Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Use Azure governance to establish the tooling that you need to support cloud governance, compliance auditing, and automated guardrails.
Design area review
Roles or functions: Azure governance originates from cloud governance. You might need to implement the cloud platform or a cloud center of excellence to define and apply certain technical requirements. Governance focuses on enforcing operations and security requirements, which might require cloud security, central IT, or cloud operations.
Scope: Consider your decisions from identity, network, security, and management design area reviews. Your team can compare review decisions from automated governance, which is part of the Azure landing zone accelerator. Review decisions can help you determine what to audit or enforce and what policies to automatically deploy.
Out of scope: Azure governance establishes the foundation for networking. But it doesn't address compliance-related components, such as advanced network security or automated guardrails to enforce networking decisions. You can address these networking decisions when you review compliance design areas that are related to security and governance. The cloud platform team should address initial networking requirements before addressing more complex components.
New (greenfield) cloud environment: To start your cloud journey, create a small set of subscriptions. You can use Bicep deployment templates to create your new Azure landing zones. For more information, see Azure landing zones Bicep—Deployment flow.
Existing (brownfield) cloud environment: If you want to apply proven-practice Azure governance principles to existing Azure environments, consider the following guidance:
Establish a management baseline for your hybrid or multicloud environment.
Implement Microsoft Cost Management features, like billing scopes, budgets, and alerts, to ensure that you don't exceed your expense limit.
Use Azure Policy to enforce governance guardrails on Azure deployments and trigger remediation tasks to bring existing Azure resources into a compliant state.
Consider using the Microsoft Entra entitlement management feature to automate Azure access request workflows, access assignments, reviews, and expiration.
Use Azure Advisor recommendations to ensure cost optimization and operational excellence in Azure, both of which are core principles of the Microsoft Azure Well-Architected Framework.
The Azure landing zones Bicep—Deployment flow repository contains Bicep deployment templates that can accelerate your greenfield and brownfield Azure landing zone deployments. These templates have integrated Microsoft proven-practice governance guidance.
Consider using the Azure landing zone default policy assignments Bicep module to get a head start on ensuring compliance for your Azure environments.
For more information, see Brownfield environment considerations.
Design area overview
Your organization's cloud adoption journey starts with strong controls for government environments.
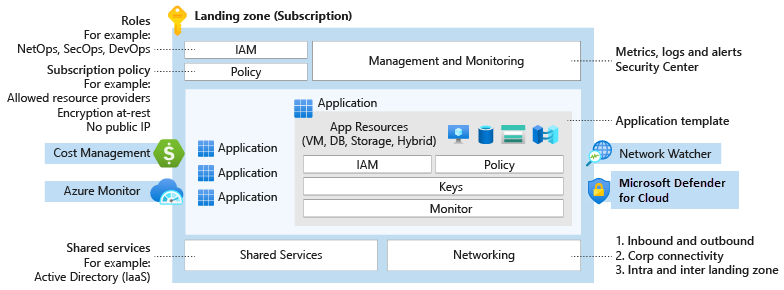
Governance provides mechanisms and processes for maintaining control over platforms, applications, and resources in Azure.
Explore the following considerations and recommendations to make informed decisions as you plan your landing zone.
The governance design area focuses on design decisions for your landing zone. For information about governance processes and tools, see Govern in the Cloud Adoption Framework for Azure.
Azure governance considerations
Azure Policy helps ensure security and compliance for enterprise technical estates. Azure Policy can enforce vital management and security conventions across Azure platform services. Azure Policy supplements Azure role-based access control (RBAC), which controls actions for authorized users. Cost Management can also help support your ongoing governance cost and spending in Azure or other multicloud environments.
Deployment considerations
Change advisory review boards can hinder your organization's innovation and business agility. Azure Policy replaces such reviews with automated guardrails and adherence audits to improve workload efficiency.
Determine which Azure policies you need based on your business controls or compliance regulations. Use the policies included in the Azure landing zone accelerator as a starting point.
Use the policies included in Azure landing zones reference implementation to consider other policies that might align to your business requirements.
Enforce automated networking, identity, management, and security conventions.
Manage and create policy assignments by using policy definitions that you can reuse at multiple inherited assignment scopes. You can have centralized baseline policy assignments at the management, subscription, and resource group scope.
Ensure continuous compliance with compliance reporting and auditing.
Understand that Azure Policy has limits, such as the restriction of definitions at any particular scope. For more information, see Policy limits.
Understand regulatory compliance policies. The policies might include HIPAA, PCI-DSS, or SOC 2 Trust Services Criteria.
Cost management considerations
Consider the structure of your organization's cost and recharging model. Determine the key data points that accurately convey your cloud services spend.
Choose the structure of tags that fits your cost and recharging model to help track your cloud spend.
Use the Azure pricing calculator to estimate the expected monthly costs for using Azure products.
Get Azure Hybrid Benefit to help reduce the cost of running your workloads in the cloud. You can use your on-premises Software Assurance-enabled Windows Server and SQL Server licenses on Azure. You can also use Red Hat and SUSE Linux subscriptions.
Get Azure reservations and commit to one-year or three-year plans for multiple products. Reservation plans provide resource discounts, which can significantly reduce your resource costs by up to 72% compared to pay-as-you-go prices.
Get the Azure savings plan for compute to save up to 65% compared to pay-as-you-go prices. Pick a one-year or three-year commitment that applies to compute services, regardless of your region, instance size, or operating system. Pick a plan for compute components, like virtual machines, dedicated hosts, container instances, Azure premium functions, and Azure app services. Combine an Azure savings plan with Azure reservations to optimize compute cost and flexibility.
Use Azure policies to allow specific regions, resource types, and resource SKUs.
Use the rule-based policy of Azure Storage lifecycle management to move blob data to the appropriate access tiers or to expire data at the end of the data lifecycle.
Use Azure dev/test subscriptions to get a discount on access to select Azure services for nonproduction workloads.
Use automatic scaling to dynamically allocate and deallocate resources to match your performance needs, which saves money.
Use Azure Spot Virtual Machines to take advantage of unused compute capacity at a low cost. Spot Virtual Machines is great for workloads that can handle interruptions, for example batch-processing jobs, dev/test environments, and large-compute workloads.
Select the right Azure services to help reduce costs. Some Azure services are free for 12 months and some are always free.
Select the right compute service for your application to help improve cost efficiency. Azure offers many ways to host your code.
Resource management considerations
Determine if the groups of resources in your environment can share required configurations, a common lifecycle, or common access constraints (such as RBAC) to help provide consistency.
Choose an application or workload subscription design that's appropriate for your operation needs.
Use standard resource configurations within your organization to ensure a consistent baseline configuration.
Security considerations
- Enforce tools and guardrails across the environment as part of a security baseline.
- Notify the appropriate people when you find deviations.
- Consider using Azure Policy to enforce tools, such as Microsoft Defender for Cloud, or guardrails, such as the Microsoft cloud security benchmark.
Identity management considerations
Determine who has access to audit logs for identity and access management.
Notify the appropriate people when suspicious sign-in events occur.
Consider using Microsoft Entra reports to govern activity.
Consider sending Microsoft Entra ID logs to the central Azure Monitor Logs workspace for the platform.
Explore Microsoft Entra ID Governance features, like access reviews and entitlement management.
Non-Microsoft tooling
Use AzAdvertizer to get Azure governance updates. For example, you can find insights about policy definitions, initiatives, aliases, security, and regulatory compliance controls in Azure Policy or Azure RBAC role definitions. You can also get insight into resource provider operations, Microsoft Entra role definitions and role actions, and first-party API permissions.
Use Azure Governance Visualizer to keep track of your technical governance estate. You can use the policy version checker feature for Azure landing zones to keep your environment up to date with the latest Azure landing zone policy release state.
Azure governance recommendations
Deployment acceleration recommendations
Identify required Azure tags and use the append policy mode to enforce usage. For more information, see Define your tagging strategy.
Map regulatory and compliance requirements to Azure Policy definitions and Azure role assignments.
Establish Azure Policy definitions at the top-level root management group because they might be assigned at inherited scopes.
Manage policy assignments at the highest appropriate level with exclusions at bottom levels, if necessary.
Use Azure Policy to control resource provider registrations at the subscription or management group levels.
Use built-in policies to minimize operational overhead.
Assign the built-in Resource Policy Contributor role at a specific scope to enable application-level governance.
Limit the number of Azure Policy assignments at the root management group scope to avoid managing exclusions at inherited scopes.
Cost management recommendations
- Use Cost Management to implement financial oversight on resources in your environment.
- Use tags, such as the cost center or project name, to append the resource metadata. This approach helps enable granular analysis of expenses.
Azure governance in the Azure landing zone accelerator
The Azure landing zone accelerator provides organizations with mature governance controls.
For example, you can implement:
- A management group hierarchy that groups resources by function or workload type. This approach encourages resource consistency.
- A rich set of Azure policies that enables governance controls at the management group level. This approach helps verify that all resources are in scope.