Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes how to configure and back up Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) using Azure portal. You can also backup AKS using Azure PowerShell.
You can use Azure Backup to back up AKS clusters (cluster resources and persistent volumes attached to the cluster) by using the Backup extension, which must be installed in the cluster. The Backup vault communicates with the cluster via the Backup extension to perform backup and restore operations.
Prerequisites
Things to ensure before you configure backup for AKS cluster:
Currently, AKS Backup supports only Azure Disk Storage-based persistent volumes enabled by CSI driver. Backup data can be stored as snapshots in Operational Tier or can also be moved to Vault Tier for long term storage along with snapshots. The Backup vault and AKS cluster can be in different subscriptions within same tenant and region.
AKS Backup uses a blob container and a resource group to store the backups. The blob container holds the AKS cluster resources. Persistent volume snapshots are stored in the resource group. The AKS cluster and the storage locations must be in the same region. Learn how to create a blob container.
Currently, AKS Backup supports once-a-day backups. It also supports more frequent backups (in 4-hour, 8-hour, and 12-hour intervals) per day. This solution allows you to retain your data for restore for up to 360 days. Learn how to create a backup policy.
You need to install the Backup extension to configure backup and restore operations for an AKS cluster. Learn more about the Backup extension.
Make sure you have
Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration,Microsoft.DataProtection, andMicrosoft.ContainerServiceregistered for your subscription before you initiate backup configuration and restore operations.Make sure you complete all prerequisites before you initiate a backup or restore operation for AKS Backup.
For more information on supported scenarios, limitations, and availability, see the support matrix.
Create a Backup vault
A Backup vault is a management entity that stores recovery points treated over time. A Backup vault also provides an interface to do the backup operations. Operations include taking on-demand backups, doing restores, and creating backup policies. AKS Backup requires the Backup Vault and the AKS cluster to be located in the same region. However, they can reside in different subscriptions as long as they are within the same tenant. Learn how to create a Backup vault.
Note
A Backup vault is a new resource that's used to back up newly supported datasources. A Backup vault is different from a Recovery Services vault.
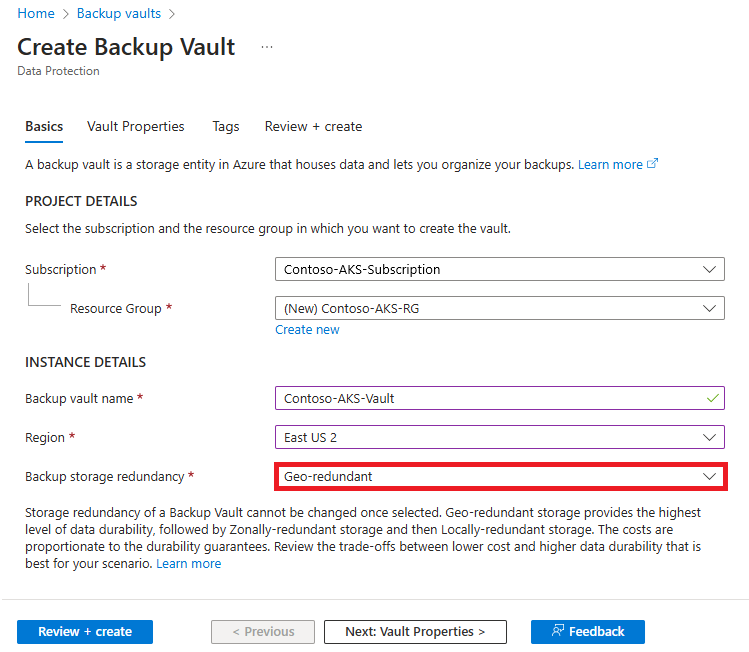
If you want to use Azure Backup to protect your AKS clusters from any regional outage, you can enable Cross Region Restore. To enable Cross Region Restore, you need to:
Set the Backup Storage Redundancy parameter as Geo-Redundant during vault creation. Once the redundancy for a vault is set, you can't disable it.
Set the Cross Region Restore parameter under Vault Properties as Enabled. Once this parameter is enabled, you can't disable it.
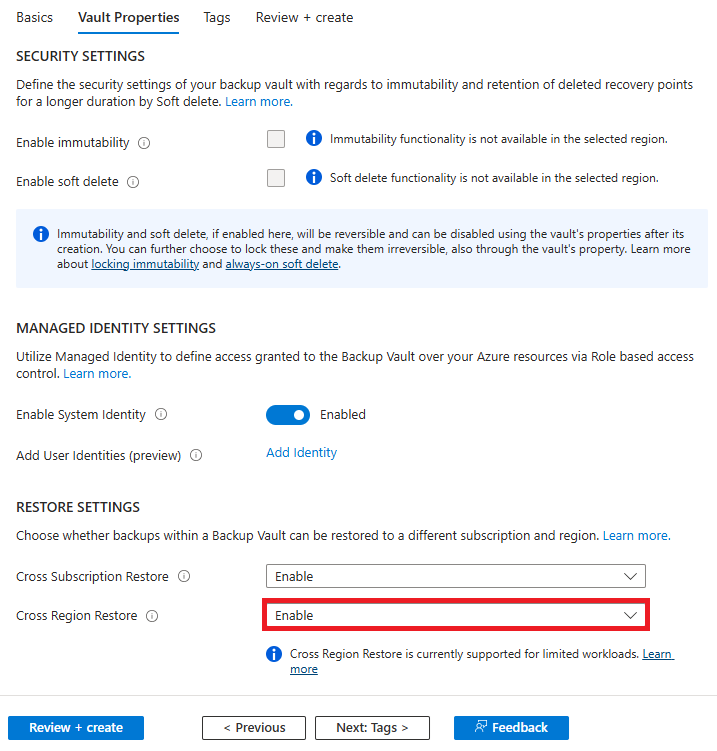
Create a Backup Instance using a Backup Policy with retention duration set for Vault-standard datastore. Every recovery point stored in this datastore will be in the secondary region.
Create a Backup policy
Before you configure backups, you need to create a Backup policy that defines the frequency of backups and the retention duration of backups.
To create a backup policy:
Go to the Backup vault that you created, and select Manage > Backup policies > Add.
Enter a name for the backup policy.
For Datasource type, select Kubernetes Services.
On the Schedule + retention tab, define the backup schedule.
- Backup Frequency: Select the backup frequency (hourly or daily), and then choose the retention duration for the backups.
- Retention Setting: A new backup policy has the Default rule defined by default. You can edit this rule and can’t delete it. The default rule defines the retention duration for all the operational tier backups taken. You can also create additional retention rules to store backups for a longer duration that are taken daily or weekly.
Note
- In addition to first successful backup of the day, you can define the retention rules for first successful backup of the week, month, and year. In terms of priority, the order is year, month, week, and day.
- You can copy backups in the secondary region (Azure Paired region) stored in the Vault Tier, which you can use to restore AKS clusters to a secondary region when the primary region is unavailable. To opt for this feature, use a Geo-redundant vault with Cross Region Restore enabled.
When the backup frequency and retention settings are configured, select Next.
On the Review + create tab, review the information, and then select Create.
Install Backup extension and configure backup
You can use AKS Backup to back up an entire cluster or specific cluster resources that are deployed in the cluster. You can also protect a cluster multiple times per the deployed application's schedule and retention requirements or security requirements.
Note
To set up multiple backup instances for the same AKS cluster:
- Configure backup in the same Backup vault but using a different backup policy.
- Configure backup in a different Backup vault.
Install the Backup extension
To configure backups for an AKS cluster:
In the Azure portal, go to the AKS cluster that you want to back up.
From the service menu, under Settings, select Backup.
To prepare the AKS cluster for backup or restore, select Install Extension to install the Backup extension in the cluster.
Provide a storage account and blob container as input.
Your AKS cluster backups are stored in this blob container. The storage account must be in the same region and subscription as the cluster.
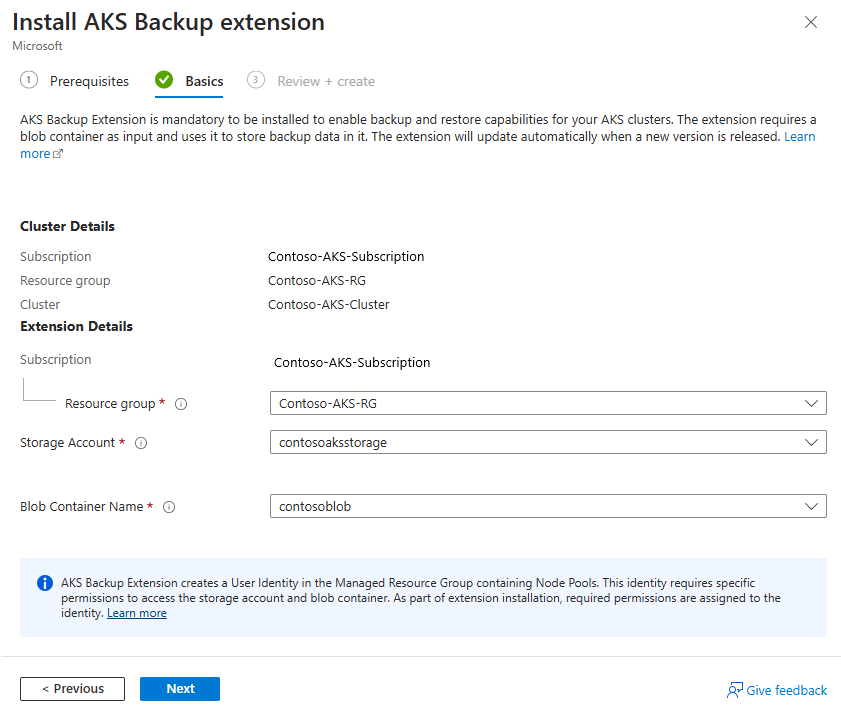
Select Next. Review the extension installation details, and then select Create.
The extension installation begins.
Configure backup
When the Backup extension is installed successfully, select Configure backup.
Select the Backup vault that you created earlier. The Backup vault should have Trusted Access enabled for the AKS cluster to be backed up. To enable Trusted Access, select Grant Permission. If it's already enabled, select Next.
On the Backup policy tab, select the backup policy, which defines the schedule for backups and their retention period, and then select Next.
On the Datasources tab, select Add/Edit to define the backup instance configuration.
On the Select Resources to Backup pane, define the cluster resources that you want to back up.
Learn more about backup configurations.
For Snapshot resource group, select the resource group to use to store the persistent volume (Azure Disk Storage) snapshots, and then select Validate.
When validation is finished, if required roles aren't assigned to the vault in the snapshot resource group, an error appears:
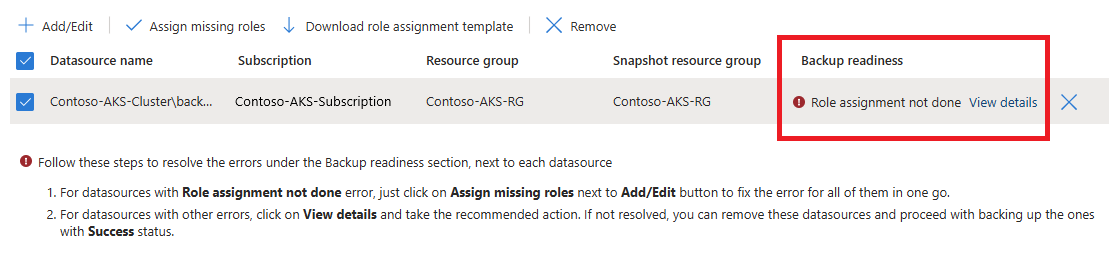
To resolve the error, under Datasource name, select the checkbox for the datasource, and then select Assign missing roles.
When the role assignment completes, select Next > Configure backup.
Backup configurations
Azure Backup for AKS allows you to define the application boundary within AKS cluster that you want to back up. You can use the filters that are available within backup configurations to choose the resources to back up and also to run custom hooks. The defined backup configuration is referenced by the value for Backup Instance Name. The below filters are available to define your application boundary:
Select Select Namespaces to backup. You can either select All to back up all existing and future namespaces in the cluster, or you can select specific namespaces for backup.
The following namespaces are skipped from Backup configurations:
kube-system,kube-node-lease, andkube-public.Expand Additional Resource Settings to see filters that you can use to choose cluster resources to back up. You can choose to back up resources based on the following categories:
Labels: You can filter AKS resources by using labels that you assign to types of resources. Enter labels in the form of key/value pairs. You can combine multiple labels using
ANDlogic. For example, if you enter the labelsenv=prod;tier!=web, the process selects resources that have a label with theenvkey and theprodvalue, and a label with thetierkey for which the value isn'tweb.API groups: You can also include resources by providing the AKS API group and kind. For example, you can choose for backup AKS resources like Deployments. You can access the list of Kubernetes defined API Groups here.
Other options: You can enable or disable backup for cluster-scoped resources, persistent volumes, and secrets. Cluster-scoped resources and persistent volumes are enabled by default.
Note
You should add the labels to every single YAML file that is deployed and to be backed up. This includes namespace-scoped resources like persistent volume claims, and cluster-scoped resources like persistent volumes.
If you want to exclude specific Persistent Volume Claims from your backups, add the annotation velero.io/exclude-from-backup=true. This Velero annotation is supported by Azure Backup for AKS.
Use hooks during AKS Backup
This section describes how to use a backup hook to create an application-consistent snapshot of the AKS cluster with MySQL deployed (a persistent volume that contains the MySQL instance).
You can use custom hooks in AKS backup to accomplish application-consistent snapshots of volumes. The volumes are used for databases that are deployed as containerized workloads.
By using a backup hook, you can define the commands to freeze and unfreeze a MySQL pod so that an application snapshot of the volume can be taken. The Backup extension then orchestrates the steps of running the commands in the hooks and takes the volume snapshot.
An application-consistent snapshot of a volume with MySQL deployed is taken by doing the following actions:
- The pod running MySQL is frozen so that no new transaction is performed on the database.
- A snapshot is taken of the volume as backup.
- The pod running MySQL is unfrozen so that transactions can be done again on the database.
To enable a backup hook as part of the backup configuration flow to back up MySQL:
Write the custom resource for backup hook with commands to freeze and unfreeze a PostgreSQL pod.
You can also use the following sample YAML script postgresbackuphook.yaml, which has predefined commands:
apiVersion: clusterbackup.dataprotection.microsoft.com/v1alpha1 kind: BackupHook metadata: # BackupHook CR Name and Namespace name: bkphookname0 namespace: default spec: # BackupHook Name. This is the name of the hook that will be executed during backup. # compulsory name: hook1 # Namespaces where this hook will be executed. includedNamespaces: - hrweb excludedNamespaces: labelSelector: # PreHooks is a list of BackupResourceHooks to execute prior to backing up an item. preHooks: - exec: command: - /sbin/fsfreeze - --freeze - /var/lib/postgresql/data container: webcontainer onError: Continue # PostHooks is a list of BackupResourceHooks to execute after backing up an item. postHooks: - exec: container: webcontainer command: - /sbin/fsfreeze - --unfreeze onError: Fail timeout: 10sBefore you configure a backup, you must deploy the backup hook custom resource in the AKS cluster.
To deploy the script, run the following command:
kubectl apply -f mysqlbackuphook.yamlWhen the deployment is finished, you can configure backups for the AKS cluster.
Note
As part of a backup configuration, you must provide the custom resource name and the namespace that the resource is deployed in as input.
Next steps
- Restore an Azure Kubernetes Service cluster using Azure portal, Azure PowerShell
- Manage Azure Kubernetes Service cluster backups
- About Azure Kubernetes Service cluster backup

