageClassName" value: "premium" - operation: remove path: "/metadata/labels/test"- The previous
configmapapplies the JSON patch to all the Persistent Volume copies in thenamespacesbar andfoowith a name that starts withmysqlandmatch label foo: bar. The JSON patch replaces thestorageClassNamewithpremiumand removes the labeltestfrom the Persistent Volume copies. - Here, the
namespaceis the original namespace of the backed-up resource, and not the new namespace to which the resource is going to be restored. - You can specify multiple JSON patches for a particular resource. The patches are applied according to the order specified in the
configmap. The next patch is applied in order. If multiple patches are specified for the same path, the last patch overrides the previous patches. - You can specify multiple
resourceModifierRulesin theconfigmap. The rules are applied according to the order specified in theconfigmap.
- The previous
Create a resource modifier reference in the restore configuration
When you perform a restore operation, provide the
ConfigMap nameand thenamespacewhere it deploys as part of restore configuration. These details need to be provided under Resource Modifier Rules.
Operations supported by Resource Modifier
Add
You can use the Add operation to add a new block to the resource JSON. In the following example, the operation adds new container details to the specification with a deployment.
version: v1 resourceModifierRules: - conditions: groupResource: deployments.apps resourceNameRegex: "^test-.*$" namespaces: - bar - foo patches: # Dealing with complex values by escaping the yaml - operation: add path: "/spec/template/spec/containers/0" value: "{\"name\": \"nginx\", \"image\": \"nginx:1.14.2\", \"ports\": [{\"containerPort\": 80}]}"Remove
You can use the Remove operation to remove a key from the resource JSON. In the following example, the operation removes the label with
testas key.version: v1 resourceModifierRules: - conditions: groupResource: persistentvolumeclaims resourceNameRegex: "^mysql.*$" namespaces: - bar - foo labelSelector: matchLabels: foo: bar patches: - operation: remove path: "/metadata/labels/test"Replace
You can use the Replace operation to replace a value for the path mentioned to an alternate one. In the following example, the operation replaces the
storageClassNamein the PVC withpremium.version: v1 resourceModifierRules: - conditions: groupResource: persistentvolumeclaims resourceNameRegex: "^mysql.*$" namespaces: - bar - foo labelSelector: matchLabels: foo: bar patches: - operation: replace path: "/spec/storageClassName" value: "premium"Copy
You can use the Copy operation to copy a value from one path from the resources defined to another path.
version: v1 resourceModifierRules: - conditions: groupResource: deployments.apps resourceNameRegex: "^test-.*$" namespaces: - bar - foo patches: - operation: copy from: "/spec/template/spec/containers/0" path: "/spec/template/spec/containers/1"Test
You can use the Test operation to check if a particular value is present in the resource. If the value is present, the patch is applied. If the value isn't present, the patch isn't applied. In the following example, the operation checks whether the PVCs have
premiumasStorageClassNameand replaces it withstandard, if true.version: v1 resourceModifierRules: - conditions: groupResource: persistentvolumeclaims resourceNameRegex: ".*" namespaces: - bar - foo patches: - operation: test path: "/spec/storageClassName" value: "premium" - operation: replace path: "/spec/storageClassName" value: "standard"JSON patch
This
configmapapplies the JSON patch to all the deployments in the namespaces by default andnginxwith the name that starts withnginxdep. The JSON patch updates the replica count to12for all such deployments.version: v1 resourceModifierRules: - conditions: groupResource: deployments.apps resourceNameRegex: "^nginxdep.*$" namespaces: - default - nginx patches: - operation: replace path: "/spec/replicas" value: "12"JSON merge patch
This
configmapapplies the JSON merge patch to all the deployments in the namespaces default andnginxwith the name that starts withnginxdep. The JSON merge patch will add or update the labelappwith the valuenginx1.version: v1 resourceModifierRules: - conditions: groupResource: deployments.apps resourceNameRegex: "^nginxdep.*$" namespaces: - default - nginx mergePatches: - patchData: | { "metadata" : { "labels" : { "app" : "nginx1" } } }Strategic merge patch
This
configmapapplies the strategic merge patch to all the pods in the namespace default with the name starting withnginx. The strategic merge patch updates the image of containernginxtomcr.microsoft.com/cbl-mariner/base/nginx:1.22.version: v1 resourceModifierRules: - conditions: groupResource: pods resourceNameRegex: "^nginx.*$" namespaces: - default strategicPatches: - patchData: | { "spec": { "containers": [ { "name": "nginx", "image": "mcr.microsoft.com/cbl-mariner/base/nginx:1.22" } ] } }
Which backup storage tier does AKS backup support?
Azure Backup for AKS supports two storage tiers as backup datastores:
Operational Tier: The Backup extension installed in the AKS cluster first takes the backup by taking volume snapshots via CSI driver. It then stores cluster state in a blob container in your own tenant. This tier supports a lower recovery point objective (RPO) with the minimum duration of four hours between two backups. Additionally, for Azure disk-based volumes, the Operational Tier supports quicker restores.
Vault Tier: To store backup data for a longer duration at a lower cost than snapshots, AKS backup supports vault-standard datastores. According to the retention rules set in the backup policy, the first successful backup (of a day, week, month, or year) is moved to a blob container outside your tenant. This datastore not only allows longer retention, but also provides ransomware protection. You can also move backups stored in the vault to another region (Azure-paired region) for recovery by enabling Geo-redundancy and Cross Region Restore in the Backup vault.
Note
You can store the backup data in a vault-standard datastore via Backup Policy by defining retention rules. Only one scheduled recovery point per day is moved to the Vault Tier. However, you can move any number of on-demand backups to the vault according to the rule selected.
Understand pricing
You incur charges for:
Protected instance fee: Azure Backup for AKS charges a protected instance fee per namespace per month. When you configure backup for an AKS cluster, a protected instance is created. Each instance has a specific number of namespaces that are backed up as defined in the backup configuration. For more information on the AKS backup pricing, see Pricing for Azure backup and select Azure Kubernetes Service as the workload.
Snapshot fee: Azure Backup for AKS protects a disk-based Persistent Volume by taking snapshots that are stored in the resource group in your Azure subscription. These snapshots incur snapshot storage charges. Because the snapshots aren't copied to the Backup vault, backup storage costs don't apply. For more information on snapshot pricing, see Managed Disks pricing.
Backup storage fee: Azure Backup for AKS also supports storing backups in the Vault Tier. You can store backups in the Vault Tier by defining retention rules for vault standard in the backup policy, with one restore point per day eligible to be moved into the vault. Restore points stored in the Vault Tier are charged a separate fee (called a Backup storage fee) according to the total data stored (in gigabytes) and redundancy type enable on the Backup vault.