Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
An Azure Batch pool contains one or more compute nodes that execute user-specified workloads in the form of Batch tasks. To enable Batch functionality and Batch pool infrastructure management, compute nodes must communicate with the Azure Batch service.
Batch supports two types of communication modes:
- Classic: the Batch service initiates communication with the compute nodes.
- Simplified: the compute nodes initiate communication with the Batch service.
This article describes the simplified communication mode and the associated network configuration requirements.
Tip
Information in this document pertaining to networking resources and rules such as NSGs doesn't apply to Batch pools with no public IP addresses that use the node management private endpoint without internet outbound access.
Warning
The classic compute node communication mode will be retired on 31 March 2026 and replaced with the simplified communication mode described in this document.
Supported regions
Simplified compute node communication in Azure Batch is currently available for the following regions:
- Public: all public regions where Batch is present except for West India.
- Government: USGov Arizona, USGov Virginia, USGov Texas.
- China: all China regions where Batch is present except for China North 1 and China East 1.
Differences between classic and simplified modes
The simplified compute node communication mode streamlines the way Batch pool infrastructure is managed on behalf of users. This communication mode reduces the complexity and scope of inbound and outbound networking connections required in baseline operations.
Batch pools with the classic communication mode require the following networking rules in network security groups (NSGs), user-defined routes (UDRs), and firewalls when creating a pool in a virtual network:
Inbound:
- Destination ports
29876,29877over TCP fromBatchNodeManagement.<region>
- Destination ports
Outbound:
- Destination port
443over TCP toStorage.<region> - Destination port
443over TCP toBatchNodeManagement.<region>for certain workloads that require communication back to the Batch Service, such as Job Manager tasks
- Destination port
Batch pools with the simplified communication mode only need outbound access to Batch account's node management endpoint (see Batch account public endpoints). They require the following networking rules in NSGs, UDRs, and firewalls:
Inbound:
- None
Outbound:
- Destination port
443over ANY toBatchNodeManagement.<region>
- Destination port
Outbound requirements for a Batch account can be discovered using the List Outbound Network Dependencies Endpoints API. This API reports the base set of dependencies, depending upon the Batch account pool communication mode. User-specific workloads might need extra rules such as opening traffic to other Azure resources (such as Azure Storage for Application Packages, Azure Container Registry) or endpoints like the Microsoft package repository for virtual file system mounting functionality.
Benefits of simplified mode
Azure Batch users utilizing the simplified mode benefit from simplification of networking connections and rules. Simplified compute node communication helps reduce security risks by removing the requirement to open ports for inbound communication from the internet. Only a single outbound rule to a well-known Service Tag is required for baseline operation.
The simplified mode also provides more fine-grained data exfiltration control over the classic communication mode since outbound communication to Storage.<region> is no longer required. You can explicitly lock down outbound communication to Azure Storage if necessary for your workflow. For example, you can scope your outbound communication rules to Azure Storage to enable your AppPackage storage accounts or other storage accounts for resource files or output files.
Even if your workloads aren't currently impacted by the changes (as described in the following section), it's recommended to move to the simplified mode. Future improvements in the Batch service might only be functional with simplified compute node communication.
Potential impact between classic and simplified communication modes
In many cases, the simplified communication mode doesn't directly affect your Batch workloads. However, simplified compute node communication has an impact for the following cases:
- Users who specify a virtual network as part of creating a Batch pool and do one or both of the following actions:
- Explicitly disable outbound network traffic rules that are incompatible with simplified compute node communication.
- Use UDRs and firewall rules that are incompatible with simplified compute node communication.
- Users who enable software firewalls on compute nodes and explicitly disable outbound traffic in software firewall rules that are incompatible with simplified compute node communication.
If either of these cases applies to you, then follow the steps outlined in the next section to ensure that your Batch workloads can still function in simplified mode. It's strongly recommended that you test and verify all of your changes in a dev and test environment first before pushing your changes into production.
Required network configuration changes for simplified mode
The following steps are required to migrate to the new communication mode:
- Ensure your networking configuration as applicable to Batch pools (NSGs, UDRs, firewalls, etc.) includes a union of the modes, that is, the combined network rules of both classic and simplified modes. At a minimum, these rules would be:
- Inbound:
- Destination ports
29876,29877over TCP fromBatchNodeManagement.<region>
- Destination ports
- Outbound:
- Destination port
443over TCP toStorage.<region> - Destination port
443over ANY toBatchNodeManagement.<region>
- Destination port
- Inbound:
- If you have any other inbound or outbound scenarios required by your workflow, you need to ensure that your rules reflect these requirements.
- Use one of the following options to update your workloads to use the new communication mode.
- Create new pools with the
targetNodeCommunicationModeset to simplified and validate that the new pools are working correctly. Migrate your workload to the new pools and delete any earlier pools. - Update existing pools
targetNodeCommunicationModeproperty to simplified and then resize all existing pools to zero nodes and scale back out.
- Create new pools with the
- Use the Get Pool API, List Pool API, or the Azure portal to confirm the
currentNodeCommunicationModeis set to the desired communication mode of simplified. - Modify all applicable networking configuration to the simplified communication rules, at the minimum (note any extra rules needed as discussed above):
- Inbound:
- None
- Outbound:
- Destination port
443over ANY toBatchNodeManagement.<region>
- Destination port
- Inbound:
If you follow these steps, but later want to switch back to classic compute node communication, you need to take the following actions:
- Revert any networking configuration operating exclusively in simplified compute node communication mode.
- Create new pools or update existing pools
targetNodeCommunicationModeproperty set to classic. - Migrate your workload to these pools, or resize existing pools and scale back out (see step 3 above).
- See step 4 above to confirm that your pools are operating in classic communication mode.
- Optionally restore your networking configuration.
Specify the communication mode on a Batch pool
The targetNodeCommunicationMode property on Batch pools allows you to indicate a preference to the Batch service for which communication mode to utilize between the Batch service and compute nodes. The following are the allowable options on this property:
- Classic: creates the pool using classic compute node communication.
- Simplified: creates the pool using simplified compute node communication.
- Default: allows the Batch service to select the appropriate compute node communication mode. For pools without a virtual network, the pool may be created in either classic or simplified mode. For pools with a virtual network, the pool always defaults to classic until 30 September 2024. For more information, see the classic compute node communication mode migration guide.
Tip
Specifying the target node communication mode indicates a preference for the Batch service, but doesn't guarantee that it will be honored. Certain configurations on the pool might prevent the Batch service from honoring the specified target node communication mode, such as interaction with no public IP address, virtual networks, and the pool configuration type.
The following are examples of how to create a Batch pool with simplified compute node communication.
Azure portal
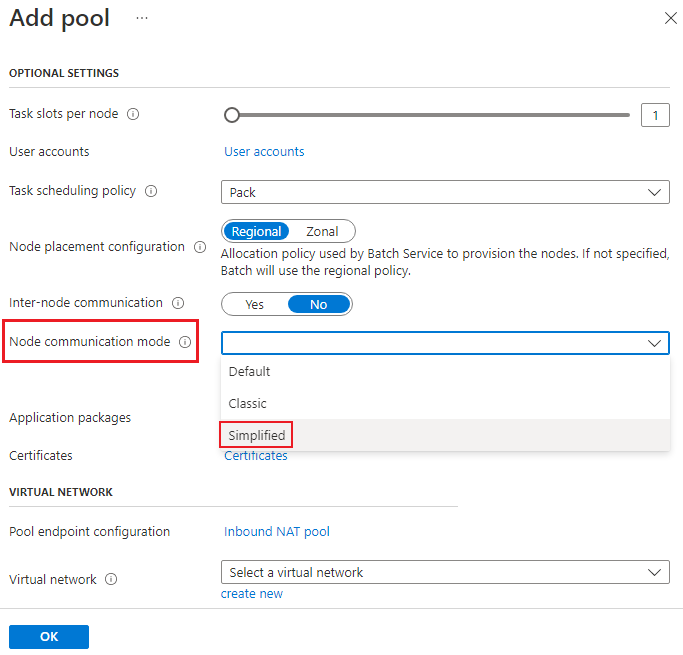
First, sign in to the Azure portal. Then, navigate to the Pools blade of your Batch account and select the Add button. Under OPTIONAL SETTINGS, you can select Simplified as an option from the pull-down of Node communication mode as shown:
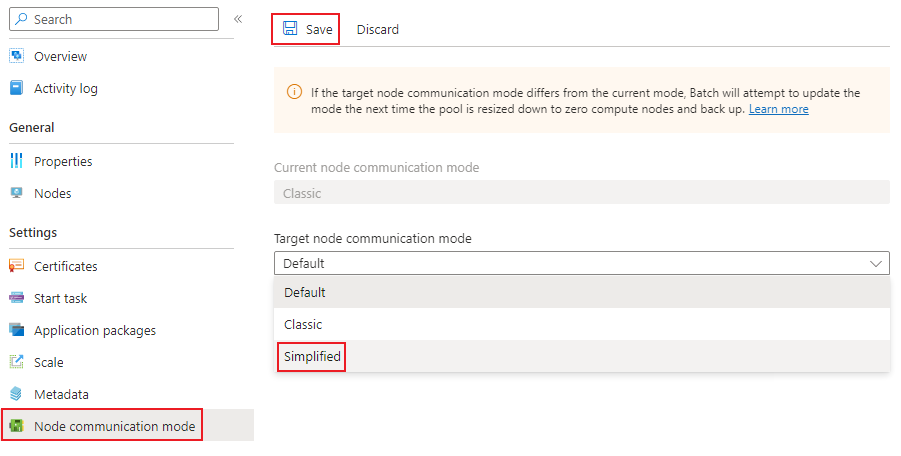
To update an existing pool to simplified communication mode, navigate to the Pools blade of your Batch account and select the pool to update. On the left-side navigation, select Node communication mode. There you can select a new target node communication mode as shown below. After selecting the appropriate communication mode, select the Save button to update. You need to scale the pool down to zero nodes first, and then back out for the change to take effect, if conditions allow.
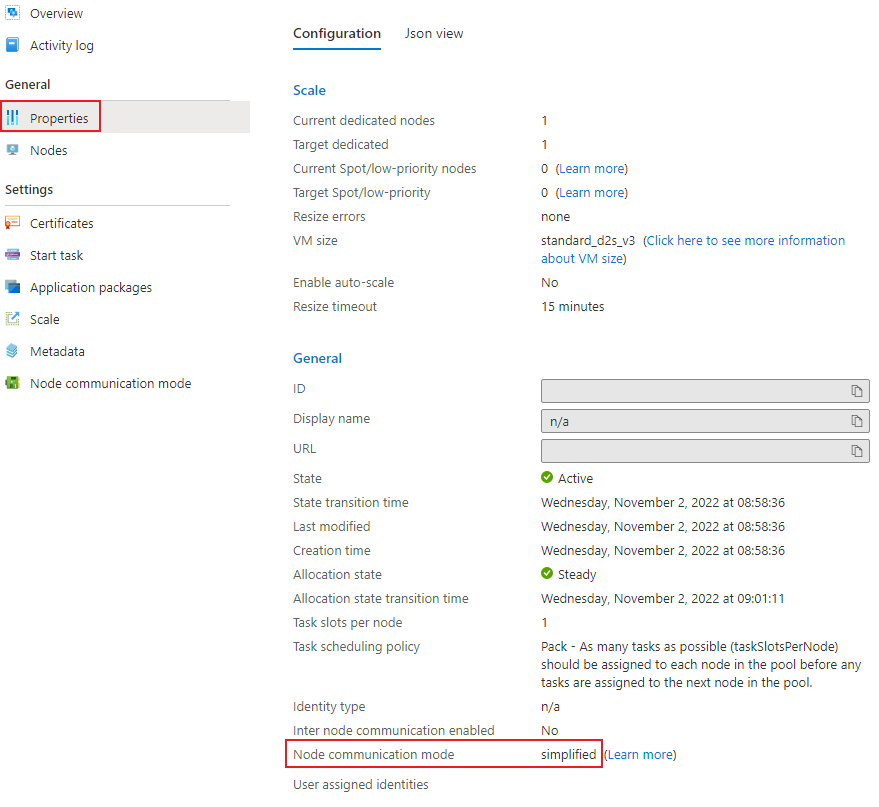
To display the current node communication mode for a pool, navigate to the Pools blade of your Batch account, and select the pool to view. Select Properties on the left-side navigation and the pool node communication mode appears under the General section.
REST API
This example shows how to use the Batch Service REST API to create a pool with simplified compute node communication.
POST {batchURL}/pools?api-version=2022-10-01.16.0
client-request-id: 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000
Request body
"pool": {
"id": "pool-simplified",
"vmSize": "standard_d2s_v3",
"virtualMachineConfiguration": {
"imageReference": {
"publisher": "Canonical",
"offer": "0001-com-ubuntu-server-jammy",
"sku": "22_04-lts"
},
"nodeAgentSKUId": "batch.node.ubuntu 22.04"
},
"resizeTimeout": "PT15M",
"targetDedicatedNodes": 2,
"targetLowPriorityNodes": 0,
"taskSlotsPerNode": 1,
"taskSchedulingPolicy": {
"nodeFillType": "spread"
},
"enableAutoScale": false,
"enableInterNodeCommunication": false,
"targetNodeCommunicationMode": "simplified"
}
Limitations
The following are known limitations of the simplified communication mode:
- Limited migration support for previously created pools without public IP addresses. These pools can only be migrated if created in a virtual network, otherwise they won't use simplified compute node communication, even if specified on the pool.
- Cloud Service Configuration pools are not supported for simplified compute node communication and are deprecated. Specifying a communication mode for these types of pools aren't honored and always results in classic communication mode. We recommend using Virtual Machine Configuration for your Batch pools.
Next steps
- Learn how to use private endpoints with Batch accounts.
- Learn more about pools in virtual networks.
- Learn how to create a pool with specified public IP addresses.
- Learn how to create a pool without public IP addresses.
- Learn how to configure public network access for Batch accounts.